 osmosis-demo-lab.pdf
osmosis-demo-lab.pdf
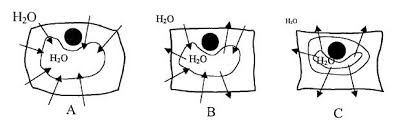
4) Observe plasmolysis in Elodea. Background. Osmosis is the process whereby water moves across a cell membrane by diffusion. Diffusion takes place when the
 DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS
DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS
• ESSENTIAL FOR CELLS. • WATER MOVES ACROSS THE CELL MEMBRANE BY OSMOSIS. IT DEPENDS ON THE CONCENTRATION OF WATER INSIDE AND OUTSIDE. THE CELL. Page 12. Follow
 Reverse Osmosis Concentrate Treatment Research Results and
Reverse Osmosis Concentrate Treatment Research Results and
Nov 19 2020 Although the ozone and open-water treatment cells did not remove all contaminants
 DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS
DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS
Most cells achieve this control by delicate cell membranes that can often regulate different substances by slowing down the movement of some molecules while
 An Overview of Osmosis Study in Living Cells and its Implication in
An Overview of Osmosis Study in Living Cells and its Implication in
Apr 3 2022 It was found in the case of water movements across the cell membranes [4]
 Cellular Processes: Energy and Communication
Cellular Processes: Energy and Communication
In walled cells osmosis is affected not only by the solute concentration but also by the resistance to water movement in the cell by the cell wall. This
 Osmosis and Osmoregulation
Osmosis and Osmoregulation
• Water moves in and out of cells. →Cells swell or shrink. • This has profound effects on the brain. – Neurologic function is altered. – Rapid shrinking can
 4 Homeostasis and Cell Transport.pdf
4 Homeostasis and Cell Transport.pdf
through osmosis and diffusion. The cell membrane also separates the cell's internal environment from the external world. Page 20
 Effect of Immersion Time in Osmosis and Ultrasound on Papaya Cell
Effect of Immersion Time in Osmosis and Ultrasound on Papaya Cell
Feb 9 2009 Ultrasound-assisted osmotic dehydration induced a gradual distortion in the shape of the cells
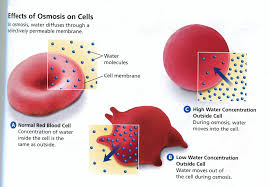
 Measuring osmosis and hemolysis of red blood cells
Measuring osmosis and hemolysis of red blood cells
No change in cell volume occurs in isotonic NaCl and
 Gummy Bear Chemistry and Osmosis
Gummy Bear Chemistry and Osmosis
The Cell Membrane. • Cells are surrounded by a lipid bilayer which is a semi-permeable membrane. • Semi-permeable means that only.
 What is the difference between osmosis and diffusion?
What is the difference between osmosis and diffusion?
Examples of Diffusion: Examples of diffusion include perfume filling a whole room and the movement of small molecules across a cell membrane. One of the
 osmosis-demo-lab.pdf
osmosis-demo-lab.pdf
The effect of water loss on plant cells is shown in the diagram below. Figure 1. A. Plant cell placed in pure water. This cell will become inflated because the
 Measuring osmosis and hemolysis of red blood cells
Measuring osmosis and hemolysis of red blood cells
No change in cell volume occurs in isotonic NaCl and
 12 4 ELECTRO-OSMOSIS IN CHARA AND NITELLA CELLS P. H.
12 4 ELECTRO-OSMOSIS IN CHARA AND NITELLA CELLS P. H.
are used to reappraise the possibility that electro-osmosis in cells may be explained in terms of electro-osmotic coupling in cell walls alone. INTRODUCTION.
 DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS
DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS
Most cells achieve this control by delicate cell membranes that can often regulate different substances by slowing down the movement of some molecules while
 Bend a Carrot
Bend a Carrot
Learning Objectives: Students understand the process of osmosis This experiment investigates the movement of water into and out of cells. The.
 Cellular Processes: Energy and Communication
Cellular Processes: Energy and Communication
In walled cells osmosis is affected not only by the solute concentration but also by the resistance to water movement in the cell by the cell wall. This
 Zeta-Potentials of Intact Cell Monolayers Determined by Electro
Zeta-Potentials of Intact Cell Monolayers Determined by Electro
Mar 14 2017 Key words: electrophoresis; electro-osmosis; Zeta potential; monolayers; viability. Introduction. The ??-potential of a cell surface as ...
 Another Lesson from Plants: The Forward Osmosis-Based Actuator
Another Lesson from Plants: The Forward Osmosis-Based Actuator
water-driven processes in plant cells and tissues and thus can be used as guide for designing osmosis-based actuators in a biomimetic approach.
 Lab 3 Osmosis: How Does the Concentration of Salt in Water
Lab 3 Osmosis: How Does the Concentration of Salt in Water
Osmosis refers specifically to the diffusion of water molecules In cells water cannot simply diffuse FIGURE L3 2 across the membrane However special openings in the (a) Red blood cells in saltwater solution membrane allow for easy flow of water molecules so cells can and (b) normal red blood cells take in or get rid of water when needed
 DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS
DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS
1 Define osmosis 2 Understand the concept of water potential gradient 3 Understand the concept of hypotonic isotonic and hypertonic solutions 4 Understand how animals and plant cells respond to immersion in solutions which are of different concentration to their cytoplasm
 Why is osmosis important to the survival of a cell?
Why is osmosis important to the survival of a cell?
Lab 4: Osmosis and Diffusion The plasma membrane enclosing every cell is the boundary that separates the cell from its external environment It is not an impermeable barrier but like all biological membranes is selectively permeable controlling which molecules move into and out of the cell
 DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS - Yavapai College
DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS - Yavapai College
Osmosis is the movement of water through a selectively permeable membrane Flow movement is dependent upon the concentration of dissolved substances (solutes) on either side of the membrane Consequently water passes from an area of high concentration of water molecules to an area of low concentration of water molecules
 Lab 3: Osmosis in Model & Living Cells Objectives: To - WRUV
Lab 3: Osmosis in Model & Living Cells Objectives: To - WRUV
Osmosis: the diffusion of water molecules across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of greater concentration of water to an area of lesser concentration of water Waterpotential:a measure of the chemical potential of water molecules A combination of osmotic and pressure potentials (see p 3)
 Searches related to osmosis in cells filetype:pdf
Searches related to osmosis in cells filetype:pdf
The processes of diffusion osmosis and filtration are responsible for the movement of materials into and out of body cells as well as the exchange of molecules between body fluid compartments These processes involve some basic principles of physics which will be demonstrated in this laboratory
Why is osmosis important to the survival of a cell?
- This obviously is essential to the survival of a cell. The most important function of osmosis is stabilising the internal environment of an organism by keeping the water and intercellular fluids levels balanced. In all living organisms, nutrients and minerals make their way to the cells because of osmosis.
What factors determines the osmosis of a cell?
- Factors that Affect Osmosis. Concentration gradient: The greater the concentration difference, the faster the rate of osmosis. Temperature: The higher the temperature, the faster the rate of osmosis Example of osmosis in a living cell (human being) In the human body system, the kidney cleans the blood by filtering out waste substances.
How do osmosis help the cell maintain homeostasis?
- Osmosis is the diffusion of water. Osmosis helps cells maintain homeostasis because a cell needs to maintain a specific water balance so that chemical reactions can take place. Osmosis can also be used to balance out the concentration of other molecules (such as sugar or salt) present on either side of a cell membrane.