 Crystal Field Theory
Crystal Field Theory
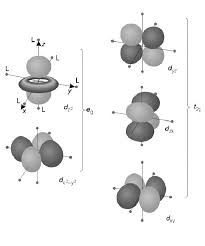
The splitting of d orbital energies and its consequences are at the heart of crystal field theory. Page 5. 5. CFT-Octahedral Complexes. •For the Oh
 Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
19-Dec-2018 As originally developed crystal field theory was used to describe the electronic structure of metal ions in crystals
 Untitled
Untitled
Crystal field Theory (CFT):. Developed by H. Bethe and van. Vleck. Originally crystal field theory was applied to transition metal ions in ionic crystals.
 MSCCH-17/18/19 Course Code-CHE-501 Unit- 6 Crystal Field
MSCCH-17/18/19 Course Code-CHE-501 Unit- 6 Crystal Field
CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT). In view of the weaknesses of Valence Bond Theory (VBT) an alternative bonding model was applied to transition metal complexes.
 Crystal Field Theory
Crystal Field Theory
❖ Electric field generated by the ligands influences the distribution of electrons in the metal ions i.e. d-orbital splitting. ❖ The bonding between the
 CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT)
CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT)
Crystal Field Theory was proposed by the physicist Hans Bethe in 1929 to describe the bonding in coordination complexes and to rationalize and predict some
 Coordination Compounds
Coordination Compounds
(vi) It does not distinguish between weak and strong ligands. The crystal field theory (CFT) is an electrostatic model which considers the metal-ligand bond to
 CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT) This theory advanced by Bethe
CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT) This theory advanced by Bethe
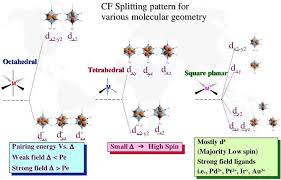
7) Different crystal fields will have different effects on the relative energies of the five d orbitals. Crystal field splitting of d-orbitals: The out come of
 Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
Crystal Field Theory (CFT). The bonding of transition metal complexes can be explained by two approaches: crystal field theory and molecular orbital theory.
 Crystal Field Theory
Crystal Field Theory
Crystal field theory. (CFT) is a bonding model that explains many important properties of transition-metal complexes including their colors
 Crystal Field Theory
Crystal Field Theory
The splitting of d orbital energies and its consequences are at the heart of crystal field theory. Page 5. 5. CFT-Octahedral Complexes. •For the Oh
 Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
Dec 19 2018 As originally developed
 CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT)
CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT)
Crystal Field Theory was proposed by the physicist Hans Bethe in 1929 to describe the bonding in coordination complexes and to rationalize and predict some
 Topic: Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
Topic: Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
The crystal field splitting is measured in terms of energy difference between t2g and eg orbital and is denoted by a symbol ?o . It is generally measured
 Chemistry Notes for class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds .pdf
Chemistry Notes for class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds .pdf
By using spectroscopic data for a number of coordination compounds having the same metal ions but different ligand
 Coordination Compounds
Coordination Compounds
(vi) It does not distinguish between weak and strong ligands. The crystal field theory (CFT) is an electrostatic model which considers the metal-ligand bond to
 ATOICV1-7-1-Limitation-of-Crystal-Field-Theory.pdf
ATOICV1-7-1-Limitation-of-Crystal-Field-Theory.pdf
The main drawback of the crystal field theory is that it does not consider the covalent character in metal-ligand bonding at all. It treats the metal-ligand
 Crystal Field Theory
Crystal Field Theory
Crystal field theory. (CFT) is a bonding model that explains many important properties of transition-metal complexes including their colors
 Crystal Field Splitting in an Octahedral Field
Crystal Field Splitting in an Octahedral Field
as e. The crystal field splitting in the tetrahedral field is intrinsically smaller than in the octahedral field For most purposes the relationship may be
 B.Sc. III YEAR INORGANIC CHEMISTRY-III
B.Sc. III YEAR INORGANIC CHEMISTRY-III
2.4 AN ELEMENTARY IDEA OF CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY. In view of the above weaknesses an alternative bonding model was applied to transition metal complexes.
1 | P a g e
www.ncerthelp.com (Visit for all ncert solutions in text and videos, CBSE syllabus, note and many more)
Chemistry Notes for class 12 Chapter 9
Coordination Compounds
Coordination compounds are those addition molecular compounds which retain their identity in solid state as well as in dissolved state. In these compounds. the central metal atom or ion is linked by ions or molecules with coordinate bonds. e.g., Potassium ferrocyanide, K4 [Fe(CN)6].Double Salts
These are the addition molecular compounds which are stable in solid state but dissociate into4·(NH4)2SO4 . 6H2O get dissociated
into Fe2+, NH+4 and SO2-4 ions.Terms Related to Coordination Compounds
1. Complex ion or Coordination Entity
It is an electrically charged species in which central metal atom or ion is surrounded by number of ions or neutral molecules. (i) Cationic complex entity It is the complex ion which carries positive charge. e.g., [Pt(NH3)4]2+ (ii) Anionic complex entity It is the complex ion which carries negative charge. e.g., [Fe(CN)6]4-2. Central Atom or Ion
The atom or ion to which a fixed number of ions or groups are bound is .ned central atom or ion. It is also referred as Lewis acid. e.g., in (NiCI2(H2O)4]. Ni is central metal atom. It is generally transition element or inner-transition element.3. Ligands
2 | P a g e
www.ncerthelp.com (Visit for all ncert solutions in text and videos, CBSE syllabus, note and many more)
Ligands is electron donating species (ions or molecules) bound to the Central atom in the coordination entity. These may be charged or neutral. LIgands are of the following types : (i) Unidentate It is a ligand, which has one donor site, i.e., the ligand bound to a metal ion through a single donor site. e.g., H2O, NH3, etc. (ii) Didentate It is the ligand. which have two donor sites. (iii) Polydentate It is the ligand, which have several donor sites. e.g., [EDTA]4- is hexadentate ligand. (iv) Ambidentate ligands These are the monodentate ligands which can ligate through two different sites, e.g., NO-2, SCN-, etc. (v) Chelating ligands Di or polydentate ligands cause cyclisation around the metal atom which are known as chelate IS , Such ligands USes two or more donor atoms to bind a single metal ion and are known as chelating ligands. More the number of chelate rings, more is the stability of complex. The stabilisation of coordination compounds due to chelation is known as chelate effect.ʌquotesdbs_dbs14.pdfusesText_20
[PDF] cse 2221 osu reddit
[PDF] cse 2221 project 10
[PDF] cse 2221 sequence
[PDF] cse 2221 syllabus
[PDF] cse 2231
[PDF] cse 2321
[PDF] cse2221 homepage
[PDF] cspire
[PDF] cspire customer service contact number
[PDF] cspire customer service email
[PDF] cspire customer service jobs
[PDF] cspire customer service pay bill
[PDF] cspire customer service text
[PDF] css cheat sheet codecademy
