GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PE2 UNIT GUIDE
GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PE2 UNIT GUIDE
The predominant energy system being used at rest is the aerobic system. Example 1: In netball the ATP-PC system would be the predominant energy system used when
 training-for-cardiovascular-fitness.pdf
training-for-cardiovascular-fitness.pdf
Cardiovascular (aerobic) exercise: • increases your energy and stamina. • helps control blood pressure. • improves your blood lipid profile (cholesterol).
 Personal Development Health and Physical Education - 2009 HSC
Personal Development Health and Physical Education - 2009 HSC
Specific sporting example where the energy system is dominant. Shot • Endurance training – training aerobic energy system resistance training for endurance.
 Energy System Interaction and Relative Contribution During
Energy System Interaction and Relative Contribution During
[76] ATP-PCr = alactic component of the anaerobic en- ergy system. 738. Gastin. © Adis International Limited. All rights reserved. Sports Med 2001; 31 (10)
 chapter 3 physiologic responses and long-term adaptations to
chapter 3 physiologic responses and long-term adaptations to
respiratory fitness or aerobic power (Jorgensen et al. 1977). Lactate Threshold. Lactate is the primary by-product of the anaerobic glycolytic energy system.
 2014 HSC Personal Development Health and Physical Education
2014 HSC Personal Development Health and Physical Education
• Recognises and names an anaerobic energy system. OR. • Provides a • Provides examples of Indigenous Australian physical activity or sport participation. 1.
 2019 HSC Personal Development Health and Physical Education
2019 HSC Personal Development Health and Physical Education
the lactic acid and aerobic energy systems. Carbohydrate loading involves a AND/OR Australian sporting identity. 2. • Provides some relevant information about ...
 energy and training module
energy and training module
The darker grey represents the anaerobic lactic system. As athletes increase intensity for example
 2017 HSC Personal Development Health and Physical Education
2017 HSC Personal Development Health and Physical Education
ATP/PC is an anaerobic energy system that does not require oxygen compared to the aerobic Provides specific examples of the relationship between sport and ...
 energy and training module
energy and training module
The darker grey represents the anaerobic lactic system. As athletes increase intensity for example
 mark scheme – a-level physical education – 7582/1 – june 2019
mark scheme – a-level physical education – 7582/1 – june 2019
1 Jun 2019 Works anaerobic energy system required in games with applied example/aerobic energy ... Give a sporting example for each type. [4 marks].
 The effects of exercise and sports performance on the energy systems.
The effects of exercise and sports performance on the energy systems.
The body's energy systems facilitate the process of making energy. carbohydrates through the aerobic energy system. ... Sport example. 1-3 seconds.
 WINGATE ANAEROBIC TEST - Educational Athletics
WINGATE ANAEROBIC TEST - Educational Athletics
Many sports involve quick bursts of speed at high intensities. term energy system of aerobic metabolism (see Figure 1). Figure 1. ... For example as a.
 Learning aim B - Know about the different energy systems used
Learning aim B - Know about the different energy systems used
Using two selected sports explain how the body uses both the anaerobic and aerobic energy systems. 2B.D2. Compare and contrast how the energy systems are used.
 Mark scheme G453 Principles and concepts across different areas
Mark scheme G453 Principles and concepts across different areas
House system introduced (formed basis for sports teams) or inter-house games may not always be supported by relevant practical examples.
 Open and closed loop control
Open and closed loop control
correct energy systems movement patterns and muscles as closely as possible to the way they are used in their sport. For example
 Subject Sport Exercise and Health Science Title The Effect of
Subject Sport Exercise and Health Science Title The Effect of
This investigation focuses on the potential effect that aerobic exercise or the use of the aerobic energy system has upon anaerobic power
 ENERGY SYSTEMS: NUTRITION & METABOLISM
ENERGY SYSTEMS: NUTRITION & METABOLISM
SSP / IBDP Sports Exercise & Health Science 2014 / Energy Systems: 5.2 The Anaerobic Glycolysis Energy System. 32. 5.3 The Aerobic Energy System.
 Gymnastics NZ
Gymnastics NZ
The anaerobic alactic lactic acid
The effects of exercise and
sports performance on the energy systems.Introduction.
All movement requires energy.
The method by which our body generates energy is determined by the intensityand durationof the activity undertaken.
Activities that require short bursts of effort (sprinting or jumping) require the body to produce large amounts of energy over a short period of time.
A marathon runner would require energy production over a longer period and at a slower rate.Introduction.
The body's energy systems facilitate the process of making energy. The energy systems of the body can work aerobicallyor anaerobically. All energy systems work together but the type of activity and its intensity will determine which system is predominant.The role of ATP in exercise.
Energy makes our muscle fibre contract.
We get energy from the following fuels-
-Phosphocreatine -Carbohydrates/ glycogen -Fats The body maintains a continuous supply of energy through the use of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).How is ATP broken down for muscular
contraction and then resynethsised?The process is supported
by an enzyme ATPase which breaks off the final phosphate and releases energy.ATP can then be
resynthesisedby adding aPhosphate back on (ADP+
P = ATP.
How does ATP work?
Energy is made by converting ATP into ADP.
By binding a phosphate back with the ADP, ATP is resynthesised. Our muscles have very small amounts of ATP stored in them, so to replenish ATP quickly, the body uses a number of systems.A muscle cell has enough ATP to last 3 seconds.
The ATP-PC (alacticsystem).
Anaerobic.
Important in sports such as sprinting,
shot put.High intensity, short duration exercise
(10 seconds).How does the ATP-PC system replenish ATP?
It takes place in the sarcoplasm.
The fuel used is phosphocreatine (PC).
PC breaks down into creatineand phosphate with energy using the enzyme creatinekinase.1 ATP is resynthesized per 1 molecule of PC.
ADP+PC= 1ATP
Remember-
The body breaks down carbohydrates from the foods we eat and converts them into glucose. When the body does not need to use the glucose for energy, it stores some of it in the liver and muscles. This is then used for energy production and is known as glycogen.The Lactate System/ Anaerobic glycolysis.
Higher intensity over a longer
period eg. 400m.Anaerobic.
60-90 seconds maximal work
uses this system.Describe the process of Anaerobic Glycolysis.
Glycogen is converted into glucose.
Glucose is broken down into pyruvic acid using glycolytic enzymes.Pyruvate is then converted into lactic acid.
This breakdown resynthesizes 2 ATP.
Lactic Acid Production.
Lactic acid is a by product of anaerobic glycolysis. Lactic acid accumulates and diffuses into tissue fluid and blood.If it is not removed quickly it builds up to impede muscle contraction and causes fatigue. It also cause pain and the performer may have to stop.
A performer would need 8 minutes of recovery time and the removal of lactic acid.Aerobic System.
Long term energy system.
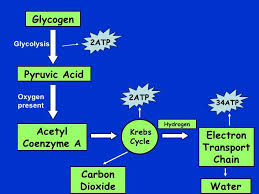
If plenty of oxygen is available, glycogen
and fatty acids break down to yield large amounts of ATP (38 in total).Carbon dioxide and water are waste
products.The Krebs Cycle
The process of the krebscycle occurs in the mitochondria.Pyruvatecombines with CoA to create Acetyl CoA.
Acetyl CoA combines withoxaloaceticacid to make citric acid.The by product is carbon dioxide.
The H+ ions are transported to the electron transport chain.2 ATP are made.
Describe the process of ATP production from
carbohydrates through the aerobic energy system.Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose.
Glucose is broken down into glycogen.
This then goes into the krebscycle and enters the electron transport chain.Jasmine is a county rugby player and she trains
regularly to improve her performance.Evaluatethe importance of the aerobic system for
Jasmine's rugby performance.
UNSTUCK-
What type of exercise intensity will this system be suited to? When during the rugby game will this system be used?What stores are replenished during recovery?
Identify what is removed during recovery.
How much ATP is made using this system?
When would this system NOT be useful?
Jasmine is a county rugby player and she trains regularly to improve her performance.Evaluatethe importance of the aerobic system for
Jasmine's rugby performance.
The aerobic system is used in low intensity exercise. It is the main source of energy when jogging, resting during her games. When recovering, phosphocreatine stores will be replenished and lactic acid will be removed.High number of ATP are made.
Aerobic system is not useful when sprinting down the wing. The ATP-PC system would be better suited to this.
Evaluate the importance of the aerobic energy
system for elite 100m sprinters in competition and training. Consider why is might be useful for the 100m sprinter. Consider why is might not be useful for the 100m sprinter.Evaluate the importance of the aerobic energy
system for elite 100m sprinters in competition and training.Aerobic Glycolysis.
Krebs Cycle
Electron Transport Chain.
ATP Generated in ETC.
38 molecules of ATP are generated in the ETC.
Depending on the intensity and duration of the exercise and your level of fitness, recovery from this energy system can range frona few hours to 2-3 days.Let's Remember.
1.Identify what ATP stands for?
2.How long does the ATP store last for?
3.Draw out how ATP is made.
4.Identify the system a 100m sprinter would use to generate ATP?
5.Explain how the ATP-PC system generates ATP.
6.Explain how lactic acid is made and the effects it has on the body.
7.Where does the aerobic energy production occur?
Apply our knowledge.
Describe the process of ATP production from carbohydrates through the aerobic energy system. (5 marks) Evaluate the importance of the aerobic energy system for elite 100m sprinters in competition and training. (6 marks)The Energy Systems in combination
Draw out and complete the table (pg5).
DurationClassificationEnergysupplied bySport example1-3 secondsAnaerobicATP (in the muscles)A punchin boxing
3-10 seconds
10-45 seconds
45seconds-2 minutes
2 minutes-4 minutes
Over 4 minutes
Exam Preparation.
Revision session:
Split the learners into small groups and give each group a different specification topic. Ask each group to design revision question cards for their topic. On completion, photocopy each set of resources and give to the other groups as revision material.Adaptations of the energy systems to
exercise.Increased CreatineStores-
Short duration, interval training using high intensity exercise improves your ability to produce anaerobic work.
Body adapts by storing more creatinein the muscles which will improve the ATP-PC system. You can then exercise for longer anaerobically using fast and powerful movements.Increased tolerance to lactic acid-
Anaerobic training will stimulate the muscles to be better at tolerating lactic acid and clearing it. With endurance training, the capillary network extends allowing greater volumes of blood to supply the muscles with oxygen and nutrients. Muscles will use fat as a fuel source more efficiently and can work harder for longer without fatiguing. The body's madžimal odžygen consumption increases.Aerobic Energy System.
Aerobic system can produce more energy
As the cardiovascular system improves, more oxygen can be delivered which is needed to produce ATP.Lactic can be oxidised and removed.
Increased use of fats as an energy source.
Fat is the primary energy source during low intensity exercise. Fat combustion powers almost all exercise at approx. 25% of aerobic capacity. Fat oxidation increases as exercise continues for a long time and glycogen depletes.A trained athlete has a greater opportunity to burn fat than a non trained athlete as they are more efficient at delivering oxygen to the working muscles as well as a greater number of mitochondria.
Aerobic Capacity
The maximum amount of oxygen that can be consumed during maximal exercise.Increased storage of glycogen and increased
numbers of mitochondria. Muscles increase their oxidative capacity with regular training. This is because- Long term exercise increases the number of mitochondria in the muscle cells.Increase supply of ATP
Increase in the number of enzymes involved in respiration. The muscles can store more glycogen meaning that anaerobic glycolysis can continue for longer.Exam Questions.
Explain why it is an advantage for long distance runners to have high numbers of mitochondria. (2 marks)Additional Factors affecting the energy
systems.Diabetes and hypoglycaemic attack-
This is where the glucose in your blood is too high. It prevents glucose being used as a fuel for energy. Hypoglycaemia is low glucose levels in your blood. If you have low levels then you will not have the energy to carry on with activities.Children's lack of lactate system-
Lactate system is not fully developed in children. Therefore during high intensity exercise lactic acid builds up.
quotesdbs_dbs21.pdfusesText_27[PDF] aerobic exercise at home for beginners
[PDF] aerobic exercise at home for stomach
[PDF] aerobic exercise at home for weight loss
[PDF] aerobic exercise at home to reduce belly fat
[PDF] aerobic exercise at home video
[PDF] aerobic exercise at home videos free download
[PDF] aerobic exercise cardio
[PDF] aerobic exercise definition acsm
[PDF] aerobic exercise definition anatomy
[PDF] aerobic exercise definition fitness
[PDF] aerobic exercise definition heart rate
[PDF] aerobic exercise definition pe
[PDF] aerobic exercise definition psychology
[PDF] aerobic exercise definition quizlet