 1 The Basic HTTP GET-response interaction
1 The Basic HTTP GET-response interaction
embedded objects and HTTP authentication and security. 1 The Basic HTTP GET-response interaction. 1. Start up your web browser. 2. Start up the Wireshark
 Wireshark Lab: HTTP SOLUTION
Wireshark Lab: HTTP SOLUTION
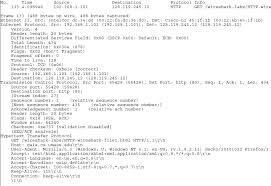
The HTTP CONDITIONAL GET/response interaction. Here's a screenshot after Answer: there were three HTTP GET messages sent: packet 10 in the trace (to get the ...
 Ethereal Lab: HTTP
Ethereal Lab: HTTP
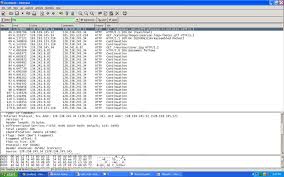
Page 1. Ethereal Lab: HTTP. 1. The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction. No. Time. Source. Destination. Protocol Info. 1190 131.859385 128.238.245.34. 128.119.
 COEN 445 Communication Networks and Protocols Lab 2
COEN 445 Communication Networks and Protocols Lab 2
Stop Wireshark packet capture. Page 4. 1.The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction. (Cont.).
 Lab 1: Applications
Lab 1: Applications
Step 1: The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction. Let's begin our exploration of HTTP by downloading a very simple HTML file - one that is very short and
 Ethereal Lab: HTTP
Ethereal Lab: HTTP
1. The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction. Let's begin our exploration of HTTP by downloading a very simple HTML file - one that is very short and contains
 Wireshark Lab: Assignment 2w (Optional)
Wireshark Lab: Assignment 2w (Optional)
1. The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction. Let's begin our exploration of HTTP by downloading a very simple HTML file -one that is very short and contains
 Lab Assignment 2 ECE325 2020 Spring
Lab Assignment 2 ECE325 2020 Spring
1. The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction. Let's begin our exploration of HTTP by downloading a very simple HTML file - one that is very short and contains
 Wireshark Lab: HTTP v6.1
Wireshark Lab: HTTP v6.1
1. 1. The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction. Let's begin our exploration of HTTP by downloading a very simple HTML file - one that is very short and
 Wireshark Lab: HTTP
Wireshark Lab: HTTP
1. The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction. Let's begin our exploration of HTTP by downloading a very simple HTML file - one that is very short and contains
 1 The Basic HTTP GET-response interaction
1 The Basic HTTP GET-response interaction
1 The Basic HTTP GET-response interaction. 1. Start up your web browser. 2. Start up the Wireshark packet sniffer. Enter “http” in the display-filter-
 Wireshark Lab: HTTP SOLUTION
Wireshark Lab: HTTP SOLUTION
The HTTP CONDITIONAL GET/response interaction. Here's a screenshot after doing the two identical HTTP GETs: First GET then a reply
 Ethereal Lab: HTTP
Ethereal Lab: HTTP
Ethereal Lab: HTTP. 1. The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction. No. Time. Source. Destination. Protocol Info. 1190 131.859385 128.238.245.34. 128.119.245.12.
 Ethereal Lab: HTTP
Ethereal Lab: HTTP
Before beginning these labs you might want to review Section 2.2 of the text. 1. The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction. Let's begin our exploration of HTTP
 Wireshark Lab: HTTP
Wireshark Lab: HTTP
1. The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction 1. Start up your web browser. 2. Start up the Wireshark packet sniffer as described in the Introductory lab ...
 COEN 445 Communication Networks and Protocols Lab 2
COEN 445 Communication Networks and Protocols Lab 2
Stop Wireshark packet capture. Page 4. 1.The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction. (Cont.).
 Wireshark Lab: Assignment 2w (Optional)
Wireshark Lab: Assignment 2w (Optional)
1. The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction 1. Start up your web browser. 2. Start up the Wireshark packet sniffer as described in the Introductory lab ...
 Homework Problems
Homework Problems
Please complete all six homework problems and the twenty-one lab problems. Homework Problems. 1. Part I: The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction.
 Wireshark Lab: HTTP v6.1
Wireshark Lab: HTTP v6.1
want to review Section 2.2 of the text.1. 1. The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction. Let's begin our exploration of HTTP by downloading a very simple HTML
 1. Is your browser running HTTP version 1.0 or 1.1? What version of
1. Is your browser running HTTP version 1.0 or 1.1? What version of
25-Feb-2010 See screenshot of response with Alice's Adventures... 3. Page 4. 10. Now inspect the contents of the second HTTP GET request from your ...
 1 The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction
1 The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction
several aspects of the HTTP protocol: the basic GET/response interaction HTTP message formats retrieving large HTML files retrieving HTML files with embedded objects and HTTP authentication and security Before beginning these labs you might want to review Section 2 2 of the text 1 The Basic HTTP GET/response interaction
 Wireshark Lab: HTTP v7 - Harvey Mudd College
Wireshark Lab: HTTP v7 - Harvey Mudd College
explore several aspects of the HTTP protocol: the basic GET/response interaction HTTP message formats retrieving large HTML files retrieving HTML files with embedded objects and HTTP authentication and security
1. Is your browser running HTTP version 1.0 or 1.1? What version of HTTP is the server
running? HTTP 1.1 (see screenshot)2. What languages (if any) does your browser indicate that it can accept to the server? en-US
(US English) as shown in prior screenshot3. What is the IP address of your computer? Of thespinlab.wpi.eduserver? My computer
is 10.211.55.3 (this is a virtual IP address assigned by my virtual machine software) and the destination is 130.215.16.168. See prior screenshot.4. What is the status code returned from the server to your browser? 200 OK (see prior screen-
shot)5. When was the HTML le that you are retrieving last modied at the server? We can lter
messages byhttp.last_modifiedand we see that the HTTP response I received for the html 1 le doesn't show this eld. We do have ahttp.last_modifiedeld in the favicon response however, as shown in the screenshot below. This says the favicon was last modied on Feb25, 2010.6. How many bytes of content are being returned to your browser? Content-length = 209 bytes.
See screenshot below.
27. By inspecting the raw data in the packet content window, do you see any headers within the
data that are not displayed in the packet-listing window? If so, name one. No. The raw data appears to match up exactly with what is shown in the packet-listing window.8. Inspect the contents of the rst HTTP GET request from your browser to the server. Do you
see an \IF-MODIFIED-SINCE" line in the HTTP GET? No.9. Inspect the contents of the server response. Did the server explicitly return the contents of
the le? How can you tell? See screenshot of response with Alice's Adventures... 310. Now inspect the contents of the second HTTP GET request from your browser to the server.
Do you see an \IF-MODIFIED-SINCE:" line in the HTTP GET? If so, what information follows the \IF-MODIFIED-SINCE:" header? Yes. If-Modified-Since: Wed, 12 Mar 2014 17:29:08 GMT\r\n.See screenshot below.
411. What is the HTTP status code and phrase returned from the server in response to this second
HTTP GET? Did the server explicitly return the contents of the le? Explain. As seen in the previous screenshot, we get a HTTP/1.1 304 Not Modied Response. This is much shorter than the full response packet seen previously which contained all of Alice in Wonderland.12. How many HTTP GET request messages were sent by your browser (again, ignoring requests
for favicon.ico)? Just one.13. How many data-containing TCP segments were needed to carry the single HTTP response?
From the screenshot below, there are 4 TCP segments. 514. What is the status code and phrase associated with the response to the HTTP GET request?
HTTP/1.1 200 OK (as seen in previous screenshot)
15. Are there any HTTP status lines in the transmitted data associated with a TCP- induced
\Continuation"? No.16. How many HTTP GET request messages were sent by your browser? To which Internet
addresses were these GET requests sent? Three: 130.215.16.168, 130.215.36.26, 208.122.28.10.See screenshot below.
617. Can you tell whether your browser downloaded the two images serially, or whether they were
downloaded from the two web sites in parallel? Explain. Based on the timestamps, it appears the images were downloaded serially. Also, the source port is incrementing each time from64444, 64445, 64446 which means that the images were received serially over separate TCP
connections.18. What is the server's response (status code and phrase) in response to the initial HTTP GET
message from your browser? HTTP/1.1 401 Authorization Required (see screenshot below) 719. When your browser's sends the HTTP GET message for the second time, what new eld is
included in the HTTP GET message? Authorization eld. See screenshot below. 820. Copy the string of text that appears after \Authorization: Basic ", and enter it into the Base64
decoder here {http://www.motobit.com/util/base64-decoder-encoder.asp. Make sure to click on \decode". To what ASCII string does the Base64 string decode to? (Hint: you should see the username and password for the course website embedded in the string). No need since Wireshark has already done the decoding. See the previous screenshot. Our credentials are clearly visible in Wireshark. 9quotesdbs_dbs14.pdfusesText_20[PDF] 10 1/2 characters per inch (non proportional)
[PDF] 100 middle earth
[PDF] 100 pure new zealand controversy
[PDF] 1000 common french phrases pdf
[PDF] 1000 english phrases with meanings pdf
[PDF] 1000 free instagram followers trial without password
[PDF] 1000 interesting facts pdf
[PDF] 1000 most common french words pdf
[PDF] 102 500 lpic 1 exam 102 part 2 of 2 version 5.0
[PDF] 104th district michigan map
[PDF] 1200 paris street sudbury
[PDF] 126 rue de l'université 75355 paris 07 sp
[PDF] 12th century europe map
[PDF] 1300 paris street
