 Test 4 Amines/Acids Mechanisms Practice Answers
Test 4 Amines/Acids Mechanisms Practice Answers
Some Practice Problems for the Amines/Acids Test 4. Draw the Mechanisms for the following Reactions. Page 4 has some synthesis-‐design practice problems. 1. 2
 STEM Success Center
STEM Success Center
Worksheet. Chem 202 Chapter 24 Amines and Heterocycles. Nomenclature Basicity of Amines
 Reactions of Amines
Reactions of Amines
o Example of resonance versus charge: A carboxylate anion with serious You should be able to handle any ranking problems involving either amines as bases or ...
 Practice-Sets-All-Organic-Chemistry-2.pdf
Practice-Sets-All-Organic-Chemistry-2.pdf
Practice!Problems!for!the!Amines/Acids!Test!4! Draw!the!Mechanisms!for!the!following!Reactions!
 CHAPTER 7 AMINES
CHAPTER 7 AMINES
Practice problem: Write the equation for the neutralization of trimethylamine with formic acid. This neutralization reaction can occur in amino acids within the
 Answers to Practice Sets - Organic Chemistry II Table of Contents
Answers to Practice Sets - Organic Chemistry II Table of Contents
Practice!Problems!for!the!Amines/Acids!Test!4! Draw!the!Mechanisms!for!the!following!Reactions!
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – PRACTICE EXERCISE Elimination
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – PRACTICE EXERCISE Elimination
Elimination Reactions and Alkene Synthesis. 1) One of the products that 31) Similar to the previous problem but this time Hoffman's product is desired.
 Chapter 6 Amines and Amides
Chapter 6 Amines and Amides
Learn the major chemical reactions of amines and amides and learn how to predict the products of amide synthesis and hydrolysis reactions. • Learn some of the
 Jasperse Acid-Base Chemistry. Extra Practice Problems
Jasperse Acid-Base Chemistry. Extra Practice Problems
The base ionization constant Kb describes which of the following reactions for a weak base B
 Chem 345 – Organic Reactions Chapter 23 Prepared by José Laboy
Chem 345 – Organic Reactions Chapter 23 Prepared by José Laboy
The Gabriel synthesis provides a primary amine after hydrolysis of the imide in either acid or base media. In the mechanism shown above the hydrolysis is.
 Reactions of Amines
Reactions of Amines
You should be able to handle any ranking problems involving either amines as bases or their conjugate ammoniums as acids. This should include relative to non-
 Test 4 Amines/Acids Mechanisms Practice Answers
Test 4 Amines/Acids Mechanisms Practice Answers
Some Practice Problems for the Amines/Acids Test 4. Draw the Mechanisms for the following Reactions. Page 4 has some synthesis-?design practice problems.
 Chapter 6 Amines and Amides
Chapter 6 Amines and Amides
Learn the major chemical reactions of amines and amides and learn how to The disposal of waste nitrogen from the body is a problem which different ...
 Practice-Sets-All-Organic-Chemistry-2.pdf
Practice-Sets-All-Organic-Chemistry-2.pdf
problem practice set which are also included in the class notes. Test 3 PS2: Retrosynthesis + Synthesis Design Practice ... Amines/Ammoniums.
 Chapter 23 The Chemistry of Amines
Chapter 23 The Chemistry of Amines
23.49 (b) Excess methyl iodide will form the quaternary salt (CH3)3CN. +. (CH3)3 I–; the reaction will not stop at the secondary amine shown in the problem.
 23.11 SYNTHESIS OF AMINES
23.11 SYNTHESIS OF AMINES
PROBLEMS. 23.26 Design a synthesis of methyl orange (Eq. 23.49) using aniline as the only In this example acidic hydrolysis gives the ammonium salt
 Schedule: Which Lecture Videos and Practice-Set Videos Go with
Schedule: Which Lecture Videos and Practice-Set Videos Go with
Additional Practice Sets/Videos: Retrosynthesis Problems; Acid-Base Practice 31 Diazonium Chemistry; Amine Synthesis by Reductive Amination of Carbonyls.
 chapter-7-amines.pdf
chapter-7-amines.pdf
Practice problem: Write the equation for the neutralization of trimethylamine with formic acid. This neutralization reaction can occur in amino acids within
 Practice Set Answer Keys Organic Chemistry I Table of Contents
Practice Set Answer Keys Organic Chemistry I Table of Contents
Test 3 PS4: Test 3 Extra Synthesis Practice (6 pages) C. Rank the basicity of the following sets: Multiple Variable Problems ... Amines/Ammoniums.
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – PRACTICE EXERCISE Elimination
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – PRACTICE EXERCISE Elimination
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I – PRACTICE EXERCISE. Elimination Reactions and Alkene Synthesis Amines can be nucleophiles or bases. Increasing their steric bulk ...
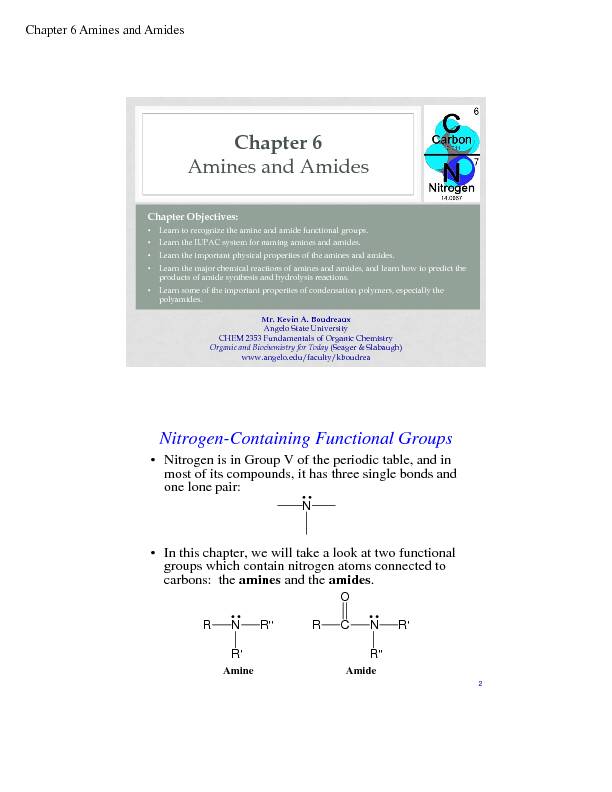
Chapter 6 Amines and Amides
Mr. Kevin A. Boudreaux
Angelo State University
CHEM 2353 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
Organic and Biochemistry for Today (Seager & Slabaugh) www.angelo.edu/faculty/kboudreaChapter Objectives:
•Learn to recognize the amine and amide functional groups. •Learn the IUPAC system for naming amines and amides. •Learn the important physical properties of the amines and amides. •Learn the major chemical reactions of amines and amides, and learn how to predict the products of amide synthesis and hydrolysis reactions. •Learn some of the important properties of condensation polymers, especially the polyamides.Chapter 6
Amines and Amides
2Nitrogen-Containing Functional Groups
• Nitrogen is in Group V of the periodic table, and in most of its compounds, it has three single bonds and one lone pair:
• In this chapter, we will take a look at two functional groups which contain nitrogen atoms connected to carbons: the amines and the amides.
RCO N R"R' Amide NRR'' R' Amine NChapter 6 Amines and Amides
3Classification and
Nomenclature of Amines
4Amines
• Amines and amides are abundant in nature. They are a major component of proteins and enzymes, nucleic acids, alkaloid drugs, etc. (Alkaloids are N-containing, weakly basic organic compounds; thousands of these substances are known.)
•Aminesare organic derivatives of ammonia, NH 3 , in which one or more of the three H's is replaced by a carbon group.• Amines are classified as primary(1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary(3°), depending on how many carbon groups are connected to the nitrogen atom.
NRR'' R'3° Amine
NRH H1° Amine
NRH R'2° Amine
NHH HAmmonia
Chapter 6 Amines and Amides
5Examples: Classifying Amines
• Classify the following amines as primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°). NCH 3 CH 2 CH 2 H H NCH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 2 CHCH 3 NH 2 NCH 3 CH 2 H CH 3NH N 6Nomenclature of Amines
•Simple 1°, 2°, and 3° amines: common (trivial) names are obtained by alphabetically arranging the names of the alkyl substituents on the nitrogen and adding the suffix -amine(e.g., ethylmethylamine).
•Amines in the IUPAC system: the "e" ending of the alkane name for the longest chain is replaced with -amine. The amine group is located by the position number. Groups that are attached to the nitrogen atom are located using "N" as the position number. More complex primary amines are named with - NH
2 as the aminosubstituent.•Aromatic amines: named as derivatives of the parent compound aniline. Substituents attached to the nitrogen are indicated by using "N-" as the location number.
NH 2 anilineChapter 6 Amines and Amides
7Examples: Nomenclature of Amines
• Provide common names for the following 2° and 3°amines; for 1° amines, provide common and/or IUPAC names where possible.
CH 3 NH 2 CHquotesdbs_dbs2.pdfusesText_2[PDF] amine reactions with hcl
[PDF] amine salt + naoh
[PDF] amine solubility in naoh
[PDF] amine to alcohol
[PDF] amines amides and amino acids are categories of isomers
[PDF] amines and amides practice problems
[PDF] amines and amides worksheet
[PDF] amines and diazonium salts
[PDF] amines class 12 important questions
[PDF] amines class 12 ncert notes
[PDF] amines class 12 ncert pdf
[PDF] amines class 12 ncert pdf download
[PDF] amines class 12 ncert solutions pdf download
[PDF] amines class 12 notes pdf
