Fonctions logarithmes népérien et décimal
La fonction logarithme népérien notée ln
TS courslogarithme
CHAPITRE 11 : FONCTION NEPERIEN. FONCTION LOGARITHME
FONCTION. LOGARITHME DECIMAL. 1. Fonction népérien (logarithme d'une fonction composée). Théorème. Si u
cours chap
LOGARITHME NEPERIEN
On note a = ln b ce qui se lit logarithme népérien de b . On appelle fonction logarithme décimal et on note log la fonction définie sur ] 0 ...
ln
FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN (Partie 1)
décimaux ne sont pas d'usage courant et les opérations posées telles que nous les utilisons La fonction logarithme népérien notée ln
LogT
Annexe B : Le calcul d'incertitude
arrondie pour obtenir le même nombre de décimales que l'incertitude. Logarithme : Prendre le logarithme népérien (ln) de chaque côté de l'équation.
annexe B calcul incertitude
La fonction logarithme
5.2 Application sur le logarithme décimal . La création de la fonction logarithme népérien est à l'origine
La fonction logarithme neperien
La fonction logarithme décimal
Pour x strictement positif log(x) = ln(x) ln(10). (avec ln(10) = 2
LogarithmeDecimal
FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN
exp et ln sont symétriques par rapport à la droite d'équation y = x. - Dans le domaine scientifique on utilise la fonction logarithme décimale
LogTS
Logarithmes
La fonction logarithme népérien : définie sur ] 0 ; +G [ la dérivée est ( ln x )' = 1 x.
logarithme
Fonction Logarithme népérien 1. De l'exponentielle au logarithme
logarithme en 1 et la limite en 0 de ln(1+x) x . On évoque la fonction logarithme décimal pour son utilité dans les autres disciplines. ◇ [SI] Gain lié à une
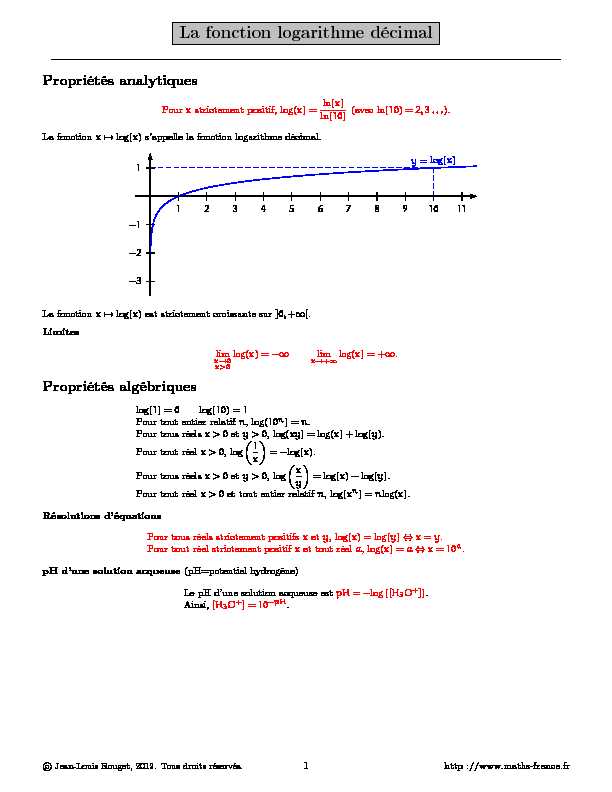
La fonction logarithme décimal
Propriétés analytiques
Pourxstrictement positif, log(x) =ln(x)ln(10)(avec ln(10) =2,3...). La fonctionx?→log(x)s"appelle la fonction logarithme décimal. 1 -1 -2 -31 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11y=log(x) La fonctionx?→log(x)est strictement croissante sur]0,+∞[.Limites
limx→0x>0log(x) = -∞limx→+∞log(x) = +∞.Propriétés algébriques
log(1) =0log(10) =1Pour tout entier relatifn, log(10n) =n.
Pour tous réelsx > 0ety > 0, log(xy) =log(x) +log(y).Pour tout réelx > 0, log?1
x? = -log(x).Pour tous réelsx > 0ety > 0, log?x
y? =log(x) -log(y). Pour tout réelx > 0et tout entier relatifn, log(xn) =nlog(x).Résolutions d"équations
Pour tous réels strictement positifsxety, log(x) =log(y)?x=y. Pour tout réel strictement positifxet tout réela, log(x) =a?x=10a. pH d"une solution acqueuse(pH=potentiel hydrogène)Le pH d"une solution acqueuse est
pH= -log([H3O+]).Ainsi,
[H3O+] =10-pH. c ?Jean-Louis Rouget, 2012. Tous droits réservés.1 http ://www.maths-france.frLa fonction logarithme décimal
Propriétés analytiques
Pourxstrictement positif, log(x) =ln(x)ln(10)(avec ln(10) =2,3...). La fonctionx?→log(x)s"appelle la fonction logarithme décimal. 1 -1 -2 -31 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11y=log(x) La fonctionx?→log(x)est strictement croissante sur]0,+∞[.Limites
limx→0x>0log(x) = -∞limx→+∞log(x) = +∞.Propriétés algébriques
log(1) =0log(10) =1Pour tout entier relatifn, log(10n) =n.
Pour tous réelsx > 0ety > 0, log(xy) =log(x) +log(y).Pour tout réelx > 0, log?1
x? = -log(x).Pour tous réelsx > 0ety > 0, log?x
y? =log(x) -log(y). Pour tout réelx > 0et tout entier relatifn, log(xn) =nlog(x).Résolutions d"équations
Pour tous réels strictement positifsxety, log(x) =log(y)?x=y. Pour tout réel strictement positifxet tout réela, log(x) =a?x=10a. pH d"une solution acqueuse(pH=potentiel hydrogène)Le pH d"une solution acqueuse est
pH= -log([H3O+]).Ainsi,
[H3O+] =10-pH. c ?Jean-Louis Rouget, 2012. Tous droits réservés.1 http ://www.maths-france.fr- logarithme népérien decimal
- conversion logarithme decimal neperien
- relation logarithme neperien et decimal