 SVT-SPC-ACT 2-RESSOURCES protocole oxydation du glucose
SVT-SPC-ACT 2-RESSOURCES protocole oxydation du glucose
réactifs et les produits : le glucose C6H12O6 réagit avec le dioxygène O2 pour former du dioxyde de carbone CO2 et de l'eau H2O. Une équation chimique
 équations bilans
équations bilans
énergie de mouvement par une réaction chimique la combustion du glucose
 NZQA - NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90932) 2018
NZQA - NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90932) 2018
of CO and / or C (soot). • Links complete and incomplete combustion to the amount of oxygen and products produced. AND. One balanced symbol equation.
 How many water molecules produce during the complete oxidation
How many water molecules produce during the complete oxidation
water involvement in the aconitase reaction can be Complete Oxidation of Glucose? ... Sum of all reactions for combustion of glucose.
 NZQA - NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90932) 2021
NZQA - NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90932) 2021
oxygen gas that is needed from the atmosphere for complete combustion to occur Glucose is converted ... (ii) Complete combustion of ethanol equations:.
 Level 2 Chemistry (91164) 2015
Level 2 Chemistry (91164) 2015
23/11/2015 TOTAL. Level 2 Chemistry 2015 ... O(?)
 Level 1 Chemistry (90932) 2012
Level 1 Chemistry (90932) 2012
22/11/2012 (d) Identify and evaluate ONE effect that a product of the complete combustion reaction for ethanol would have on the environment.
 Stoichiometry of the water molecules in glucose oxidation revisited
Stoichiometry of the water molecules in glucose oxidation revisited
from glucose combustion in a calorimeter (eqn 2) by glucose molecule we can rewrite the overall reaction (eqn. 1) of the complete biological oxidation ...
 Thermochemistry
Thermochemistry
The total quantity of matter and energy in the universe is fixed. For example the combustion reaction that occurs when using an oxyacetylene torch.
 Chemistry 30 2017 Released Diploma Examination Items
Chemistry 30 2017 Released Diploma Examination Items
Fermentation of fruits and grains converts glucose to ethanol and carbon dioxide as Ethyne
 Energie des combustions - Correction - AlloSchool
Energie des combustions - Correction - AlloSchool
a Ecrire les équations des réactions de combustion complète du glucose et de la butyrine solide C6H12O6 ( æ)+6 O 6 (g) ?6 CO (g)+6 H 6O (g) 2 C15H26O6 ( æ)+37 O 6 (g) ?30 CO (g)+26 H 6O (g) b Calculer les masses molaires du glucose et de ma butyrine
 Chapter 2 Thermodynamics of Combustion - NRC
Chapter 2 Thermodynamics of Combustion - NRC
2: (2 11) Note that on the reactant side there are 2·(1+3 76) or 9 52 mol of air and its molecular mass is 28 96 kg/kmol In this text the reactions are balanced using 1 mol of fuel This is done here to simplify the calculations of the heat of reaction and ?ame temperature later in the chapter
What is the equation for combustion of glucose?
The equation for the combustion of glucose is: C6H12O6 (s) + 6O2 (g) -->6CO2 (g) + 6H2O (g). How many grams of H2O will be produced when 8.064g of glucose is burned? What is the combustion reaction of sucrose? Is combustion exothermic or endothermic, and why?
What is the balanced chemical equation for glucose?
Explanation: The complete combustion of glucose will give carbon dioxide and water, therefore, the balanced chemical equation can be written as: C6H 12O6(s) +6O2(g) ? 6CO2(g) + 6H 2O(g)
What is the total heat released during the combustion of glucose?
O(l) A 2.50 g sample of glucose and an excess of O 2 (g) were placed in a calorimeter. After the reaction was initiated and proceeded to completion, the total heat released by the reaction was calculated to be 39.0 kJ. (b) Calculate the value of ?H°, in kJ mol?1, for the combustion of glucose. 2.50 g ×612 6 1 mol C H O 180.16 g C H O 612 6
What is the formula for combustion of sucrose?
Combustion of sucrose is given by the chemical equation, C/b> + 12 O2 ——> 12CO2 + 11 H2O… What is true for combustion of sucrose?
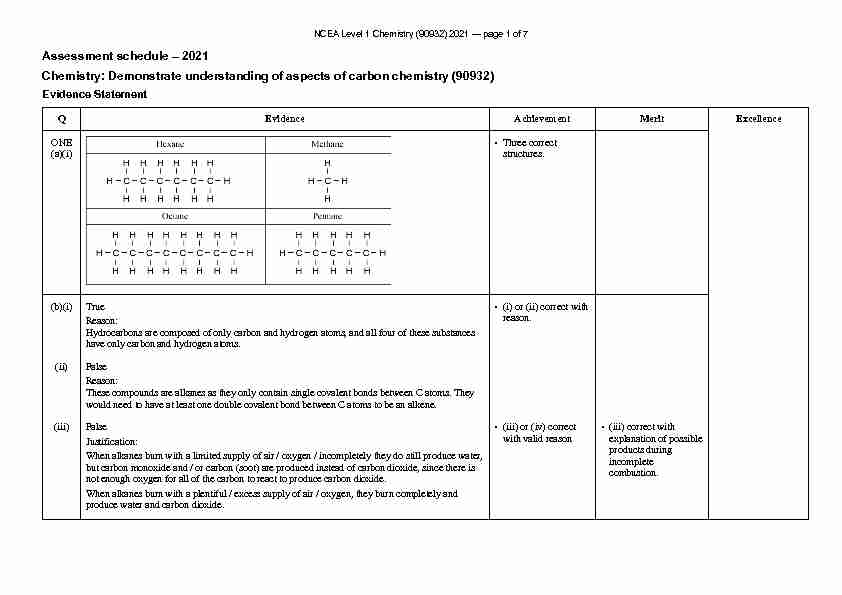 NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90932) 2021 - page 1 of 7
NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90932) 2021 - page 1 of 7 Assessment schedule - 2021
Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of aspects of carbon chemistry (90932)Evidence Statement
Q Evidence Achievement Merit Excellence
ONE (a)(i) • Three correct structures. (b)(i) TrueReason:
Hydrocarbons are composed of only carbon and hydrogen atoms, and all four of these substances have only carbon and hydrogen atoms. • (i) or (ii) correct with reason. (ii) FalseReason:
These compounds are alkanes as they only contain single covalent bonds between C atoms. They would need to have at least one double covalent bond between C atoms to be an alkene. (iii) FalseJustification:
When alkanes burn with a limited supply of air / oxygen / incompletely they do still produce water, but carbon monoxide and / or carbon (soot) are produced instead of carbon dioxide, since there is not enough oxygen for all of the carbon to react to produce carbon dioxide. When alkanes burn with a plentiful / excess supply of air / oxygen, they burn completely and produce water and carbon dioxide. • (iii) or (iv) correct with valid reason • (iii) correct with explanation of possible products during incomplete combustion. NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90932) 2021 - page 2 of 7 (iv) FalseJustification:
Methanol burns cleanly in air as it already contains an oxygen atom, reducing the amount of oxygen gas that is needed from the atmosphere for complete combustion to occur AND There is no relationship between the production of methanol from natural gas and its combustion outcome. • (iv) correct with full explanation.(c)(i) The process of fermentation involves the conversion of a solution of glucose molecules (in water /
moisture) into ethanol and carbon dioxide in warm, anaerobic conditions using yeast as a catalyst. Yeast is a living organism and requires warmth and moisture to carry out fermentation / anerobic conditions is without a supply of oxygen otherwise the fermentation products will be different.Equation:
C 6 H 12 O 6 → 2C 2 H 5OH + 2CO
2 • Glucose is converted into ethanol. • Explains the process with links to the conditions required. ORONE unbalanced
symbol equation (i) fermentation or (ii) combustion. • Fermentation process explained fully, including all required conditions. ANDONE equation from
(i) OR (ii) correctly balanced. (ii) Complete combustion of ethanol equations: ethanol + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water C 2 H 5OH + 3O
2 → 2CO 2 + 3H 2 O • Word equation completed correctly. (iii) Advantages of burning ethanol compared to burning petrol include: • Ethanol contains fewer C atoms than fuels such as petrol, so less greenhouse gas emissions (CO 2 ), which contribute to climate change / global warming due to increased trapping of infra-red radiation / heat and this affects the environment with rising sea levels / melting of polar ice /
unusual weather changes etc. OR CO 2 is absorbed by the ocean / reacts with water in clouds to form (carbonic) acid and this decreases the pH of the ocean, affecting marine ecosystems OR causes acid rain which can erode buildings, etc. • Cleaner burning than fuels such as petrol (which are more likely to undergo incomplete combustion); produces less C / soot. These carbon particles can produce visual pollution in the environment, e.g. blackening of limestone walls and monuments as carbon particles are deposited on them, or slow down photosynthesis due to carbon particles coating leaves, which prevents entry / exit of gases and water, or carbon particles in waterways affecting fish and plants, etc. • Ethanol is renewable, whereas fuels such as petrol are non-renewable. Renewable fuels are produced from plants which remove carbon / carbon dioxide from the atmosphere as they grow, resulting in lower net / overall contributions to greenhouse gas emissions when combusted. Non- renewable hydrocarbon-based fuels only add further carbon / carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, without taking any away, resulting in greater impacts to greenhouse gas levels.Allow for other valid advantages.
• Gives one advantage of using ethanol as a fuel. OR • Gives one disadvantage of using petrol as a fuel. • Links an advantage of burning ethanol to a reason. OR • Links a disadvantage of burning petrol to a reason. • Discusses TWO advantages of using ethanol over petrol as a fuel. Must include explanation of effects on environment. NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90932) 2021 - page 3 of 7NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5 M6 E7 E8
No response;
no relevant evidence.1a 2a 3a 4a 3m 4m 1e 2e
NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90932) 2021 - page 4 of 7Q Evidence Achievement Merit Excellence
TWO (a)A: methanol
B: heptane
C: ethanol
Compound B is heptane as it is an alkane, which means it is insoluble in water because the attraction between heptane and water is less than the attraction between heptane molecules. It also has the highest boiling point due to the greater molecular mass / number of C atoms, which requires more energy to overcome and form a gas. Compounds A and C are the two alcohols since they are soluble in water, which is because they contain an -OH group. This means that the attractions between the alcohols and water are greater than the attractions between alcohol molecules. Compound A is methanol and Compound C is ethanol since Compound A has a lower boiling point. Methanol has a lower molecular mass / number of C atoms than ethanol, so less heat energy is required to overcome the forces of attraction between molecules and form gaseous molecules. • All three compounds correct. • One description of solubility OR boiling point. • Explains solubility with reference to attractions between compound - water, and compound - compound. • Links greater number of carbons / higher molecular mass to increased forces between molecules to more heat energy required to overcome and hence a higher boiling point.Fully justifies all three
choices with reference to structure and properties of all three compounds. (b) Butane gas burner warning: If butane gas burners are used indoors or in confined spaces, incomplete combustion can occur due to a shortage of oxygen. If there is enough oxygen for complete combustion to occur, then carbon dioxide and water will be produced, which do not affect human health. However, if there is a shortage of oxygen then incomplete combustion occurs and C (soot) and CO are produced, which are harmful to human health. C (soot) can be inhaled and cause respiratory problems and damage the heart; it is also a carcinogen. CO is a poisonous gas, as it binds to red blood cells (preventing oxygen binding) leading to oxygen deficiency, and may cause death. Balanced symbol equations for combustion of butane:Sufficient oxygen / complete combustion
2C 4 H 10 + 13O 2 → 8CO 2 + 10H 2O (or C
4 H 10 + 6½O 2 → 4CO 2 + 5H 2 O )Limited oxygen / incomplete combustion
2C 4 H 10 + 9O 2 → 8CO + 10H 2 O (Accept balanced alternatives with different # CO and C.) Equations may have C and / or CO.) • States that incomplete combustion may occur. • States a product of incomplete combustion. • States a valid effect of incomplete combustion on human health. • Explains that incomplete combustion may occur due to lack of oxygen / air indoors or in confined space. ORExplains that complete
combustion will only occur if sufficient oxygen / air in open space. • Gives unbalanced symbol equation for either complete or incomplete combustion of butane. • Full explanation of ONE product of incomplete combustion to an effect on human health.Explains TWO effects of
incomplete combustion products on human health. ANDCorrect balanced
equation for incomplete or complete combustion.NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5 M6 E7 E8
No response;
no relevant evidence.1a 2a 3a 4a 3m 4m 1e 2e
NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90932) 2021 - page 5 of 7Q Evidence Achievement Merit Excellence
THREE (a)(i)A: methane, CH
4B: nonane, C
9 H 20C: eicosane, C
20 H 42• Correct identification of all 3 fractions OR
Methane has the lowest
boiling point, then nonane, then eicosane. (ii) Crude oil consists of a mixture of hydrocarbons, including alkanes, of different sizes. A distillation tower can be used to separate different alkanes because of their different molecular masses and hence different boiling points. Smaller molecules have a smaller mass and therefore weaker intermolecular forces between molecules and hence lower boiling points. As shown in the diagram, heated crude oil containing hydrocarbons, including eicosane, methane and nonane, enters the tower near the base. The column is hotter at the bottom and cooler at the top. In the tower smaller hydrocarbons with lower boiling points are collected higher up in the tower while larger molecules with higher boiling points are collected lower down in the tower. The vapour, containing methane (A) rises to the top since it has a low molecular mass (only 1 C atom) and having a very low boiling point, it remains a gas at the lower temperature. The top of the tower is not cool enough to condense the methane, so it leaves as gaseous molecules. Nonane has a higher molecular mass than methane (9 carbons) and so has a higher boiling point than methane. The vapour containing nonane (B) rises about halfway up the tower where the temperature is lower that its boiling point and then condenses as the particles hit the cool 'caps', and the liquid containing nonane is collected and leaves the tower. Eicosane has the highest molecular mass of the three compounds (20 carbons) and so has the highest boiling point. The vapour containing eicosane does not rise very far in the tower before it reaches a temperature lower than its boiling point and so the particles hit the caps and condense to form liquid eicosane, which leaves the tower at point C. • Recognises the separation of the (lighter and heavier) fractions depends on differences in the boiling points. ORRecognises that the top
of the tower is cooler / bottom of tower is hotter. • Correct identification of fractions. ANDLinks the size of
TWO of the
hydrocarbons A, B, C to their boiling points and where the fraction collects in the tower. • Comprehensive description of distillation tower, separation process of the two selected compounds in the distillation tower with links to molecular mass, boiling point, and place in the tower where the fractions are collected. NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90932) 2021 - page 6 of 7 (b)(i) • Steps 1 and 2 are correctly named. • Describes conditions for either Step 1 or 2. • TWO compounds correct. • All THREE Achieved points correct NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90932) 2021 - page 7 of 7 (ii) C 6 H 14 is an alkane, so only contains carbon to carbon single bonds. For a hydrocarbon to undergo polymerisation, it must contain a carbon-to-carbon double bond, which can be broken. The carbon atoms will then form single bonds with neighbouring monomers / molecules to form a long chain molecule. Therefore C 6 H 14 (hexane) cannot form polypropene (or any other polymer). Ethene does contain carbon-to-carbon double bonds and can therefore undergo polymerisation when the carbon-to-carbon double bonds are broken, and single covalent bonds are formed between carbon atoms of neighbouring molecules, forming a long carbon chain molecule (polyethene). However, it only contains two carbon atoms, so when it undergoes polymerisation, both carbon atoms in the monomer unit bond with carbon atoms on neighbouring molecules. Ethene cannot form compound C, polypropene, as it does not contain a third carbon atom (as propene does) to form methyl groups along the chain of carbon atoms. • Recognises that C=C required for polymerisation. • Explains why C 6 H 14 cannot form polypropene. ANDIdentifies that ethene
only contains two carbons so cannot form polypropene. ORFull explanation of
C 6 H 14 linking to polymerisation process. • Comprehensive explanation of why C 6 H 14 and ethene cannot be used to make polypropene, with reference to their structures, and the structure of polypropene.NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5 M6 E7 E8
No response;
no relevant evidence.1a 2a 3a 4a 1m 2m 1e 2e
Cut Scores
Not Achieved Achievement Achievement with Merit Achievement with Excellence0 - 8 9 - 12 13 - 18 19 - 24
quotesdbs_dbs29.pdfusesText_35[PDF] réaction endothermique
[PDF] combustion du charbon dans l'air
[PDF] les combustions 4ème cours
[PDF] combustion du carbone définition
[PDF] identifier le dioxyde de carbone
[PDF] combustion de l'aluminium
[PDF] combustion du fer et du soufre
[PDF] oxyde magnétique de fer formule
[PDF] combustion du fer dans le dioxygène tableau d avancement
[PDF] combustion du fer wikipedia
[PDF] oxyde de fer fe2o3
[PDF] formule chimique de l'alumine
[PDF] combustion du zinc
[PDF] masse molaire co2
