 Crystal Field Theory
Crystal Field Theory
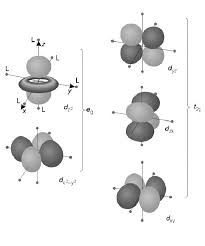
The splitting of d orbital energies and its consequences are at the heart of crystal field theory. Page 5. 5. CFT-Octahedral Complexes. •For the Oh
 Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
19-Dec-2018 As originally developed crystal field theory was used to describe the electronic structure of metal ions in crystals
 Untitled
Untitled
Crystal field Theory (CFT):. Developed by H. Bethe and van. Vleck. Originally crystal field theory was applied to transition metal ions in ionic crystals.
 MSCCH-17/18/19 Course Code-CHE-501 Unit- 6 Crystal Field
MSCCH-17/18/19 Course Code-CHE-501 Unit- 6 Crystal Field
CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT). In view of the weaknesses of Valence Bond Theory (VBT) an alternative bonding model was applied to transition metal complexes.
 Crystal Field Theory
Crystal Field Theory
❖ Electric field generated by the ligands influences the distribution of electrons in the metal ions i.e. d-orbital splitting. ❖ The bonding between the
 CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT)
CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT)
Crystal Field Theory was proposed by the physicist Hans Bethe in 1929 to describe the bonding in coordination complexes and to rationalize and predict some
 Coordination Compounds
Coordination Compounds
(vi) It does not distinguish between weak and strong ligands. The crystal field theory (CFT) is an electrostatic model which considers the metal-ligand bond to
 CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT) This theory advanced by Bethe
CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT) This theory advanced by Bethe
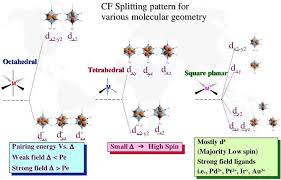
7) Different crystal fields will have different effects on the relative energies of the five d orbitals. Crystal field splitting of d-orbitals: The out come of
 Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
Crystal Field Theory (CFT). The bonding of transition metal complexes can be explained by two approaches: crystal field theory and molecular orbital theory.
 Crystal Field Theory
Crystal Field Theory
Crystal field theory. (CFT) is a bonding model that explains many important properties of transition-metal complexes including their colors
 Crystal Field Theory
Crystal Field Theory
The splitting of d orbital energies and its consequences are at the heart of crystal field theory. Page 5. 5. CFT-Octahedral Complexes. •For the Oh
 Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
Dec 19 2018 As originally developed
 CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT)
CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT)
Crystal Field Theory was proposed by the physicist Hans Bethe in 1929 to describe the bonding in coordination complexes and to rationalize and predict some
 Topic: Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
Topic: Crystal Field Theory (CFT)
The crystal field splitting is measured in terms of energy difference between t2g and eg orbital and is denoted by a symbol ?o . It is generally measured
 Chemistry Notes for class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds .pdf
Chemistry Notes for class 12 Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds .pdf
By using spectroscopic data for a number of coordination compounds having the same metal ions but different ligand
 Coordination Compounds
Coordination Compounds
(vi) It does not distinguish between weak and strong ligands. The crystal field theory (CFT) is an electrostatic model which considers the metal-ligand bond to
 ATOICV1-7-1-Limitation-of-Crystal-Field-Theory.pdf
ATOICV1-7-1-Limitation-of-Crystal-Field-Theory.pdf
The main drawback of the crystal field theory is that it does not consider the covalent character in metal-ligand bonding at all. It treats the metal-ligand
 Crystal Field Theory
Crystal Field Theory
Crystal field theory. (CFT) is a bonding model that explains many important properties of transition-metal complexes including their colors
 Crystal Field Splitting in an Octahedral Field
Crystal Field Splitting in an Octahedral Field
as e. The crystal field splitting in the tetrahedral field is intrinsically smaller than in the octahedral field For most purposes the relationship may be
 B.Sc. III YEAR INORGANIC CHEMISTRY-III
B.Sc. III YEAR INORGANIC CHEMISTRY-III
2.4 AN ELEMENTARY IDEA OF CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY. In view of the above weaknesses an alternative bonding model was applied to transition metal complexes.
Crystal Field Splitting in an Octahedral Field
e gEnergy 3/5 oot 2g 2/5 oe g - The higher energy set of orbitals (d z2 and d x2-y2 t 2g - The lower energy set of orbitals (d xy d yz and d xz o or 10 Dq -The energy separation between the two levels The e orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0 6 The e g orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0 6 o The t 2g orbitals to be stabilized to the extent of 0.4 ǻ oTetrahedral Field
t 2 2 5Energy
2 5 t t e3/5 tThe higher energy set of orbitals (d
xz ,d yz ,d xy ) is labeled as t 2 an d the lowe r ener gy set d z 2 an d d x 2 y 2 is labeled 2 gy z x y as e. The crystal field splitting in the tetrahedral field is intrinsically smaller than in the octahedral field For most purposes the relationship may be represented as 4 9 field For most purposes the relationship may be represented as t 4 9 oOctahedral Vs Tetrahedral
yEnergy [Ti(H 2 O) 6 3+ -a d 1 systemThe single electron in the t
2g orbitals absorb energy in the form of light and gets excited to the e g orbitals. In case of [Ti(H 2 O) 6 3+ , this corresponds to 520 nm (20,300 cm -1520 nm
(243 kJ/mol)Factors Affecting the Magnitude of ǻ
1. Higher oxidation states of the metal atom correspond to larger .
=10,200 cm -1 for [Co II (NH 3 6 2+ and 22,870 cm -1 for [Co III (NH 3 6 3+ =32,200 cm -1 for [Fe II (CN) 6 4- and 35,000 cm -1 for [Fe III (CN) 6 3-2. In groups, heavier analogues have larger .
For hexaammine complexes [M
III (NH 3 6 3+22 870
1 (C ) 22870
cm 1 (C o
34,100 cm
-1 (Rh)41,200 cm
-1 (Ir)3. Geometry of the metal coordination unit affects greatly.
Tetrahedral complexes ML
4 have smaller than octahedral ones ML 6 = 10,200 cm -1 for [Co II (NH 3 6 2+5,900 cm
-1 for [Co II (NH 3 4 2+4. Nature of the ligands.
For [Co
quotesdbs_dbs11.pdfusesText_17[PDF] cse 2221 osu reddit
[PDF] cse 2221 project 10
[PDF] cse 2221 sequence
[PDF] cse 2221 syllabus
[PDF] cse 2231
[PDF] cse 2321
[PDF] cse2221 homepage
[PDF] cspire
[PDF] cspire customer service contact number
[PDF] cspire customer service email
[PDF] cspire customer service jobs
[PDF] cspire customer service pay bill
[PDF] cspire customer service text
[PDF] css cheat sheet codecademy
