Scatterplots and Correlation
For a correlation coefficient of zero the points have no direction
scatterplots and correlation notes
Covariance and Correlation
28-Jul-2017 The reverse is not true in general: if the covariance of two random variables is 0 they can still be dependent! Page 2. –2–. Properties of ...
covariance
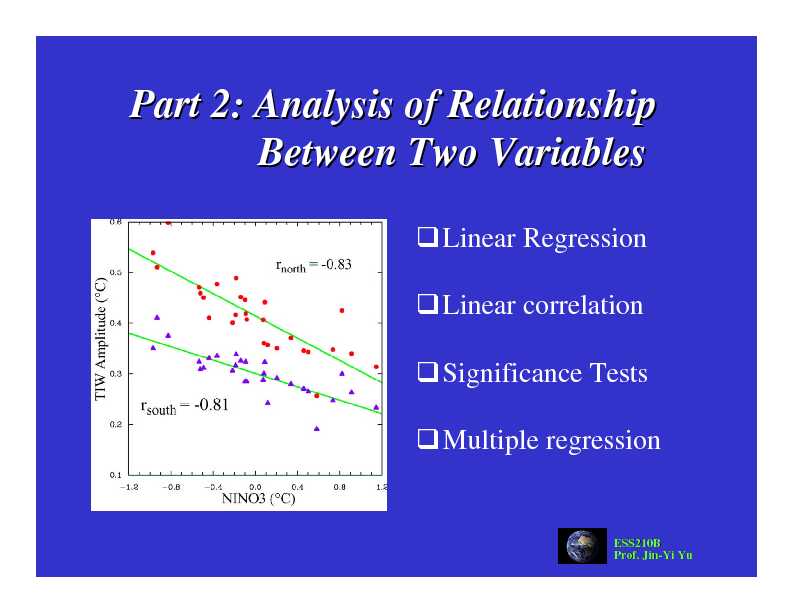
Part 2: Analysis of Relationship Between Two Variables
coefficients a and b to produce a minimum value of the error Q. a. 0. = intercept When the true correlation coefficient is not expected to be zero.
lecture. .regression.all
An Angular Transformation for the Serial Correlation Coefficient
In fact when p * 0 the distributions are quite distinct. He deduces that 'compared with the transformation of the ordinary correlation coefficient
Lecture 24: Partial correlation multiple regression
http://www.ernestoamaral.com/docs/soci420-17fall/Lecture24.pdf
On the Appropriateness of the Correlation Coefficient with a 0 1
a 0 1 Dependent Variable. JOHN NETER and E. SCOTT MAYNES*. This article deals with the use and misuse of the correlation coefficient when the.
correlation coefficient −0.6 −0.4 −0.2 0 0.2 0.4 0.6
Page 1. 40. oW. 20 o. W. 0 o. 20o. E. 40 o. E. 50 o S. 40 o S. 30 o S. 20 o S. 10 o S. 0 o correlation coefficient. −0.6. −0.4. −0.2. 0. 0.2. 0.4. 0.6.
os f
A General Correlation Coefficient for Directional Data and Related
(2.1) to define a correlation coefficient for the bivariate circular case. If 0 and b are circular variables 0 4
Performance of Some Correlation Coefficients When Applied to Zero
01-Nov-2007 Key words: zero-clustered data Pearson correlation
Conditions for Rank Correlation to Be Zero
the two rankings to be zero. This correlation is measured in turn
ESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
Part 2: Analysis of Relationship Part 2: Analysis of RelationshipBetween Two Variables
Between Two Variables
Linear Regression
Linear correlation
Significance Tests
Multiple regression
ESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
Linear RegressionLinear Regression
Y= a X+ b
• To find the relationship between Y and X which yields values of Y with the least error.Dependent
Variable
Independent
Variable
ESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
Predictor and Predictor and PredictandPredictand
In meteorology, we want to use a variable xto predict another variabley. In this case, the independent variable x is called the "predictor". The dependent variable y is called the "predictand"Y = a + b X
the independent variable the predictor the dependent variable the predictandESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
Linear RegressionLinear Regression
We have Npaired data point (x
i , y i that we want to approximate their relationship with a linear regression:The errors produced by this linear
approximation can be estimated as:The least square linear fit chooses
coefficients a and b to produce a minimum value of the error Q. a 0 = intercept a 1 = slope (b)ESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
Least Square FitLeast Square Fit
Coefficients a and b are chosen such that the error Q is minimum:This leads to:
Solve the above equations, we get the linear regression coefficients: where covariance between xand y variance of x b=ESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
ExampleExample
ESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
RR 22--valuevalue R 2 -value measures the percentage of variation in the values of the dependent variable that can be explained by the variation in the independent variable. R 2 -value varies from 0 to 1.
A value of 0.7654 means that 76.54% of the
variance in y can be explained by the changes in X. The remaining 23.46% of the variation in y is presumed to be due to random variability.ESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
Significance of the Regression CoefficientsSignificance of the Regression Coefficients There are many ways to test the significance of the regression coefficient.Some use t-test to test the hypothesis that b=0.
The most useful way for the test the significance of the regression is use the "analysis of variance"which separates the total variance of the dependent variable into two independent parts: variance accounted for by the linear regressionand the error variance.ESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
How Good Is the Fit?How Good Is the Fit?
The quality of the linear
regression can be analyzed using the "Analysis ofVariance".
The analysis separates the
total variance of y(S y2 ) into the part that can be accounted for by the linear regression (b 2 S x2 ) and the part that can not be accounted for by the regression (S 2 S y2 = b 2 S x2 + S 2 0ESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
Variance AnalysisVariance Analysis
To calculate the total variance, we need to know the "mean"DOF=N-1 If we know the mean and the regression slope (B), then the regression line is set The DOF of the regressed variance is only 1 (the slope). The error variance is determined from the difference between the total variance (with DOF = N-1) and the regressed variance (DOF=1) The DOFESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
Part 2: Analysis of Relationship Part 2: Analysis of RelationshipBetween Two Variables
Between Two Variables
Linear Regression
Linear correlation
Significance Tests
Multiple regression
ESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
Linear RegressionLinear Regression
Y= a X+ b
• To find the relationship between Y and X which yields values of Y with the least error.Dependent
Variable
Independent
Variable
ESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
Predictor and Predictor and PredictandPredictand
In meteorology, we want to use a variable xto predict another variabley. In this case, the independent variable x is called the "predictor". The dependent variable y is called the "predictand"Y = a + b X
the independent variable the predictor the dependent variable the predictandESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
Linear RegressionLinear Regression
We have Npaired data point (x
i , y i that we want to approximate their relationship with a linear regression:The errors produced by this linear
approximation can be estimated as:The least square linear fit chooses
coefficients a and b to produce a minimum value of the error Q. a 0 = intercept a 1 = slope (b)ESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
Least Square FitLeast Square Fit
Coefficients a and b are chosen such that the error Q is minimum:This leads to:
Solve the above equations, we get the linear regression coefficients: where covariance between xand y variance of x b=ESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
ExampleExample
ESS210BESS210B
Prof. JinProf. Jin--Yi YuYi Yu
RR 22--valuevalue R 2 -value measures the percentage of variation in the values of the dependent variable that can be explained by the variation in the independent variable. R 2 -value varies from 0 to 1.