 ME 201
ME 201
ME 201 Thermodynamics. 1. ME 201. Thermodynamics. Second Law Practice Problems. 1. Ideally which fluid can do more work: air at 600 psia and 600°F or steam at.
 Chapter 20: Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
Chapter 20: Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
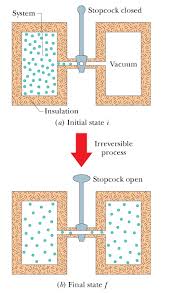
Heat does not transfer from the ice to the water (though this would not violate the law of energy conservation). AS > 0. Page 19. Sample Problem. Water is
 More problems on second law of thermodynamics
More problems on second law of thermodynamics
Understand the energy balance for a flow system and solve numericals on the applications on energy balance. Write the entropy balance equation.
 Untitled
Untitled
Thermodynamics problems: SOLUTIONS. Easy: Probability. Suppose you shuffle a dP. T=T₂. Page 15. A4 Using the differential form of the first law of ...
 1 Chapter 20 Entropy and second law of thermodynamics 1 Content
1 Chapter 20 Entropy and second law of thermodynamics 1 Content
S (extensive) F (extensive)
 Counterintuitive effect of gravity on the heat capacity of a metal
Counterintuitive effect of gravity on the heat capacity of a metal
18-Apr-2015 It is found that this solution violates the second law of thermodynamics ... problems-and-solutions/1967/1st_IPhO_1967.pdf. 15. Page 16. 2 Rudolf ...
 LECTURE NOTES ON THERMODYNAMICS
LECTURE NOTES ON THERMODYNAMICS
31-Oct-2023 The objective of the course is to survey practical and theoretical problems in classical thermodynamics. The emphasis is on the axiomatic ...
 Solutions Manual for Thermodynamics and Chemistry
Solutions Manual for Thermodynamics and Chemistry
09-Jun-2020 The sign of S is positive as predicted by the second law for an irreversible process in an isolated system. 4.5 Refer to the apparatus shown ...
 Problem Solutions
Problem Solutions
The entropy of the oxide is 51.0 kJ/K per kilomole. According to the second law of thermodynamics the entropy of a closed system suffering any transformation
 The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems Heat Transfer
The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems Heat Transfer
Solution: Assume that i) the gas is a closed system ii) the moving boundary is only But from the second law point of view
 SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS (Numerical Problem
SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS (Numerical Problem
SECOND LAW OF. THERMODYNAMICS. (Numerical Problem Solution) e-content for B.Sc Physics (Honours). B.Sc Part-I. Paper-II. Dr. Ayan Mukherjee.
 ME 201
ME 201
Thermodynamics. Second Law Practice Problems. 1. Ideally which fluid can do more work: air at 600 psia and 600°F or steam at. 600 psia and 600°F. Solution:.
 Chapter 20: Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
Chapter 20: Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
Heat does not transfer from the ice to the water (though this would not violate the law of energy conservation). AS > 0. Page 19. Sample Problem. Water is
 LECTURE NOTES ON THERMODYNAMICS
LECTURE NOTES ON THERMODYNAMICS
14-Feb-2010 These notes emphasize problem-solving and rigorous development of the ... 1850: Rudolf Julius Emanuel Clausius formalizes the second law of ...
 The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems Heat Transfer
The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems Heat Transfer
Solution: The energy content of the oven is increased during this process. a) The energy transfer to the oven is not caused by a temperature difference between
 Second Law and Entropy
Second Law and Entropy
Second law of thermodynamics - State the second law of thermodynamics as it Entropy - Solve problems involving the following concepts: (a) efficiency.
 Thermodynamic Properties and calculation
Thermodynamic Properties and calculation
First Law of Thermodynamic: ?Combining the first and second laws in reversible process ... other hand the answers to parts (a) and (b) show.
 Solution of Quiz 1: First Law of Thermodynamics
Solution of Quiz 1: First Law of Thermodynamics
12-Sept-2012 (d) The atom will undergo centre of mass motion with energy E3 ? E2. (e) The gaseous atoms collide with one another transferring the residual ...
 Problem Solutions
Problem Solutions
According to the second law of thermodynamics the entropy of a closed system suffering any transformation can not diminish.
 1 Solutions to sample quiz problems and assigned problems
1 Solutions to sample quiz problems and assigned problems
Quiz Problem 5. Use the Master equation to prove the second law of thermodynamics i.e. in a closed system. dS/dt ? 0. Solution. see lecture notes page 10.
 Second Law Problems - Michigan State University
Second Law Problems - Michigan State University
Thermodynamics Second Law Practice Problems Ideally which fluid can do more work: air at 600 psia and 600°F or steam at600 psia and 600°F Solution: The maximum work a substance can do is given by its availablity We willassume that we have a closed system so that÷
 Thermodynamics: The Three Laws of Thermodynamics - Equations
Thermodynamics: The Three Laws of Thermodynamics - Equations
The second law of thermodynamics asserts that processes occur in a certain direction and that the energy has quality as well as quantity The first law places no restriction on the direction of a process and satisfying the first law does not guarantee that the process will occur
 Chapter 7 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
Chapter 7 THE SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS
Second Law of Thermodynamics and Thermal Energy Reservoirs 7-1C Water is not a fuel; thus the claim is false 7-2C Transferring 5 kWh of heat to an electric resistance wire and producing 5 kWh of electricity 7-3C An electric resistance heater which consumes 5 kWh of electricity and supplies 6 kWh of heat to a room
 Chapter 5 The Second Law of Thermodynamics - Saylor Academy
Chapter 5 The Second Law of Thermodynamics - Saylor Academy
The second law of thermodynamics states that processes occur in a certain direction not in just any direction Physical processes in nature can proceed toward equilibrium spontaneously: Water flows down a waterfall Gases expand from a high pressure to a low pressure Heat flows from a high temperature to a low temperature
 Searches related to second law of thermodynamics problems and solutions pdf filetype:pdf
Searches related to second law of thermodynamics problems and solutions pdf filetype:pdf
2 Second law of thermodynamics If a closed system is in a configuration that is not the equilibrium configuration the most probable consequence will be that the entropy of the system will increase monotonically If an irreversible process occurs in a closed system the entropy of the system always increases; it never decreases
What are the first three laws of thermodynamics?
- There three laws are: The first law of thermodynamics is the law of the conservation of energy; it states that energy cannot be created nor destroyed. An example is when the chlorophyll absorbs light and transforms it into chemical energy.
How many laws of thermodynamics are there?
- Traditionally, thermodynamics has recognized three fundamental laws, simply named by an ordinal identification, the first law, the second law, and the third law. [1] [2] [3] A more fundamental statement was later labelled as the zeroth law, after the first three laws had been established.
What does first law of thermodynamics mean?
- The first law of thermodynamics, also known as the law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but it can be changed from one form to another. According to this law, some heat given to the system is used to change the internal energy while the rest is used in doing work by the system.
Name:Roll no:
Attempt all questions.
1. As a result of some process, the internal energy of a system is increased. According to the first law of thermodynamics, ∆Eint=Q+W. How can one tell that the increase was due to orderly macroscopic workWor due to the flow of energy through disorderly microscopic meansQ? (a) By measuring the temperature of the system before and after the process. (b) By measuring the temperature of the surroundings before and after the process. (c) It is not possible to distinguish betweenWandQ. (d) Both (a) and (b) are correct.Answer 1:
(a) is incorrect because the internal energy has disordered (random) and ordered parts. You can change the internal energy without change in temperature. For example, by bringing a magnet close to or moving it away from an iron piece, the iron can be magnetized or demagnetized. Its internal energy therefore changes (e.g. it can subsequently do work by lifting an iron piece). Yet its temperature hasn't changed. OnceWorQhas been transferred to a system, it is difficult to tell what caused a change in the internal energy to begin with. This is like depositing money in a "bank". Once the money is there, it is unnecessary to know, where the money came from. The only way to tell whetherWorQcontributed to the change in internal energy is by looking at the surroundings. For example, measure its temperature. If the temperature goes down, there has been a flow of energyQfrom the surrounding to the system. Hence the correct answer is (b). 2. Man learnt the use of fire to raise the temperature of objects much earlier than the use of mechanical work, e.g. in steam engines. Could you think of a reason why this could be true?Answer 2:
Fire results in chaotic motion of air molecules in contact with an object whom we wishDate: 12 Sep, 20121
Max. marks:15Time Allowed:15 minutes
to call "heat".This process involves the disorganized, unconstrained collisions between molecules. Mechanical work, however requires a much higher degree of ordered control and hence sophistication. Therefore one could imagine that man mastered the use of fire much earlier than steam engine could be invented. 3. What temperature is required to have 25% of H atoms in the first excited state and75% in the ground state? The value ofkBis 8.6105eV/K
(a) room temperature300 K (b)9.9104K (c)7.4104K (d)2.5104K (e) infinite temperature.Answer 3:
Since we know that, for hydrogen atom,
N 2 N1+N2= 0.25 =1
4 N 1+N2 N 2= 4 N 1 N2+ 1 = 4
N 1 N 2= 3 N 2=N1 3 N2 N 1=1 3 = exp( (E2E1) k BT) (E2E1) kBT= ln1
3 (E2E1) kBT= ln3
)T=E2E1 k Bln310.2 eV
8.6105eV/Kln310104K.
Hence (b) is the correct answer.
4. Blow air onto your hand with your mouth wide open and then your lips puckered. When does the air look cooler and why? Assume the process is so fast thatQ= 0Date: 12 Sep, 20122
Max. marks:15Time Allowed:15 minutes
(i.e. the process is adiabatic.) (a) (b)Answer 4:
It is cooler when the lips are puckered. As air is blown out of the lips, it expands. The expanding breath of air does orderly, macroscopic work on its surroundings pushing molecules away,W <0. As a result the internal energy decreases, ∆Eint=W+Q=W <0. This causes the air to become cooler.
5. Molecules in the combustion chamber of a rocket engine are in a high state of random motion. When the molecules are expelled through a nozzle in a more ordered state, what will their temperature be as their temperature in the chamber before being ex- hausted? AssumeQ= 0. (a) temperature will be lower (b) temperature will be higher (c) temperature will be the same (d) we can't be sure.Answer 5:
In adiabatic expansion work is done on the cost of internal energy, lowering the tem- perature of the molecules in the chamber, therefore (a) is correct. Same reasoning applies asQ4. 6. Meteorologists use the first law of thermodynamics in its adiabatic form (i.e.Q= 0). Using statement of the first law, argue why the temperature in a rising cloud falls as it goes to higher altitudes?Date: 12 Sep, 20123
Max. marks:15Time Allowed:15 minutes20 Co
10 C5 C
o o increasing altitude (a) the temperature falls because we are away from the warm surface of the earth. (b) the temperature falls because the air pressure decreases with altitude, and the cloud expands. (c) the temperature falls because the internal energy of the cloud decreases due to reduced pull of gravity. (d) the temperature falls because the air pressure decreases with the altitude, and the cloud contracts.Answer 6:
The temperature falls because the air pressure decreases with altitude, and the cloud expands, therefore (b) is right. 7. What happens to the air temperature in a valley when cold air blowing from the mountain tops descends into the valley?cold air blows incold air blows in air can't escape from the valley (a) the valley's temperature drops. (b) the valley's temperature rises. (c) there is no change in temperature. (d) more than one of these possibilities are correct.Answer 7:
As air descends into the valley, it compresses air already present. The increase in pressure on the valley's air means work is done on the system,W >0. Hence ∆Eint= W+Q=W >0. The temperature goes up. Therefore (b) is correct answer.Date: 12 Sep, 20124
Max. marks:15Time Allowed:15 minutes
8. A bottle contains a gas of atoms. Each atom has three energy levels as shown.EE E 12 3400 nm200 nmIncident radiation
Emitted radiation
Ultraviolet photons of wavelength 200 nm shine on the atom, enabling the transition fromE1toE3. However only a violet photon of wavelength 400 nm is emitted as a result of a downward transition. Where does the "missing energy" go? (a) The incident photon is scattered carrying away the missing energy. (b) The energy of the 400 nm photon adjusts itself to make up for the missing energy. (c) Energy need not be conserved. (d) The atom will undergo centre of mass motion with energyE3E2. (e) The gaseous atoms collide with one another, transferring the residual energyE3E2 to one another.Answer 8:
Since the incident photon is wholly absorbed, the process cannot result in centre of mass motion, as would happen in (a) or (d). Energy must be conserved. The only possibility that remains is (e). Collision between the gaseous atoms results in the atom losing its excess energy, contributing to the disordered motion of the gas molecules, hence increasing the temperature. 9. The rotational energy levels in a molecule are quantized byErot,ℓ=L22I=ℓ(ℓ+1)~2
2I, where the symbols have the usual meanings andℓ= 0,1,2,....is the rotational quan- tum number. In which of these molecules, there will be the highest population in the first excited stateErot,1at a temperature of 10 K? (a)H2(b)O2(c)N2(d)I2. The moments of inertia for these molecules (in the units of 1038gcm2) areH2= 0.05,
O2= 0.2,N2= 0.14,I2= 7.5.
Answer 9:
Date: 12 Sep, 20125
Max. marks:15Time Allowed:15 minutes
The energy spacing between theℓ= 0 andℓ= 1 levels is2~2 2I=~2 I . The spac- ing is smallest for largestI. HenceErot,1will have the most population for theI2 molecule. Lower energies mean higher populations because of the Boltzmann factor /exp(E k BT). 10. The diagram shows the potential energy curve for two atoms brought close to one another. The energy of the system is shown by the dashed line. At which of the points A, B, C, will the force be maximum and in what direction?A BC r Ou(r) (a) At A, repulsive. (b) At A, attractive. (c) At B, attractive. (d) At C, attractive. (e) At C, repulsive.Answer 10:
The force is given by the negative of the slope,du(r)/dr. The magnitude of the slope is largest at C and the direction of the slope is negative, which means that the force is positive, indicating repulsion.Date: 12 Sep, 20126
quotesdbs_dbs14.pdfusesText_20[PDF] second order differential equation rlc circuit
[PDF] second order low pass filter
[PDF] second trimester bleeding differential diagnosis
[PDF] second year computer engineering syllabus pune university 2019 20
[PDF] secondary amine reaction with hcl
[PDF] secondary amine reaction with nano2 and hcl
[PDF] secondary amine reaction with water
[PDF] secondary colors of light
[PDF] secondary consumers are eaten by larger
[PDF] secondary consumers in the desert
[PDF] secondary consumers in the ocean
[PDF] secondary consumers in the rainforest
[PDF] secondary consumers in the savanna
[PDF] secondary consumers in the tundra
