 HbA1c conversion table
HbA1c conversion table
mmol/mol. Conversion formulas. Old. = 00915 New + 2
 A. Units Amounts and Concentrations
A. Units Amounts and Concentrations
Note the abbreviations: 1 mmol = 1 millimole; 2 mmol = 2 millimoles; 5 µmol. = 5 micromoles. Concentrations in molarities are given by expressing the number of
 Topic 6: Common Lab Calculations
Topic 6: Common Lab Calculations
For example let's say you need 5.0 mmoles of moles to do other calculations (such as calculating molar equivalents or determining the limiting.
 Care of Children and Young People with an HbA1C greater than 75
Care of Children and Young People with an HbA1C greater than 75
4. 5. HbA1c 58-75 mmols/mol. 5. 6. HbA1c 75 mmol/mol or above. 6. 7. Basic steps comparison chart. 8. 8. Appendix 1: Parents and Young People Education
 NICE Guideline Template
NICE Guideline Template
5. • intensify drug treatment and. 1. • agree a target and aim for an HbA1c level of 53 mmol/mol (7.0%). [new 2015]. 2. 1.3.4.2 Self-monitoring of blood
 Electronic Supplementary Information
Electronic Supplementary Information
4 (1 mmol) KOtBu (0.5 mmol)
 4 Calculations Used in Analytical Chemisty
4 Calculations Used in Analytical Chemisty
Ex. 4-1. How many moles and millimoles of benzoic acid (M=122.1 g/mol) are Ex 4-5. Describe the preparation of 2.00 L of 0.108 M BaCl2 from BaCl2 · 2H2O.
 (Chapter 12) Electrolyte Solutions: Milliequivalents Millimoles
(Chapter 12) Electrolyte Solutions: Milliequivalents Millimoles
https://uomustansiriyah.edu.iq/media/lectures/4/4_2020_05_08!01_49_17_PM.pdf
 HbA1c Conversion Chart. Older DCCT-aligned (%) and newer IFCC
HbA1c Conversion Chart. Older DCCT-aligned (%) and newer IFCC
IFCC-standardised values are rounded to the nearest whole number. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. DCCT (%). IFCC. (mmol/mol).
 Glycemic Status and Thromboembolic Risk in Patients With Atrial
Glycemic Status and Thromboembolic Risk in Patients With Atrial
thromboembolism among patients with HbA1c=49–58 mmol/mol (hazard ratio 1.49; 95% CI
 [PDF] UNITÉS CONVERSIONS EQUIVALENTS & CALCULS DE DOSES
[PDF] UNITÉS CONVERSIONS EQUIVALENTS & CALCULS DE DOSES
1 oct 2014 · IV m m o l = u n ité d e ré fé re n c e FORMULE DE CONVERSION IONS MONOVALENTS IONS BIVALENTS ION TRIVALENT mmol= milliéquivalent (mEq)
 [PDF] Calculs et conversion dunités - Pharmacie des HUG
[PDF] Calculs et conversion dunités - Pharmacie des HUG
10 nov 2009 · 4 Le médicament: de la commande à l'administration CAS CLINIQUE 4 --- MILLIMOLES ET MILLIEQUIVALENTS Si la mole (mol) renseigne sur
 [PDF] mole g D D T T MM / 48800 = × × = ? ?
[PDF] mole g D D T T MM / 48800 = × × = ? ?
de volume V1=16 l et V2=14 l contenant 05 mole d'urée et o 8 moles de glucose respectivement mmol/l Le débit initial est égal a 42pmol/s
 [PDF] Corrigés exercices sur la mole les masses molaires la
[PDF] Corrigés exercices sur la mole les masses molaires la
05 mol; b 20 mmol; c 15 kmol ; on applique la relation N= n x NA 4 x 120 + 9 x 10 + 3 x 140 + 2 x 160 = 131 g mol-1 6) Squalène
 [PDF] CHIMIE Calculer les masses molaires des composés suivants
[PDF] CHIMIE Calculer les masses molaires des composés suivants
4 la concentration molaire du calcium en mol/L 4 L'azotémie (taux normal d'urée dans le sang) est comprise entre 25 et 75 mmol/L Ce
 [PDF] TABLES DES VALEURS EN UNITES CLASSIQUES ET UNITES
[PDF] TABLES DES VALEURS EN UNITES CLASSIQUES ET UNITES
0 à 4 µmol/l Sér Calcium Homme 88 à 103 mg/l 002495 220 à 258 mmol/l mmol/l LCR Glucose 05 à 08 g/l 5551 28 à 44 mmol/l
 [PDF] Chapitre 1 La quantité de matière la concentration molaire et le
[PDF] Chapitre 1 La quantité de matière la concentration molaire et le
donc n(C8H15O3N) = 289 10–5 mol METHODE 4 : Savoir calculer la quantité de matière à partir de la masse volumique ? Principe
 [PDF] Chapitre 5
[PDF] Chapitre 5
4 Ce nombre est fantastiquement grand : 602 214 076 000 000 000 000 000 soit 5 3 2 - Constante d'Avogadro Le nombre d'entités par mole est une
Comment calculer le nombre de mol ?
Il suffit d'appliquer la relation n=m/M pour déterminer le nombre de mole.Comment calculer la mole d'un atome ?
La masse molaire moléculaire est égale à la somme des masses molaires atomiques des éléments chimiques constituant la molécule. L'unité est toujours le gramme par mole, notée g. mol–1. Ainsi, la masse molaire de la molécule d'eau H2O est : M(H2O) = 2 x M(H) + M(O) = 2 x 1,00 + 16,0 = 18,0 g.Comment convertir le mmol en mg ?
(mg/dL x 0,0259 = mmol/L).- Formules de conversion du milliéquivalent :
Ainsi, 1 mEq est représenté par 1 mg d'hydrogène (1 mole) ou 23 mg de Na+, 39 mg de K+, etc.
 14
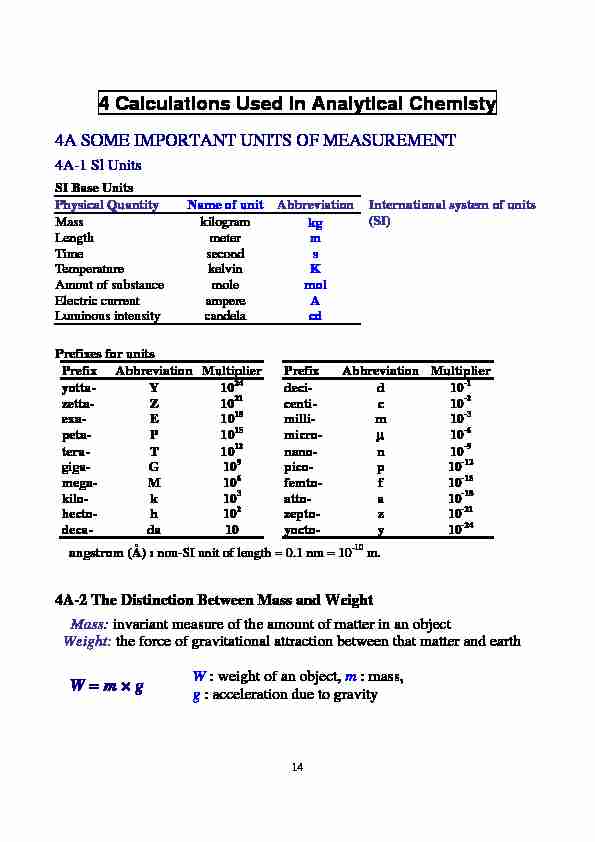
14 4 Calculations Used in Analytical Chemisty
4A SOME IMPORTANT UNITS OF MEASUREMENT
4A-1 Sl Units
SI Base Units
Physical Quantity Name of unit
AbbreviationMass kilogram kg
Length meter m
Time second
sTemperature kelvin
KAmout of substance mole
molElectric current ampere
ALuminous intensity candela
cd International system of units (SI)Prefixes for units
Prefix Abbreviation Multiplier Prefix Abbreviation Multiplier yotta- Y 1024 deci- d 10
-1 zetta- Z 10 21centi- c 10 -2 exa- E 10 18 milli- m 10 -3 peta- P 10 15 micro- 10-6 tera- T 10 12 nano- n 10 -9 giga- G 10 9 pico- p 10 -12 mega- M 10 6 femto- f 10-15 kilo- k 10 3 atto- a 10 -18 hecto- h 10 2 zepto- z 10 -21 deca- da 10 yocto- y 10 -24 angstrom (Å) : non-SI unit of length = 0.1 nm = 10 -10 m.
4A-2 The Distinction Between Mass and Weight
Mass: invariant measure of the amount of matter in an objectWeight:
the force of gravitational attraction between that matter and earthW = m g
W : weight of an object, m : mass,
g : acceleration due to gravity 154A-3 The Mole
Avogadro's number (6.022 10
23the molar mass of formaldehyde CH 2 O molO16.0g
OCH molO 1mol
molH1.0gOCH molH 2mol
molC12.0gOCH molC 1mol
222OCH
2 = 30.0 g/mol CH 2 O the molar mass of glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 molO16.0gOCH molO 6mol
molH1.0gOCH molH 12mol
molC12.0gOCH molC 6mol
222OHC
6126= 180.0 g/mol C 6 H 12 O 6 * Millimole(mmol) = 10 -3 mol
1 mfw = 10
-3 fw no. of moles of a species X ( no. mol A): X XX MmnEx. 4-1.
How many moles and millimoles of benzoic acid (M=122.1 g/mol) are contained in of the pure acid? amount g HBz = (1 mol/122.1 g) = 0.0164 mol HBz amount g HBz = (1 mmol/0.1221 g) = 16.4 mmol HBzEx. 4-2.
How many grams of Na
(22.99 g/mol) are contained in 25. of Na 2 SO 4 (142.0 g/mol)? amount Na 2 SO 4 = 25.00 g (1 mol/142.0 g) = 0.17606 mol since 1 mol of Na 2 SO 4 contains 2 mol of Na amount Na = 2 0.17606 mol = 0.35211 mol mass Na = 0.35211 mol 22.99 g/mol = 8.10 g4B SOLUTIONS AND THEIR CONCENTRATIONS
4B-1 Concentration of Solutions
Molar Concentration (C)
V nC XX solutionmLno.solute mmol no. solutionLno.solute mol no.molarity 16 Ex 4-3 Calculate the molar conc. of ethanol in an aqueous solution that contains2. of C
2 H 5OH (46.07 g/mol) in 3.50 L of solution.
no. mol = (1 mol/46.07 g) = 0.04992 mol CC2H5OH = 0.04992 mol/3.50 L = 0.01426 mol/L = 0.0143 M Analytical Molarity: total number of moles of a solute in 1 L solution (How a solution has been prepared?)Ex: 1.0 M H
2 SO 4 soln Ш dissolving 1.0 mol or H 2 SO 4 in water and diluting to exactly 1.0 L.Equilibrium or Species Molarity
: the molar conc. of a particular species in a soln. at equilibriumFormal Concentration (Formality, F)
: analytical concentrationEx: 1.00 F NaOH or H
2 SO 4Ш equilibrium molar conc. = 0.00 M
Ex 4-4.
Calculate the analytical and equilibrium molar conc. of the solute species in an aqueous solution that contains 285 mg of trichloroacetic acid (Cl 3 CCOOH, 163.4 g/mol) in 10.0 mL (the acid is 73 % ionized in water). no. mol HA = 285 mg (1 g/1000 mg) (1 mol/163.4 g) = 1.744 10 -3 molM174.0LHA mol174.0L1mL 1000
mL 10.0HA mol 101.744 3- HA C HAInitial 100%
ѳᑽࡕ27% H
0%73% + A
0%73% [HA] = 0.174 mol/L 0.27
= 0.047 mol/L = [H 3 O ] = [A-] = CHA - [HA] = 0.174 - 0.047 = 0.127 M Ex 4-5. Describe the preparation of 2.00 L of 0.108 M BaCl2 from BaCl2
· 2H
2 O (244 g/mol).2.00 L 0.108 mol/L = 0.216 mol BaCl
2· 2H
2 O0.216 mol 244 g/mol = BaCl
2· 2H
2 ODissolve of BaCl
quotesdbs_dbs33.pdfusesText_39[PDF] point critique derivee
[PDF] y=ax+b trouver b
[PDF] on prépare un volume v=0.200 l d'une eau iodée
[PDF] déterminer les réels a b et c sachant que
[PDF] p(z)=z^3-3z^2+3z+7
[PDF] déterminer les réels a b et c tels que
[PDF] déterminer les réels a et b d'une fonction exponentielle
[PDF] méthode d'identification des coefficients
[PDF] quel est mon type de mémoire
[PDF] type de mémoire humaine
[PDF] test type de mémoire visuelle auditive kinesthésique
[PDF] test de mémoire gratuit
[PDF] test type de mémoire collège
[PDF] nombre d'oxydation de l'oxygène
