 Supplementary Trigonometry Exercise Problems
Supplementary Trigonometry Exercise Problems
Find the value of the indicated trigonometric function of the angle ? in the figure. 18) A pendulum swings though an angle of 30° each second.
 LESSON 6: TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES
LESSON 6: TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES
lesson contains several examples and exercises to demonstrate this type of procedure. which suggest the second Pythagorean identity tan2 t + 1 = sec2 t.
 OER Math 1060 – Trigonometry
OER Math 1060 – Trigonometry
Angles and Their Measure. 1.1 Exercises. In Exercises 1 – 4 convert the angles into the DMS system. Round each of your answers to the nearest second.
 Trigonometry
Trigonometry
Using this method limits us to finding trig function values for angles that are accessible on the unit circle plus who wants to memorize it!!! Second Way: If
 College Trigonometry
College Trigonometry
Jul 4 2013 nearest second. 1. 63.75?. 2. 200.325?. 3. ?317.06?. 4. 179.999?. In Exercises 5 - 8
 INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
Since trigonometric functions have no restrictions there is no inverse. • With that in mind
 OCR AS Mathematics Trigonometry Section 1: Trigonometric
OCR AS Mathematics Trigonometry Section 1: Trigonometric
Apr 22 2016 (iii) In a second test
 Section 2.3 – Solving Right Triangle Trigonometry
Section 2.3 – Solving Right Triangle Trigonometry
From a second second person standing 33.0 feet farther from the ... Solution. Section 2.3 – Solving Right Triangle Trigonometry. Exercise.
 10.4 Trigonometric Identities
10.4 Trigonometric Identities
The remaining four circular functions can be expressed in terms of cos(?) and sin(?) so the proofs of their Even / Odd Identities are left as exercises.
 Exercises and Problems in Calculus John M. Erdman
Exercises and Problems in Calculus John M. Erdman
A second straight road passes through Allentown and intersects the first road ponential functions trigonometric and inverse trigonometric functions
 Trigonométrie : exercices de maths en 2de à télécharger en PDF
Trigonométrie : exercices de maths en 2de à télécharger en PDF
Trigonométrie et des exercices de maths en 2de en PDF en utilisant les formules de trigonométrie avec le cosinus sinus et tangente
 [PDF] trigonometrie exercices corriges
[PDF] trigonometrie exercices corriges
TRIGONOMETRIE - EXERCICES CORRIGES Trigonométrie rectangle Exercice n°1 Compléter les égalités en respectant bien les notations de l'énoncé cos ABC =
 [PDF] Trigonométrie dans le cercle - Lycée dAdultes
[PDF] Trigonométrie dans le cercle - Lycée dAdultes
6 sept 2014 · EXERCICE 8 Exprimer à l'aide de sin x et cos x les expressions suivantes : a) sin(-x) + cos(-x) b) sin(-x) - sin(7 + x)
 [PDF] TRIGONOMÉTRIE (II) CORRECTION DES EXERCICES
[PDF] TRIGONOMÉTRIE (II) CORRECTION DES EXERCICES
TRIGONOMÉTRIE (II) CORRECTION DES EXERCICES ÉQUATIONS ET INÉQUATIONS TRIGONOMÉTRIQUES Exercice 1 : Résolvons l'équation cos(x) = ?
 [PDF] Exercices corrigés sur le cercle trigonométrique - AlloSchool
[PDF] Exercices corrigés sur le cercle trigonométrique - AlloSchool
Cercle trigonométrique - Classe de 2nde Corrigé de l'exercice 1 ?1 Convertir les cinq mesures suivantes en radians : 222? 124? 286? 24?et 99?
 [PDF] TD Trigonométrie - 2nde
[PDF] TD Trigonométrie - 2nde
TD Trigonométrie - 2nde Exercice 1 Soit ABC un triangle équilatéral dont la mesure des côtés vaut x On note I le milieu du segment
 [PDF] Exercices de trigonométrie - 2
[PDF] Exercices de trigonométrie - 2
Exercices de trigonométrie - 2 ( Trigonométrie du triangle rectangle et non rectangle ) 1) On veut mesurer (sans altimètre) l'altitude d'une montagne
 [PDF] Cosinus sinus et tangente dun angle aigu - Meilleur En Maths
[PDF] Cosinus sinus et tangente dun angle aigu - Meilleur En Maths
Fiche exercices EXERCICE 1 ABC est un triangle rectangle en A AC=4cm AB=3cm Donner une valeur approchée de la mesure des angles ABCet
 [PDF] [PDF] Unité I Trigonométrie
[PDF] [PDF] Unité I Trigonométrie
Les exercices suivants contiennent des questions dont la complexité varie Quelques uns sont des projets simples Il se pourrait que certains élèves ne
 Exercices CORRIGES de trigonométrie (ancien programme avec les
Exercices CORRIGES de trigonométrie (ancien programme avec les
Exercices CORRIGES de trigonométrie (ancien programme avec les radians) - Site de maths du lycee La Merci (Montpellier) en Seconde ! ; Chap 09 - 1A - Conversion
Comment comprendre la Trigo ?
Dessine un cercle trigo complet en 3 étapes simples :
N'oublie pas de mettre les valeurs x=1 et y=1 Trace les demi-droites correspondantes aux 3 angles. Pour ?/4, c'est la moitié de l'angle droit, facile. Ensuite ?/6 c'est un tiers de l'angle droit, donc c'est l'angle plus petit que ?/4.Comment résoudre des équations trigonométriques ?
Il y a plusieurs choses à faire lorsqu'on résout une équation trigonométrique :
1Utiliser les définitions des rapports trigonométriques (sinus et cosinus).2Poser les restrictions, si nécessaire.3Déduire la ou les solutions en lien avec le cercle trigonométrique. 4Donner la solution générale gr? à la période.Quelles sont les formules de trigonométrie ?
Formules fondamentales :
sin² x + cos² x = 1.tg x . cotg x = 1.tg x = sin x / cos x.cotg x = cos x / sin x.1 + tg² x = 1 / cos² x.1 + cotg² x = 1 / sin² x.sec x = 1/cos x.cosec x = 1/sin x.- On définit le cosinus comme étant le rapport entre le côté adjacent à l'angle par rapport à l'hypoténuse. Le sinus est le rapport entre le côté opposé à l'angle par rapport à l'hypoténuse.
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Review
First, let's review briefly inverse functions before getting into inverse trigonometric functions: • f f -1 is the inverse • The range o = the domain o -1 , the inverse. • The domain o = the range o -1 the inverse. • y = f(x) x in the domain of f. x = f -1 (y) y in the domain o -1 f [f -1 (y)] = y y in the domain o -1 • f -1 [f (x)] = x x in the domain oTrigonometry Without Restrictions
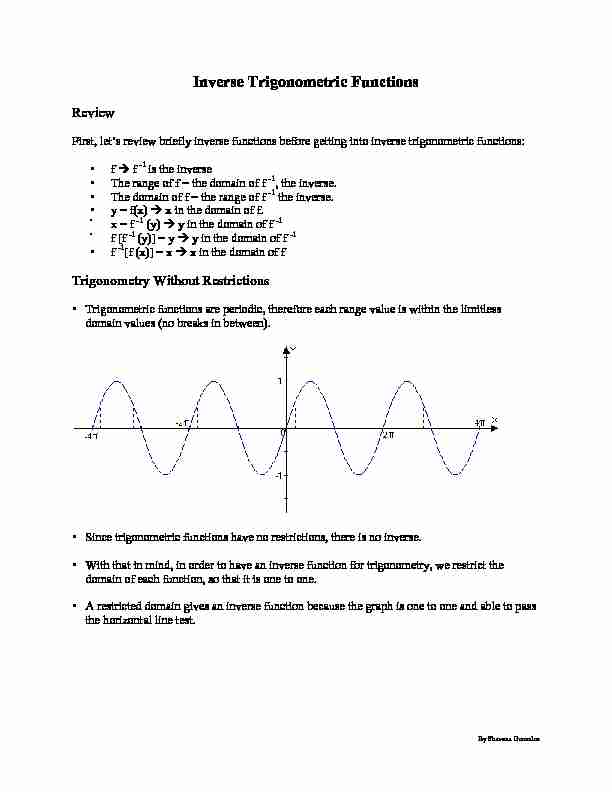
• Trigonometric functions are periodic, therefore each range value is within the limitless domain values (no breaks in between). • Since trigonometric functions have no restrictions, there is no inverse. • With that in mind, in order to have an inverse function for trigonometry, we restrict the domain of each function, so that it is one to one.• A restricted domain gives an inverse function because the graph is one to one and able to pass
the horizontal line test.By Shavana Gonzalez
Trigonometry With Restrictions
• How to restrict a domain: - Restrict the domain of the sine function, y = sin x, so that it is one to one, and not infinite by setting an interval [-ʌ/2, ʌ/2] - The restricted sine function passes the horizontal line test, therefore it is one to one - Each range value (-1 to 1) is within the limited domain (-ʌ/2, ʌ/2). • The restricted sine function benefits the analysis of the inverse sine function.Inverse Sine Function
• sin -1 or arcsin is the inverse of the restricted sine function, y = sin x, [-ʌ/2, ʌ/2] • The equations y = sin -1 x or y = arcsin x which also means, sin y = x, where - /2 < y < ʌ/2, -1 < x < 1 (remember f range is f -1 domain and vice versa).Restricted Sine vs. Inverse Sine
• As we established before, to have an inverse trigonometric function, first we need a restricted
function. • Once we have the restricted function, we take the points of the graph (range, domain, and origin), then switch the y's with the x's.By Shavana Gonzalez
Restricted Sine vs. Inverse Sine Continued ...
• For example: - These are the coordinates for the restricted sine function. (- ʌ/2, -1), (0, 0), (ʌ/2, 1) - Reverse the order by switching x with y to achieve an inverse sine function. (-1, - ʌ/2), (0, 0), (1, ʌ/2)By Shavana Gonzalez
Sine-Inverse Sine Identities
• sin (sin -1 x) = x, where -1< x < 1Example: sin (sin
-10.5) = 0.5
sin (sin -11.5) 1.5
(not within the interval or domain of the inverse sine function) • sin -1 (sin x) = x, where -ʌ/2 < x < ʌ/2 - Example: sin -1 [sin (-1.5)] = -1.5 sin -1 [sin (-2)] -2 (not within the interval or domain of the restricted sine function)Without Calculator
• To attain the value of an inverse trigonometric function without using the calculator requires
the knowledge of the Circular Points Coordinates, found in Chapter 5, the Wrapping Function section. • Here is quadrant I of the Unit Circle • The Unit Circle figure shows the coordinates of Key Circular Points. • These coordinates assist with the finding of the exact value of an inverse trigonometric function.By Shavana Gonzalez
Without Calculator
Example 1: Find the value for sin
-1 (-1/2)Answer:
• sin -1 (-1/2), is the same as sin y= -1/2, where -ʌ/2< y < ʌ/2 • Since the figure displays a mirror image of ʌ/6 on the IV quadrant, the answer is: y = - ʌ/6 = sin -1 (-1/2) • Although sin (11ʌ/6) = -1/2, y must be within the interval [-ʌ/2, ʌ/2].• Consequently, y= - ʌ/6, which is between the interval, meets the conditions for the inverse
sine function.With Calculator
• There are different types of brands on calculators, so read the instructions in the user's manual. • Make sure to set the calculator on radian mode.• If the calculator displays an error, then the values or digits used are not within the domain of
the trigonometry function - For example:If you punch in sin
-1 (1.548) on your calculator, the device will state that there is an error because 1.548 is not within the domain of sin -1By Shavana Gonzalez
Restrict Cosine Function
• The restriction of a cosine function is similar to the restriction of a sine function.• The intervals are [0, ʌ] because within this interval the graph passes the horizontal line test.
• Each range goes through once as x moves from 0 to ʌ.Inverse Cosine Function
• Once we have the restricted function, we are able to proceed with defining the inverse cosine function, cos -1 or arccos. • The inverse of the restricted cosine function y= cos x, 0 < x < ʌ, is y= cos -1 x and y = arccos x. • Which also means, cos y = x, where 0 < y < ʌ, -1< x < 1 (Remember, the domain of f is the range of f -1 , and vice versa).By Shavana Gonzalez
Restricted Cosine vs. Inverse Cosine
• The restricted cosine function has the domain, range, and x-intercept coordinates: (0,1) (ʌ/2, 0) (ʌ, -1) • The inverse cosine function switched the coordinates of the restricted function, x is now y, and y is now x: (1, 0) (0, ʌ/2) (-1, ʌ)By Shavana Gonzalez
Cosine-Inverse Cosine Identities
• cos (cos -1 x) = x, where -1< x < 1Example: cos (cos
-10.5) = 0.5
cos (cos -11.5) 1.5
(not within the interval or domain of the inverse cosine function) • cos -1 (cos x) = x, where 0 < x < ʌ - Example: cos -1 [cos (0.5)] = 0.5 cos -1 [cos (-2)] -2 (not within the interval or domain of the restricted cosine function)Cosine Inverse Solving Without Calculator:
Example 2: cos (cos
-1 0.6)Answer:
Since -1 <
0.6 < 1, then cos (cos -10.6) = 0.6 because the form is following the
cosine-inverse cosine identities.Example 3: arccos (-1/2)
Answer:
• arccos (-1/2), is the same as cos y= -1/2,where 0< y < ʌ. • Due to the fact, that the figure displays a mirror image of ʌ/4 on the II quadrant, (3ʌ/4), the answer is y= 3ʌ/4 = arccos (-1/2). • Even though cos (-3ʌ/4) = -1/2, y -3ʌ/4. The y must be within the interval [0, ʌ].By Shavana Gonzalez
Solving Cosine Inverse With Calculator
• There are different types of brands on calculators, so read the instructions in the user's manual. • Make sure to set the calculator on radian mode.• If the calculator displays an error, then the values or digits used are not within the domain of
the trigonometry function - For example:If you punch in cos
-1 (1.238) on your calculator, the device will state that there is an error because 1.238 is not within the domain of cos -1Restriction of Tangent Function
• To become a one-to-one function, we choose the interval (-ʌ/2, -ʌ/2), thus a restricted function
is formed. • The restricted tangent function passes the horizontal line test. • Each range value (y) is given exactly once as x proceeds across the restricted domain. • Now, that we have the function restricted we will use it to formulize the inverse tangent function.By Shavana Gonzalez
Inverse Tangent Function
• Signified by tan -1 or arctan y= tan -1 or y= arctan x• The definition, undifferentiated to sine and cosine, is the inverse of the restricted tan function
(y= tan x), in the interval - /2 < x < ʌ/2quotesdbs_dbs29.pdfusesText_35[PDF] valeur remarquable tangente
[PDF] valeurs remarquables trigonométrie démonstration
[PDF] valeurs remarquables arctan
[PDF] droite remarquable d'un triangle
[PDF] équation d'un cercle dans un repère orthonormé
[PDF] propriétés de 2 cercles sécants
[PDF] propriété fonction tangente
[PDF] chevalier du moyen age celebre
[PDF] seigneur qui reçoit l'hommage d'un autre seigneur
[PDF] cérémonie d'hommage moyen age
[PDF] cérémonie de l'hommage moyen age
[PDF] féodalité moyen age cm1
[PDF] territoire donné par un seigneur ? son vassal
[PDF] comment fonctionne le systeme feodal
