 Theory of electromagnetic fields
Theory of electromagnetic fields
Maxwell's equations (3) and (4) are significant for RF systems: they tell us that a time-dependent electric field will induce a magnetic field; and a time-
 A Students Guide to Maxwells Equations
A Students Guide to Maxwells Equations
01-Dec-2008 The final chapter shows how Maxwell's Equations may be combined to produce the wave equation the basis for the electromagnetic theory of light.
 Chapter Eight - ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
Chapter Eight - ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES
It can be shown from Maxwell's equations that electric and magnetic fields in an electromagnetic wave are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of.
 Chapter 4 - Maxwells Equations
Chapter 4 - Maxwells Equations
From the equation 4.9 we observe that the divergence of a vector field is a scalar quantity. Physical significance : The physical significance of the divergence
 A Students Guide to Maxwells Equations
A Students Guide to Maxwells Equations
The final chapter shows how Maxwell's Equations may be combined to produce the wave equation the basis for the electromagnetic theory of light. This book is a
 PG Sem ll Maxwells equation and its derivations
PG Sem ll Maxwells equation and its derivations
S. It is Maxwell's four equation in integral form. Thus Maxwell's equation of electromagnetism is. In differential form. 1. F∙B=P or J•Ề
 Notes 4 Maxwells Equations
Notes 4 Maxwells Equations
Maxwell's work in electromagnetism has been called the "second great unification in physics" after the first one carried out by Isaac. Newton. Maxwell
 Lecture 1 Introduction Maxwells Equations
Lecture 1 Introduction Maxwells Equations
The discipline of electromagnetic field theory and its pertinent technologies is also known as electromagnetics. It has been based on Maxwell's equations which
 Chapter 13 Maxwells Equations and Electromagnetic Waves
Chapter 13 Maxwells Equations and Electromagnetic Waves
To see how magnetic fields can be created by a time-varying electric field consider a capacitor which is being charged. During the charging process
 Lecture: Maxwells Equations
Lecture: Maxwells Equations
Jan 15 2018 Introduction to Maxwell's Equations. •. Sources of electromagnetic fields. •. Differential form of Maxwell's equation.
 Chapter 6 Maxwells Equations for Electromagnetic Waves
Chapter 6 Maxwells Equations for Electromagnetic Waves
Maxwell's Equations for. Electromagnetic Waves. 6.1 Vector Operations. Any physical or mathematical quantity whose amplitude may be decomposed into.
 A Students Guide to Maxwells Equations
A Students Guide to Maxwells Equations
Dec 1 2008 The final chapter shows how Maxwell's Equations may be combined to produce the wave equation
 Maxwells Equations
Maxwells Equations
Jan 2 2019 They are measured in units of [coulomb/m3] and [ampere/m2]. The right-hand side of the fourth equation is zero because there are no magnetic ...
 Whos Afraid of Maxwells Equations? Can Just Anyone Understand
Whos Afraid of Maxwells Equations? Can Just Anyone Understand
(Ivan Tolstoy Biographer). The special theory of relativity owes its origins to Maxwell's equations of the electromagnetic field. (Albert Einstein)
 Lecture 1 Introduction Maxwells Equations
Lecture 1 Introduction Maxwells Equations
Chew. “Quantum mechanics made simple: Lecture notes
 Notes 4 Maxwells Equations
Notes 4 Maxwells Equations
Fleisch A Student's Guide to Maxwell's Equations
 MAXWELL EQUATIONS AND YANG-MILLS THEORY Contents 1
MAXWELL EQUATIONS AND YANG-MILLS THEORY Contents 1
The Maxwell's equations are the starting point of all classical electrodynamics. In this section we will present Maxwell's equations in vector analysis form
 Maxwells Equations – The Fundamental Laws of Electromagnetism
Maxwells Equations – The Fundamental Laws of Electromagnetism
Maxwell's Equations – The Fundamental. Laws of Electromagnetism. • Ampere's Law (valid for constant currents). – The integral of is proportional to the.
 Maxwells equations The conceptual origins of and gauge theory
Maxwells equations The conceptual origins of and gauge theory
Nov 12 2014 magnetism
Lecture:
at Jefferson Laboratory, January 15-26th2018 FMarhauser
day, January 1 , 2018This Lecture
ˉThis lecture provides theoretical basics useful for follow-up lectures on resonators and waveguidesSources of electromagnetic fields
Some clarifications on all four equations
Time-varying fields AEwave equation
Example: Plane wave
ˉPhase and Group Velocity
ˉWave impedance
2A dynamical theory of the electromagnetic field
James Clerk Maxwell, F. R. S.
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 1865 155, 459-512, published 1 January 1865 -Originally there were 20 equationsSources of Electromagnetic Fields
5ˉElectromagnetic fields arise from 2 sources:
Electrical charge (Q)
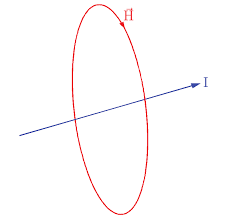
Electrical current (ܫ
to quantify the effects of fields: ௌelectric current density -total electric current per unit area S (or ܫൌௌԦܬȉ݀ԦܵStationary charge creates electric field
Moving charge creates magnetic field
ˉIf either the magnetic or electrical fields vary in time, both fields are 6DifferentialForm
D= electric flux density/displacement field (Unit: As/m2)E= electric field intensity (Unit: V/m)
ʌ= electric charge density (As/m3)
H= magnetic field intensity (Unit: A/m)
B= magnetic flux density (Unit: Tesla=Vs/m2)
J= electric current density (A/m2)
Ɋ=permeability of free space
or orGauss's law
Gauss's law for magnetism
Ampğre's law
Faraday's law of induction
(1) (2) (3) (4) form the basic of the classic electromagnetismLorentz ForceDiǀergence (Gauss') Theorem
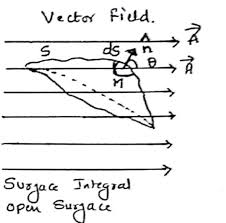
7 outwardfluxofvectorfield(Ԧܨ {divCurl (Stokes') Theorem
8Green's Theorem
{curlIntegralofcurlofvectorfield(Ԧܨ
lineintegralofvectorfield(ԦܨEdžample͗ Curl (Stokes') Theorem
9Integralofcurlofvectorfield(Ԧܨ
lineintegralofvectorfield(ԦܨExample: Curl (Stokes) Theorem
10 Example: Closed line integrals of various vector fields {curlIntegralofcurlofvectorfield(Ԧܨ
lineintegralofvectorfield(ԦܨNo curlSome curlStronger curl
No net curl
11DifferentialFormIntegralForm
D= electric flux density/displacement field (Unit: As/m2)E= electric field intensity (Unit: V/m)
H= magnetic field intensity (Unit: A/m)
B= magnetic flux density (Unit: Tesla=Vs/m2)
J= electric current density (A/m2)
Gauss' theorem
Stokes' theorem
Ɋ=permeability of free space
Gauss's law
Gauss's law for magnetism
Ampğre's law
Faraday's law of induction
ʌ= electric charge density (C/m3=As/m3)
121. Uniform field
Electric Flux & 1stMaxwell Equation
-angle between field and normal vector to surface mattersGauss: Integration over closedsurface
2. Non-Uniform field
Example: Metallic plate,
assume only surface charges on one sideDefinition of Electric Flux
13Gauss: Integration over closedsurface
Example: Capacitor
Electric Flux & 1stMaxwell Equation
1. Uniform field
-angle between field and normal vector to surface matters2. Non-Uniform field
Definition of Electric Flux
14Integration of over closed spherical surface S
Examples of non-uniform fields
Point charge Q
Principle of Superposition holds:
Electric Flux & 1stMaxwell Equation
pointing out radiallyAdd charges
15Uniform field
Magnetic Flux & 2ndMaxwell Equation
Gauss: Integration over closedsurface
Non-Uniform field
Definition of Magnetic Flux
-There are no magnetic monopoles -All magnetic field lines form loopsClosed surface:
Flux lines out = flux lines in
What about this case?
Flux lines out > flux lines in ?
-No. In violation of 2ndMadžwell's law, i.e. integration over closed surface, no holes allowed -Also: One cannot split magnets into separate poles, i.e. there always will be aNorth and South pole
16Magnetic Flux & 3rdMaxwell Equation
Faraday's law of induction
If integration path is not changing in time
-Change of magnetic flux induces an electric field along a closed loop -Note: Integral of electrical field over closed loop may be non-zero, when induced by a time-varying magnetic field -Electromotive force (EMF) ם charge traveling once around loop 17 -Change of magnetic flux induces an electric field along a closed loopMagnetic Flux & 3rdMaxwell Equation
-Electromotive force (EMF) ם -Note: Integral of electrical field over closed loop may be non-zero, when induced by a time-varying magnetic fieldIf integration path is not changing in time
charge traveling once around loop -or voltage measured at end of open loopFaraday's law of induction
18 Ampère's (circuital) Law or 4thMaxwell Equation -Note that ௌԦܬȉ݀Ԧܵ haǀe arbitrary shape as long as эS is its closed boundary -What if there is a capacitor? -While current is still be flowing (charging capacitor): tangential to a circle at any radius r of integration {conduction current IRight hand side of equation:
Left hand side of equation:
19 Ampère's (circuital) Law or 4thMaxwell Equation {displacement current I -But one may also place integration surface Sbetween plates AEcurrent does not flow through surface here -This is when the displacement field is required as a corrective 2ndsource term for the magnetic fields tangential to a circle at any radius r of integration ; Gauss's law {conduction current ILeft hand side of equation:
20 conduction current displacement current -In resistive materials the current density Jis proportional to the electric field =1/the electric resistivity (ё·m) -Generally (ʘ, T) is a function of frequency and temperaturePresence of Resistive Material
21quotesdbs_dbs4.pdfusesText_7
[PDF] maxwell's equations electromagnetic waves
[PDF] maxwell's equations explained
[PDF] maxwell's equations integral form
[PDF] may day flight crash
[PDF] may et might
[PDF] maybelline little rock jobs
[PDF] mayday calls meaning
[PDF] mayday mayday mayday
[PDF] mayday origin
[PDF] Maylis de Kerangal: dans les rapides
[PDF] mazée
[PDF] mblock
[PDF] mblock mbot
[PDF] mbot technologie college