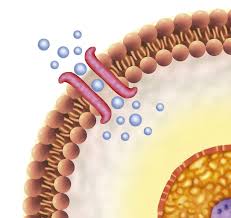
 DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS
DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS
ANSWER: THE PARTICLES DIFFUSE FROM. MORE CONCENTRATED TO LESS. CONCENTRATED What is moving during osmosis? 3. Which type of cellular transport requires ...
 Untitled
Untitled
Key. *Rules: •water goes towards higher solute. • water into cell. Period: lesser Hzo hypotonic. 6 water out of cell-. So. Date: Osmosis Worksheet. 20 Points.
 Amoeba Sisters Video Recap of Osmosis
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap of Osmosis
Your answer needs to have an arrow indicating the direction of water flow in osmosis a label for. "hypertonic
 Gummy Bear Osmosis Lab
Gummy Bear Osmosis Lab
Osmosis is a kind of diffusion. When diffusion occurs molecules move from a ☆ Conclusion: ANSWER KEY water membrane cell selectively permeable osmosis.
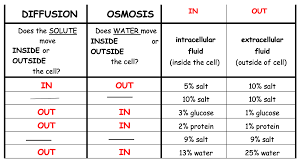 Diffusion & Osmosis worksheet ANSWERS
Diffusion & Osmosis worksheet ANSWERS
Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet. 1. How are the molecules moving in the examples below? Write OSMOSIS or DIFFUSION. a) The student sitting next to you just
 Transport Review answer keys.pdf
Transport Review answer keys.pdf
Cell Transport Review Worksheet. Complete the table by checking the correct Osmosis is the diffusion of water from an area of high concentration to an ...
 Name: Date: Gummy Bear Osmosis Lab #: ______ Purpose
Name: Date: Gummy Bear Osmosis Lab #: ______ Purpose
Round your answers to the nearest tenth. 5. Record any observations for the tap water bear on the data table below. 6. Place this bear aside on a paper towel.
 topic 1.4 answers
topic 1.4 answers
Outline the two key qualities of plasma membranes. 1 E.g. simple diffusion facilitated diffusion
 Answers
Answers
that has entered by osmosis. This maintains water levels within closely controlled limits. homeostasis. Water enters the cell by osmosis and is collected in
 Initiate Scholarship Implem ent C urriculum Submission & Publication
Initiate Scholarship Implem ent C urriculum Submission & Publication
13 Oct 2021 Sharpen your engagement strategy with learners and key stakeholders ... (Osmosis Wayne State
 Untitled
Untitled
lesser H2O. • water into cell = hypotonic key. 6 water out of cell- hypertonic solution. Period: Date: Names: Biology ~ Mr. Croft. Osmosis Worksheet.
 Cell Transport Worksheet Pdf
Cell Transport Worksheet Pdf
worksheets osmosis worksheet answer key difference in. Answer sheets are provided for each worksheet. Like passive transport worksheet answers pdf.
 Amoeba Sisters Video Recap of Osmosis
Amoeba Sisters Video Recap of Osmosis
What would occur if instead
 Diffusion & Osmosis worksheet ANSWERS
Diffusion & Osmosis worksheet ANSWERS
Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet. 1. How are the molecules moving in the examples below? Write OSMOSIS or DIFFUSION. a) The student sitting next to you just
 Cell Membrane & Tonicity Worksheet
Cell Membrane & Tonicity Worksheet
NAME__________ ANSWER KEY Cell Membrane & Tonicity Worksheet ... The process by which water diffuses across a membrane called OSMOSIS.
 Gummy Bear Osmosis Lab
Gummy Bear Osmosis Lab
Conclusion: ANSWER KEY water membrane cell selectively permeable osmosis. Why did that happen? It has to do with a process called osmosis.
 Untitled
Untitled
Cell Transport Review Worksheet Osmosis is the diffusion of water from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
 Osmosis Diffusion Lesson Pack
Osmosis Diffusion Lesson Pack
Diffusion & Osmosis Lesson Pack are learning about osmosis & diffusion! ... OSMOSIS & DIFFUSION QUIZ Answers: 1. Osmosis. 2. Selectively Permeable.
 Untitled
Untitled
BLM 3-7 Answers: The Fluid-Mosaic Model WORKSHEET. ANSWERS. 1. Define the terms diffusion and osmosis. Give an example of these two processes.
 What is the difference between osmosis and diffusion?
What is the difference between osmosis and diffusion?
Osmosis: Osmosis is the movement of solvent particles across a semipermeable membrane from a dilute solution into a concentrated solution. The solvent moves to.
 Answer Key - iBlog Teacher Websites – Dearborn Public Schools
Answer Key - iBlog Teacher Websites – Dearborn Public Schools
Osmosis Worksheet 20 Points Below are animal cells placed in beakers of various concentrations Draw an arrow to show which way the water would move by osmosis Fill in any missing percentages (water or solute) Identify the type of solution (isotonid hypertonic or hypotonic) 400/0 solute H20 10 solute H20 100/0 solute 630/0 H20 37 solute 1-120
 Osmosis Practice Worksheets and Activities with Answers
Osmosis Practice Worksheets and Activities with Answers
Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet 1 How are the molecules moving in the examples below? Write OSMOSIS or DIFFUSION a) The student sitting next to you just came from gym class and forgot to shower and you can tell D b) After sitting in the bathtub for hours your fingers start to look like prunes O
 Osmosis Practice Key - Mayfield City Schools
Osmosis Practice Key - Mayfield City Schools
Created Date: 10/30/2014 2:19:18 PM
 NAME DATE PERIOD - Chandler Unified School District
NAME DATE PERIOD - Chandler Unified School District
Define osmosis THE MOVEMENT OF WATER ACROSS A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE FROM AN AREA OF HIGH CONCENTRATION TO AN AREA OF LOW CONCENTRATION In which direction does water move across membranes up or down the concentration gradient? DOWN Define these 3 terms: isotonic- hypertonic hypotonic
 Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet - loreescience
Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet - loreescience
Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet 1 How are the molecules moving in the examples below? Write OSMOSIS or DIFFUSION a The student sitting next to you just came from gym class and forgot to shower and you can tell b After sitting in the bathtub for hours your fingers start to look like prunes c
 Searches related to osmosis worksheet answer key pdf filetype:pdf
Searches related to osmosis worksheet answer key pdf filetype:pdf
Osmosis Worksheet 20 Points Below are animal cells placed in beakers of various concentrations 1 Draw an arrow to show which way the water would move by osmosis 2 Fill in any missing percentages (water or solute) 3 Identify the type of solution (isotonic hypertonic or hypotonic) 40 H 60 80 H 2O 20 solute 75 H 2O 25 solute
What is osmosis worksheet?
- Osmosis Worksheet : Determine the solute and solvent for the solution outside the cell (environment) and for the inside of the cell. Give the direction of the net movement of water (into cell, out of cell, or into & out of cell at equal rates). Loading... Taking too long?
How should students develop osmosis skills?
- Students should work on developing this skill when completing practicals during the course. This core practical uses potato strips to demonstrate osmosis. The potato strip will lose or gain mass, due to osmosis, depending on the concentration of solutes in the solution.
Which experiment could create condition changes in the variable using osmosis?
- Osmosis contains 3 aspects that are Hypertonic, Isotonic, and Hypotonic. These aspects decide the different kind of diffusion. Hypertonic can be define as more water inside, Isotonic define as more water outside. The Osmosis experiment could create condition changing in the variable. of them is by the Potato - Salt-water experiment.
How does reverse osmosis occur in a cell?
- Reverse osmosis occurs when the water is moved across the membrane against the concentration gradient, from lower concentration to higher concentration. To illustrate, imagine a semipermeable membrane with fresh water on one side and a concentrated aqueous solution on the other side.
NAME__________ ANSWER KEY ___________________
DATE_________________ PERIOD_________
Cell Membrane & Tonicity Worksheet
Composition of the Cell Membrane & Functions
The cell membrane is also called the PLASMA membrane and is made of a phospholipid BI-LAYER. The phospholipids have a hydrophilic (water attracting) HEADS and two hydrophobic (water repelling) TAILS. The head of a phospholipid is made of an alcohol and GLYCEROL group, while the tails are chains of FATTY ACIDS. Phospholipids can move SIDEWAYS and allow water and other NON-POLAR molecules to pass through into or out of the cell. This is known as simple PASSIVE TRANSPORT because it does not require ENERGY and the water or molecules are moving WITH the concentration gradient.SKETCH AND LABEL a
phospholipid coloring the heads red and the tails blue. Another type of lipid in the cell membrane is CHOLESTEROL that makes the membrane more fluid.Embedded in the phospholipid bilayer are PROTEINS that also aid in diffusion and in cell recognition.
Proteins called INTEGRAL proteins go all the way through the bilayer, while PERIPHERAL proteins are only
on one side. Large molecules like PROTEINS or carbohydrates use proteins to help move across cellmembranes. Some of the membrane proteins have carbohydrate PARTS attached to help cells in recognize
each other and certain molecules.List 4 functions of the cell or plasma membrane:
a. CELL SIGNALING b. SELECTIVE TRANSPORT c. EXCRETION OF WASTES d. STRUCTURAL SUPPORT Correctly color code and identify the name for each part of the cell membrane.Letter Name/Color Letter Name/Color
__ A ___ Phospholipid bilayer (no color) __ H ___ Peripheral protein (red) __ B ___ Integral protein (pink) __ I ____ Cholesterol (blue) __ F ___ Fatty acid tails (orange) __ C___ Glycoprotein (green) __ G ___ Phosphate heads (yellow) __ E ___ Glycolipids (purple)Match the cell membrane structure or its function with the correct letter from the cell membrane diagram.
Letter Structure/Function
Letter Structure/Function
__ G ___ Attracts water __ F__ Repels water __ I ___ Helps maintain flexibility of membrane _ G & F Make up the bilayer __ C & E___ Involved in cell-to-cell recognition __ B__ Help transport certain materials across the cell membrane 2 Define osmosis. THE MOVEMENT OF WATER ACROSS A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE FROM AN AREA OF HIGH CONCENTRATION TO AN AREA OF LOW CONCENTRATION. In which direction does water move across membranes, up or down the concentration gradient? DOWNDefine these 3 terms:
a. isotonic- THE CONCENTRATION OF DISSOLVED PARTICLES ARE THE SAME INSIDE AND OUTSIDE THE CELL Ȃ THERE IS NO OVERALL CHANGE IN THE CELL SIZE b. hypertonic THE CONCENTRATION OF DISSOLVED PARTICLES ARE HIGHER OUTSIDE THE CELL THAN INSIDE THE CELLȂ WATER WILL LEAVE THE CELL IN AN ATTEMPT TO DILUTE THE OUTSIDECONCENTRATION
c. hypotonic THE CONCENTRATION OF DISSOLVED PARTICLES ARE LOWER OUTSIDE THE CELL THAN INSIDE THE CELLȂ WATER WILL ENTER THE CELL IN AN ATTEMPT TO DILUTE THE INSIDECONCENTRATION
Use arrows to show the direction of water movement into or out of each cell. Color and label the cell in an
isotonic environment light blue, the hypotonic environment yellow, and the hypertonic environment light
green. Match the description or picture with the osmotic condition: A. Isotonic __ C __ solution with a lower solute concentration __A __ solution in which the solute concentration is the same B. Hypertonic __ A__ condition plant cells require __ A__ condition that animal cells require C. Hypotonic __ C __ red blood cell bursts (cytolysis) __ C ___ plant cell loses turgor pressure (Plasmolysis) __ B ___ solution with a higher solute concentration __ A __ plant cell with good turgor pressure __ C___ solution with a high water concentration Label the tonicity for each solution (isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic):HYPOTONIC ISOTONIC HYPERTONIC HYPOTONIG ISOTONIC HYPERTONIC
3Transport Requiring Energy
What type of transport is represented by the following picture? ACTIVEWhat energy is being used? ATP
In which direction (concentration gradient), is the movement occurring? AGAINST Color the internal environment of the cell yellow. Color and Label the transport proteins red and the substance being moved blue. One type of active transport is called the SODIUM- POTASSIUM pump which helps muscle cells contract. This pump uses PROTEINS to move ions AGAINST the concentration gradient. The protein that is used to pump the ions through is called a TRANSMEMBRANE (INTEGRAL) protein and it changes its SHAPE to move the ions across the cell membrane. Label and color the carrier proteins red and the ions green.TONICITY AND OSMOSIS
Part I Ȃ Fill in the blanks.
A SOLVENT is a fluid in which a substance is dissolved.A SOLUTE is a substance dissolved in a solvent.
A SOLUTION is a combination of solute and solvent. The process by which water diffuses across a membrane called OSMOSIS Part II Ȃ Look at the solutions illustrated above and fill in the blanks.1. Solution B is HYPERTONIC to Solution A. This is because Solution B has a greater concentration of
SOLUTES in it than does Solution A. Solution C has no solutes dissolved in it, therefore it is HYPOTONIC to
both Solutions A and B. 42. As a relative concentration of solutes in two solutions increases, of necessity the concentration of water in
the same two solutions INCREASES. Solution A has a lower concentration of SOLUTE than does Solution C;
Solution A is also hypertonic to Solution C.
3. If you wanted to make Solution A isotonic to Solution B, you could add water to Solution B or you could
add solute to Solution A. If you took all three solutions, put them into a large container and mixed them
thoroughly, then redistributed the solution among three containers, Solution A would be ISOTONIC to Solution B. Solution A would also be ISOTONIC to Solution C, and Solution C would be ISOTONIC toSolution B.
Part III Ȃ Look at the solutions and cells illustrated above and fill in the blanks.1. Because the cytoplasms of the plant and the animal cell have equal concentrations of solutes, we can say
their cytoplasms are ISOTONIC to each other. If we put both the plant and the animal cells into Solution A,
we would expect no change in the cells, because Solution A is ISOTONIC to the cytoplasm of each cell.
would expect water to LEAVE the cells through the process of OSMOSIS. This would result in the cytoplasm
of both cells shrinking.HYPOTONIC to the cytoplasm of both cells. WATER will enter both cells through osmosis. The animal cell is
likely to BURST, unfortunately. The plant cell, however, is protected from this because of the presence of its
CELL WALL.
Refer to the U-tube pictures above when answering the questions below.1. Why did the number of water molecules on each side of the membrane change, whereas the number of
sugar molecules stayed the same? WATER MOLECULES ARE SMALL ENOUGH TO PASS THROUGH THE PORES OF THE MEMBRANE, HOWEVER, THE SUGAR MOLECULES ARE NOT.2. How does the plasma membrane of a cell compare with the membrane in the U-shaped tube?
THEY ARE BOTH SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE BASED ON SIZE OF PARTICLES 53. Explain the behavior of water molecules in the isotonic solution. WATER MOLECULES WILL MOVE INTO
AND OUT OF THE CELL CONTINUOUSLY, HOWEVER, THERE WILL BE NO OVERALL CONCENTRATIONCHANGE SINCE THE MOVEMENT SHOULD BE EQUAL.
4. Does osmosis occur if a cell is placed in an isotonic solution? NO, BECAUSE THERE IS NO
CONCENTRATION GRADIENT (AREA OF HIGH TO AREA OF LOW Ȃ ISOTONIC IMPLIES EQUALCONCENTRATIONS)
5. Why does water enter a cell that is placed in a hypotonic solution? BECAUSE THE CONCENTRATION OF
SOLUTE IS LOWER OUTSIDE THE CELL THAN IT IS INSIDE THE CELL, SO THE WATER ENTERS THE CELL TO TRY TO DECREASE/EQUALIZE THE CONCENTRATIONS ON BOTH SIDES OF THE MEMBRANE.6. What happens to the pressure inside a cell that is placed in a hypertonic solution? THE PRESSURE
DECREASES AS THE WATER LEAVES THE CELL.
7. What can happen to animal cells when placed in a hypotonic solution? Explain. ANIMAL CELLS IN
HYPOTONIC SOLUTIONS CAN RUPTURE AS MORE AND MORE WATER RUSHES INTO THE CELL. PLANT CELLS WILL NOT HAVE THIS ISSUE BECAUSE THE CELL WALL PROTECTS THE PLANT CELLS FROMRUPTURING.
8. What causes a plant to wilt? PLANTS PLACED IN A HYPERTONIC SOLUTION WILL WILT AS WATER IS
REMOVED FROM THEM RESULTING IN PLASMOLYSIS.
quotesdbs_dbs14.pdfusesText_20[PDF] osu cse components binary tree
[PDF] osu cse components stack
[PDF] osu cse documentation
[PDF] oswego ny newspapers online
[PDF] osxpmem
[PDF] other names for seven deadly sins
[PDF] otis 12 gauge shotgun cleaning kit
[PDF] otpf 3rd edition pdf
[PDF] ott business model pdf
[PDF] ottawa application login
[PDF] ottawa catholic school board calendar 2019 2020
[PDF] ottawa catholic school board strike
[PDF] ottawa county flu deaths 2019
[PDF] otto blockly
