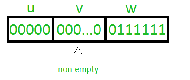 Pumping Lemma in Theory of Computation
Pumping Lemma in Theory of Computation
Pumping Lemma for Regular Languages. Theorem. Let L be a regular language Applications of Pumping Lemma. Pumping lemma is used to check whether a grammar is ...
 The Application of Pumping Lemma on Context Free Grammars
The Application of Pumping Lemma on Context Free Grammars
and the terminal strings constitute the language generated by the. PCGS. Here we apply pumping lemma on certain languages to show that they are not context
 More Applications of The Pumping Lemma
More Applications of The Pumping Lemma
– Regular Expressions. – Regular Grammars. – Properties of Regular Languages. – Languages that are not regular and the pumping lemma. • Context Free Languages.
 Some Applications of the Formalization of the Pumping Lemma for
Some Applications of the Formalization of the Pumping Lemma for
Context-free languages are highly important in computer language processing technology as well as in formal language theory. The Pumping Lemma for
 Pumping Lemma for Context-Free Languages
Pumping Lemma for Context-Free Languages
Department of Computer Science and Automation. Indian Institute of Science Bangalore. 12 October 2021. Page 2. Pumping Lemma. Applications.
 The Pumping Lemma: limitations of regular languages - Informatics
The Pumping Lemma: limitations of regular languages - Informatics
06-Oct-2015 non-regularity of languages? 3 / 15. Page 4. Showing a language isn't regular. The pumping lemma. Applying the pumping lemma. The basic ...
 The Pumping Lemma for Regular Languages
The Pumping Lemma for Regular Languages
The Pumping Lemma forRegular Languages – p.19/39. Page 69. Applications. Example 1: prove that абвгдеджзйг is not regular. The Pumping Lemma forRegular
 The Pumping Lemma: limitations of regular languages - Informatics
The Pumping Lemma: limitations of regular languages - Informatics
06-Oct-2016 Showing a language isn't regular. The pumping lemma. Applying the pumping lemma. Exercises. Which of the following languages are regular? 1.
 Pumping Lemma and Ultimate Periodicity
Pumping Lemma and Ultimate Periodicity
09-Oct-2018 Pumping lemma for regular languages. Based on a simple observation ... Example applications of Pumping Lemma. Describe Your strategy to beat ...
 BBM401-Lecture 12: Non-Context-free Languages
BBM401-Lecture 12: Non-Context-free Languages
lemma. Agha-Viswanathan. CS373. Page 6. Introduction. Applying the Pumping Lemma. Proof of the Pumping Lemma. Non-context-free languages. Pumping Lemma. Pumping
 The Application of Pumping Lemma on Context Free Grammars
The Application of Pumping Lemma on Context Free Grammars
and the terminal strings constitute the language generated by the. PCGS. Here we apply pumping lemma on certain languages to show that they are not context
 Pumping Lemma in Theory of Computation
Pumping Lemma in Theory of Computation
does not mean that the language is regular. Applications of Pumping Lemma. Pumping Lemma is to be applied to show that certain languages are not regular. It.
 CS310 : Automata Theory 2019 Lecture 11: Applications of pumping
CS310 : Automata Theory 2019 Lecture 11: Applications of pumping
28-Jan-2019 Contrapositive of pumping lemma. Recall. Theorem 11.1. Let L be a language. L is not regular if for each n
 More Applications of The Pumping Lemma
More Applications of The Pumping Lemma
Context Free Languages. – Context Free Grammars. – Derivations: leftmost rightmost and derivation trees. – Parsing and ambiguity.
 The Pumping Lemma: limitations of regular languages - Informatics
The Pumping Lemma: limitations of regular languages - Informatics
06-Oct-2016 Applying the pumping lemma. Recap of Lecture 7. Lexical classes in programming languages may typically be specified via regular languages.
 The Pumping Lemma: limitations of regular languages - Informatics
The Pumping Lemma: limitations of regular languages - Informatics
06-Oct-2015 Showing a language isn't regular ... Applying the pumping lemma ... We have hinted before that not all languages are regular. E.g..
 The Pumping Lemma: limitations of regular languages - Informatics
The Pumping Lemma: limitations of regular languages - Informatics
03-Oct-2017 Applying the pumping lemma. Recap of Lecture 7. Lexical classes in programming languages may typically be specified via regular languages.
 The pumping lemma - Informatics 2A: Lecture 8
The pumping lemma - Informatics 2A: Lecture 8
06-Oct-2011 Showing a language isn't regular. The pumping ... 3 Applying the pumping lemma ... We have hinted before that not all languages are regular.
 Pumping Lemma and Ultimate Periodicity
Pumping Lemma and Ultimate Periodicity
09-Oct-2018 Lengths of words in a regular language are “ultimately periodic.” ... Example applications of Pumping Lemma.
 proving languages not regular using Pumping Lemma
proving languages not regular using Pumping Lemma
Here is the Pumping Lemma. If L is a regular language then there is an integer n > 0 with the property that: (*) for any string x ?
?IntroductionThe Pumping Lemma is used for proving that a language isnotregular. Here is the Pumping Lemma.
IfLis a regular language, then there is an integern >0 with the property that: (*)for any stringx?Lwhere|x| ≥n, there are stringsu,v,wsuch that (i)x=uvw, (ii)v?=?, (iv)uvkw?Lfor allk?N. To prove that a languageLisnotregular, we use proof by contradiction. Here are the steps.1. Suppose thatLisregular.
2. SinceLis regular, we apply the Pumping Lemma and assert the existence of a numbern >0 that
satisfies the property (*).3. Give a particular stringxsuch that
(a)x?L, (b)|x| ≥n. This the trickiest part. A wrong choice here will make step 4 impossible.4. By Pumping Lemma, there are stringsu,v,wsuch that (i)-(iv) hold. Pick a particular numberk?N
and argue thatuvkw??L, thus yielding our desired contradiction. What follows are two example proofs using Pumping Lemma. CSC B36 proving languages not regular using Pumping Lemma Page 1 of 3 ?A (relatively) easy exampleLetL={0k1k:k?N}. We prove thatLis not regular. [step 1]By way of contradiction, supposeLis regular.
[step 2]Letnbe as in the Pumping Lemma.
[step 3]Letx= 0n1n.
Thenx?L[definition ofL]
and|x|= 2n≥n. [step 4]By Pumping Lemma, there are stringsu,v,wsuch that
(i)x=uvw, (ii)v?=?, (iv)uvkw?Lfor allk?N. Letybe the prefix ofxwith lengthn. I.e.,yis the firstnsymbols ofx.By our choice ofx,y= 0n.
By (iv),uv2w?L.(#)
Aside:We are pickingk= 2. Indeed, anyk?= 1 will do here.However,uv2w=uvvw
= 0 n+j1n ??L, [definition ofL; sincej >0,n+j?=n] which contradicts (#).ThereforeLis not regular.?
CSC B36 proving languages not regular using Pumping Lemma Page 2 of 3 ?A harder exampleLetL={(10)p1q:p,q?N,p≥q}. We prove thatLis not regular. [step 1]By way of contradiction, supposeLis regular.
[step 2]Letnbe as in the Pumping Lemma.
[step 3]Letx= (10)n1n.
Thenx?L[definition ofL]
and|x|= 3n≥n. [step 4]By Pumping Lemma, there are stringsu,v,wsuch that
(i)x=uvw, (ii)v?=?, (iv)uvkw?Lfor allk?N.Letybe the prefix ofxwith lengthn.
By our choice ofx,y= (10)n
2ifnis even, andy= (10)n-121 ifnis odd.
By (i) and (iii),uvis a prefix ofy, and
2, or 2. Combining with (ii) - depending on whether|uv|is even or odd, 2, or 2.There are 3 cases to consider:
(a)vstarts with 0 and ends with 0. (b)vstarts with 1 and ends with 1. (c)vstarts and ends with different symbols.For case (a),uv0w=uwcontains 110 as a substring.
Thusuv0w??L, [110 is not a substring of any string inL] which contradicts (iv). Similarly for case (b),uv0wcontains 00 as a substring.[details left to reader]For case (c),v= (10)iorv= (01)i, where 0< i.
So|v|= 2i.
Thusuv0w=uw= (10)n-i1n??L, [definition ofL;n-i < n] which contradicts (iv).We reach a contradiction in all cases.
ThereforeLis not regular.?
CSC B36 proving languages not regular using Pumping Lemma Page 3 of 3quotesdbs_dbs17.pdfusesText_23[PDF] application of z transform in image processing
[PDF] application of z transform in signals and systems
[PDF] application of z transform pdf
[PDF] application of z transform to solve difference equation
[PDF] application of z transform with justification
[PDF] application pour apprendre l'anglais gratuit sur pc
[PDF] application security risk assessment checklist
[PDF] applications of composite materials
[PDF] applications of dft
[PDF] applications of exponential and logarithmic functions pdf
[PDF] applications of therapeutic drug monitoring
[PDF] applied environmental microbiology nptel
[PDF] applied environmental microbiology nptel pdf
[PDF] applied information and communication technology a level
