 Solutions
Solutions
Chemistry the partial vapour pressure of each component of the solution is Another important class of solutions consists of solids dissolved in liquid ...
 D:TEXTBOOKSRATIONALISED 20222-23NehaP85
D:TEXTBOOKSRATIONALISED 20222-23NehaP85
V. 0.130. = 3.17 V – 0.21V = 2.96 V. Solution. Rationalised 2023-24. Page 10. 40. Chemistry.
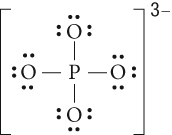 Section 4.1: Types of Chemical Bonds
Section 4.1: Types of Chemical Bonds
Page 12. Copyright © 2012 Nelson Education Ltd. Chapter 4: Chemical Bonding 7. Answers will vary. Sample answer: Coordinate covalent bonding is like you ...
 Chem 12 SM Ch5 Review final new ok revised
Chem 12 SM Ch5 Review final new ok revised
Δ = −. Statement: The enthalpy change ΔH
 Chem12 SM Ch05 Section5 3 final ok revised
Chem12 SM Ch05 Section5 3 final ok revised
Section 5.3 Questions page 313. 1. (a) Solution: Step 1: Use the balanced chemical equation to determine the bonding of each substance. H2(g) +
 Grade 12 Chemistry: A Foundation for Implementation
Grade 12 Chemistry: A Foundation for Implementation
Jan 21 2011 ... textbook. The successful implementation of Grade 12 Chemistry depends ... solutions based on this result? Explain. 3. Are there any reactions ...
 Chem12 SM Ch7 Section7.5 final ok revised
Chem12 SM Ch7 Section7.5 final ok revised
Solution: Step 1. Convert the given initial amount of cyclopropane gas to (c) The chemical system is not at equilibrium. We have been given K = 1.2 × 102 ...
 Section 8.4: Calculations Involving Acidic Solutions
Section 8.4: Calculations Involving Acidic Solutions
Section 8.4: Calculations Involving Acidic Solutions. Tutorial 1 Practice page x2 ≈ 6.2 × 10−12 x = [H+(aq)]. ≈ 2.49 × 10−6 mol/L. pH = −log(2.49 × 10 ...
 Chem12 SM Ch8 Section8e1 final ok revised
Chem12 SM Ch8 Section8e1 final ok revised
solution; an Arrhenius base forms hydroxide ions in aqueous solution. (b) A Brønsted–Lowry acid is a proton donor; a Brønsted–Lowry base is a proton.
 Grade 12 Chemistry: A Foundation for Implementation
Grade 12 Chemistry: A Foundation for Implementation
Jan 21 2011 promotes the idea that all answers are enshrined in a textbook. The successful implementation of Grade 12 Chemistry depends on a ...
 Chem12 SM Ch7 Section7.6 final revised
Chem12 SM Ch7 Section7.6 final revised
Chapter 7: Chemical Equilibrium 7.6-1 Write a balanced equation for the solution equilibrium. Ca3(PO4)2(s) ! "!# !! ... Ksp of CuI(s) = 1.3 × 10?12.
 Chem12 SM Ch05 Section5 2 final ok revised
Chem12 SM Ch05 Section5 2 final ok revised
Chapter 5: Thermochemistry. 5.2-3. Solution: Step 1: Determine the change in temperature AT . final initial. 27.8 °C 19.8 °C.
 Chem 12 SM Ch5 Review final new ok revised
Chem 12 SM Ch5 Review final new ok revised
(a) Answers may vary. Sample answer: Hydrogen gas has a high enthalpy of combustion releasing about 2.5 times the quantity of energy per gram than methane but
 Solutions
Solutions
Chemistry. Type of Solution. Solute. Solvent. Common Examples. Gaseous Solutions. Gas. Gas. Mixture of oxygen and nitrogen gases.
 Chem12 SM Ch7 Section7.5 final ok revised
Chem12 SM Ch7 Section7.5 final ok revised
Chapter 7: Chemical Equilibrium Solution: N2O4(g) ! "!# !! 2 NO2(g) ... Using the balanced chemical equation construct an ICE table for calculating.
 Chem12 SM Ch05 Section5.4 final ok revised
Chem12 SM Ch05 Section5.4 final ok revised
An enthalpy diagram of the reaction is: Page 2. Copyright © 2012 Nelson Education Ltd. Chapter 5: Thermochemistry. 5.4-2. 2. (a) Solution: Step 1: Label the
 chemistry grade 12 studen textbook
chemistry grade 12 studen textbook
CHEMISTRY GRADE 12. 2. MAIN CONTENTS. 1.1 Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixtures. 1.2 Types of Solutions. 1.3 The Solution Process.
 EngLinks
EngLinks
Grade 12 Chemistry Review Workbook. 1 of 22. 1. Organic Chemistry. General IUPAC rules for naming organic compounds: 1) The lowest numbers possible must be
 Chem12 SM Ch05 Section5 3 final ok revised
Chem12 SM Ch05 Section5 3 final ok revised
combustion of ethene gas to gaseous carbon dioxide and liquid water is an exothermic reaction. 3. Solution: Step 1: Use the balanced chemical equation:.

Copyright © 2012 Nelson Education Ltd. Chapter 5: Thermochemistry 5.2-1 Section 5.2: Calorimetry and Enthalpy Tutorial 1 Practice, page 297 1. Given: 2
HO(l)6.0 mL=V
; initial25 °C=T
; final75 °C=T
; 2HO( l)
4.18 J/(g°C)=⋅c
; 2HO(l )
1.00 g/mL=d
Required: thermal energy required, q Analysis: =ΔqmcT Solution: Step 1: Determine the mass of water, m. 6.0 mL mVd1.00 g
1 mL6.0 g=m
Step 2: Determine the change in temperature, ΔT . finalinitial75 °C25 °C
50 °C
TTT T Step 3: Calculate the quantity of thermal energy, q. 4.18 J (6.0 g) gC qmcT (50 °C1.3 kJ=q
Statement: The quantity of thermal energy required is 1.3 kJ. 2. Given: ethylene glycol4.0 kgm=
; ethylene glycol3.5 J/(g°C)c=⋅
; 250 kJq=Required: change in temperature, ΔT
Analysis: =ΔqmcT
Solution: Step 1: Convert quantities to the appropriate units. 34.0 kg4.010 gm==×
q=250 kJ=250!10 3 JStep 2: Rearrange =ΔqmcT
to solve for ΔT . 3 325010 J
3.5 J (4.010 g) gC 18 C qmcT q T mc T Statement: The temperature change of the solution was 18 °C. Copyright © 2012 Nelson Education Ltd. Chapter 5: Thermochemistry 5.2-2 3. Given: HCl(aq)50.0 mLV=
; NaOH(aq)75.0 mLV=
; initial20.2 °CT=
; final25.6 °CT=
Required: quantity of energy transferred, q Analysis: =ΔqmcT Solution: Step 1: Determine the total volume of HCl(aq) and NaOH(aq), V . HCl(aq)NaOH(aq)50.0 mL75.0 mL
125.0 mL
VVV VStep 2: Determine the total mass of two solutions , m. Since the solution contains dilute HCl(aq) and NaOH(aq), the density and heat capacity are assumed to be the same as those for water. 125.0 mL
mVd=1.00 g
1 mL125.0 gm=
Step 3: Determine the change in temperature, ΔT . finalinitial25.6 °C20.2 °C
5.4 °C
TTT T Step 4: Calculate the quantity of energy transferred, q. 4.18 J (125.0 g) gC qmcT=Δ (5.4 °C2800 Jq=
Statement: The quantity of energy transferred is 2800 J, or 2.8 kJ. Since the temperature of the surroundings (liquid water in the calorimeter) increased, the reaction was exothermic. Mini Investigation: Thermal Energy Transfer in a Coffee-Cup Calorimeter, page 297 Answers may vary. Sample answers: mass of water in calorimeter = 100.00 g mass of aluminum block = 89.80 g temperature of aluminum block = temperature of hot water bath = 80.0 °C final temperature of water in calorimeter = 27.8 °C initial temperature of tap water = 19.8 °C A. Given: 2
HO(l)100.00 gm=
; initial19.8 °CT=
; final27.8 °CT=
Required: quantity of thermal energy gained by the water, q Analysis: =ΔqmcTCopyright © 2012 Nelson Education Ltd. Chapter 5: Thermochemistry 5.2-3 Solution: Step 1: Determine the change in temperature, ΔT
. finalinitial27.8 °C19.8 °C
8.0 °C
TTT T Step 2: Calculate the quantity of thermal energy gained by the water, q. 4.18 J (100.00 g) gC qmcT=Δ (8.0 °C3300 Jq=
Statement: The quantity of thermal energy gained by the water is 3300 J, or 3.3 kJ. B. Given: Al(s)89.80 gm=
; initial80.0 °CT=
; final27.8 °CT=
; Al(s)0.900 J/(g°C)c=⋅
Required: quantity of thermal energy transferred to or from aluminum, q Analysis: =ΔqmcT Solution: Step 1: Determine the change in temperature, ΔT . finalinitial27.8 °C80.0 °C
52.2 °C
TTT T Step 2: Calculate the quantity of thermal energy transferred to or from aluminum, q. 0.900 J (89.80 g) gC qmcT=Δ (52.2 °C4220 Jq=-
Statement: Since the value of q is negative, energy is transferred from aluminum to water, and the quantity transferred is 4220 J, or 4.22 kJ. C. Answers may vary. Sample answer: There is a difference of about 0.9 kJ in the answers to A and B. The difference could be due to assumptions or experimental errors. D. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Experimental errors include thermal energy lost to the tongs, to the air on transfer from hot to cold water, to the thermometer, to the calorimeter, or to the air above the water-aluminum mixture. The investigation could be improved by taking into account the temperature changes and thus energy transferred to the thermometer, tongs, and calorimeter. Other improvements would be increasing the insulation of calorimeter and faster transfer from hot to cold water.
Copyright © 2012 Nelson Education Ltd. Chapter 5: Thermochemistry 5.2-4 Tutorial 2 Practice, page 301 1. Given: 2
HO(l )
50.0 gm=
; vap44.0 kJ/molHΔ=
Required: enthalpy change, HΔ
Analysis: vap
HnHΔ=Δ
Solution: Step 1: Calculate the amount of water in 50.0 g, 2 HO(l) n . 2 HO(l)18.02 g/molM=
2 2 2 2 HO(l) HO(l) HO(l) HO(l)50.0 g
18.02 g/mol
2.7747 mol (2 extra digits carried)
m n Mquotesdbs_dbs2.pdfusesText_2[PDF] chemistry notes for class 12 pdf
[PDF] chiffres coronavirus france 11 mai
[PDF] chiffres coronavirus france 11 mai 2020
[PDF] chiffres covid france 6 juin
[PDF] child care cost per province
[PDF] child language acquisition stages
[PDF] childhood in france vs us
[PDF] china paris agreement goals
[PDF] china population 2019 vs us
[PDF] chinese food near me open
[PDF] chinese language cantonese vs mandarin
[PDF] chinese restaurant in paris tx
[PDF] choix heure ete ou hiver france
[PDF] chômage technique code travail maroc
