 Quantum Numbers and Atomic Orbitals By solving the Schrödinger
Quantum Numbers and Atomic Orbitals By solving the Schrödinger
subshell increases with l (s < p < d < f). 3. Magnetic Quantum Number (ml): ml = -l
 schhandbook2015.pdf
schhandbook2015.pdf
3. TOPIC. Foreword. Message. A. About the S & T Scholarships Regional Office for the orientation on scholarship policies and signing of the.
 Chapter 2 Electric Fields
Chapter 2 Electric Fields
The result is. E = ?. 2?0. (2.7). 2.1.3 Forces on Charges in Electric Fields. An isolated charge q in an electric field experiences a force F = qE.
 Airplane Flying Handbook (FAA-H-8083-3B) Chapter 3
Airplane Flying Handbook (FAA-H-8083-3B) Chapter 3
Depending on the airplane's orientation to the Earth the same control actions may result in different movements of the airplane. [Figure 3-1] The pilot is
 Practice Tests Answer Keys Organic Chemistry I
Practice Tests Answer Keys Organic Chemistry I
What's "ax" in one chair flflip is "eq" in the other. 3. Process cis-trans. 4. Draw in H's on substituted carbons. (easier to see ax/eq).
 DO_s2015_44_0.pdf - DepEd
DO_s2015_44_0.pdf - DepEd
1.3 Convene the SPT for orientation vision sharing
 The Journal of Effective Teaching The Role of Intrinsic Goal
The Journal of Effective Teaching The Role of Intrinsic Goal
do students' intrinsic goal orientation self-efficacy and e-learning practice play in their learning? The target population of this research is college
 PISA 2018: Insights and Interpretations
PISA 2018: Insights and Interpretations
is why the OECD produces this triennial report on to e and the real stud on s ... Singaporeans scored at level 3 or higher in literacy in the Survey of ...
 DM_s2021_071.pdf
DM_s2021_071.pdf
Oct 22 2021 DepEd technical team
 CMO-No.-4-s.-2020-Guidelines-on-the-Implementation-of-Flexible
CMO-No.-4-s.-2020-Guidelines-on-the-Implementation-of-Flexible
Sep 2 2020 Education Act"
Practice Tests Answer Keys, Organic Chemistry I
Online Organic Chemistry I, Chem 350, Dr. Craig P. Jasperse, Minnesota State University MoorheadFor full class website, see
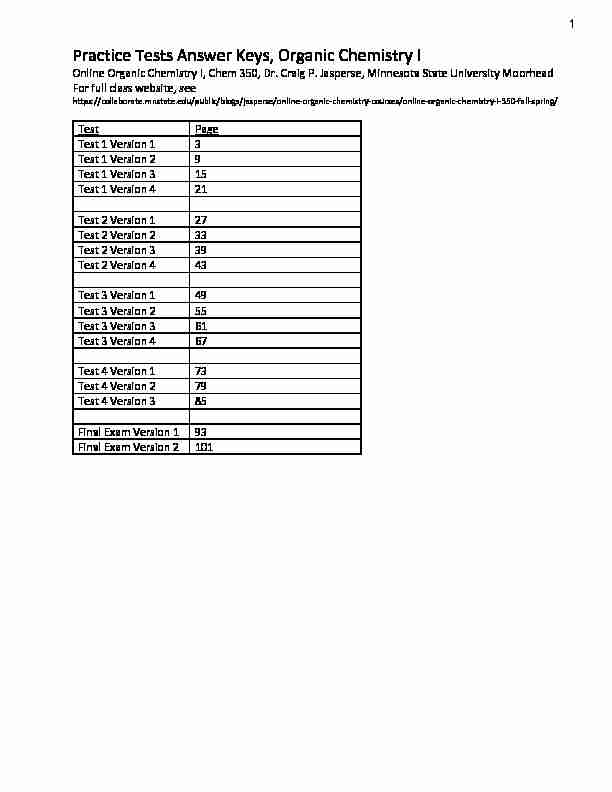
Test Page
Test 1 Version 1 3
Test 1 Version 2 9
Test 1 Version 3 15
Test 1 Version 4 21
Test 2 Version 1 27
Test 2 Version 2 33
Test 2 Version 3 39
Test 2 Version 4 43
Test 3 Version 1 49
Test 3 Version 2 55
Test 3 Version 3 61
Test 3 Version 4 67
Test 4 Version 1 73
Test 4 Version 2 79
Test 4 Version 3 85
Final Exam Version 1 93
Final Exam Version 2 101
1 21 1 JASPERSE CHEM 350 TEST 1 VERSION 1 Organic Chemistry I - Jasperse Intro and Review Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules Structure, Nomenclature, and Conformation/Stereochemistry of Alkanes 1. Draw the correct Lewis structure of CH3CN. (Needn't show 3-D geometry) (3pt) 2. Draw the correct Lewis structure for HOCH2CHO. (Needn't show 3-D geometry). (3pt) 3. Draw a 3-dimensional picture for the atoms in CH3CO2CH2NHCH3, using the hash-wedge convention. (You needn't specify lone pairs, and orbitals need not be shown). (5pt) 4. For the structure shown, what is the hybridization, electron-pair geometry, and approximate bond angle (90, 109, 120, or 180) relative to: (6pt) electron-pair bond electron-pair bond hybridization geometry angle hybridization geometry angle O-1 C-5 C-2 N-7 C-3 O-9 5. Assign any formal charges to any apropriate atoms for proline, given the structure shown (one of the body's 20 monomers from which protein and enzyme biopolymers are constructred). (3pt) HON
OH 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 NH 2 O O3Answers, Test 1 Version 11. Want normal bonding for all2. C=O (or C=C in other cases) may help
3. If you have any formal charges (not here), they must sum
to net charge of molecule (zero, in this case)4. Organization must match condensed formula sequence1. The Nitrogen is tetrahedral, so the N-H hydrogen must
either be wedged or hashed. (The lone pair doesn't need to be drawn in, but it impacts the shape of the nitrogen)2. Drawing the correct Lewis structure is essential! Do fifirst!Fine if N-H is hashed
instead of wedgedTTT2 2 6. Rank the acidity of the following, from 1 (most) to 4 (least). (4pt) 7. Which of the following represent pairs of resonance structures? (4pt) d. Both a and c e. a, b, and c are all resonance structures. 8. Draw arrows to show electron-movement in the following two steps (draw arrows for each step). Draw a circle around the atom that functions as nucleophile in step 1, and a square around the atom that functions as nucleophile in step 2. (5pt) 9. Rank the series on the basis of boiling point, 1 having highest boiling point, 3 having lowest. (3pt) 10. Rank the series on the basis of water solubility, 1 having highest solubility, 3 having lowest. (3pt) OHOH
N H O a.b. OCH3OCH3BrBrc.OOOBrBrOHOHBr+ OHStep 1(anion)Step 2+OOHOHOH43 Acidity Factors:1. charge (not relevant here)
2. Eneg
3. ResonanceNo atoms can move!Explain change in:
1. Bonds
2. Charge
3. Lone Pairs3 factors:
1. H-bonding
2. London force (# of carbons)
-both RAISE BP3. Polar vs nonpolar2 factors:
1. H-bonding (raises solubility)
2. London force (# of carbons)
-more C's reduces water solubilityH-bonding No H-bonding NoNon-polar H-bonding YesH-bonding YesH-bonding No
Polar YesH-bonding Yes
3 3 11. For each of the following pairs of resonance structures, circle the one that would make a greater contribution to the actual resonance hybrid. (4pt) 12. Cyclopropane is much more "strained" than cyclopentane. Why? (Short!) (3pt) 13. For the following acid-base reaction, a. put a box around the weakest base in the reaction b. put a circle around the weakest acid c. draw an arrow to show whether the equilbrium goes to the right or left. (4pt) 14. Classify the relationship between the pairs of molecules as either: (8pt) same compound structural isomers resonance structures geometric isomers not isomers (different molecular formulas) OCH3OCH3OO(anions)ONaO+ H2OOHO+ NaOHOH
OH CH 3 H H CH 3 H H CH 3 H H H H CH 3 Br H OH H Br H HOH52 Factors:
1. More bonds
(priority)2. Electronegativity
(if bonds are equal)Angle strain. Bonds are forced to be 60º, far from the ideal ~109º angle. Note: angle strain only appears in certain rings; For acyclics, steric and torsional are the only strains available. Base Stability factors:1. charge
2. eneg
3. resonance
1. Equilibrium favors the more stable base
2. More stable base is "weaker" base
3. "Weaker" acid + base on same side
4 4 15. Give the name for the following. (7pt) 16. Identify all the funtional groups in the following molecules. (Do not include "alkane", since that isn't "functional".) (6pt) 17. Which of the following pair will have the larger rotation barrier, relative to the bonds indicated? (3pt) 18. For the following Newman projections, rank them in stability from 1 to 4, 1 being most stable. Identify the "anti" conformation, the "gauche" conformation, and the "totally eclipsed" conformation. (6pt) 19. Draw the Newman projection for the most stable conformation of 1,2-dichloroethane. (3pt) H
CH 3 H ON O OH OOCH 3 H H CH 3H H CH 3 H H H H CH 3 H 3 C H H H H CH 3 H 3 C H H H 3 C HH6TTT1. cis/trans for di-subbed rings
2. Alphabetize substituents
3. Numbering
4. Know isopropyl and t-butyl1. Longest chain
2. Alphabetize substituents
3. Number from end near
substituentcis-1-isopropyl-3-methylcyclohexane4-ethyl-3-methylheptaneBest: staggered and "anti"Worst: Totally eclipsed5 5 20. Draw the two chair conformations of cis-1-ethyl-4-methylcyclohexane. (You don't have to draw all the hydrogens). (5pt) 21. W hich is more stable, cis- or tra ns-1-t-butyl-2-methylcyclohexane? Draw the best conformation of the more stable isomer. (4pt) 22. Draw as many structural isomers as you can for C6H14. Be careful not to draw the same isomer twice! I will take off points for duplicating! (6pt) 7TTT1. Make sure you've really
drawn "flflipped" chairs2. What's "ax" in one chair flflip is
"eq" in the other.3. Process cis-trans
4. Draw in H's on substituted
carbons (easier to see ax/eq).1. More stable chair has both substituents equatorial2. Process cis-transAlkane Acyclic: C
n H 2n+2Alkane Cyclic: C
n H 2nBeware of drawing same
thing twice! 81 JASPERSE CHEM 350 TEST 1 VERSION 2 Organic Chemistry I - Jasperse Intro and Review Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules Structure, Nomenclature, and Conformation/Stereochemistry of Alkanes 1. Draw the correct Lewis structure of CH3CO2CH2COCH3. (Needn't show 3-D geometry) (3pt) 2. Draw a 3-dimensional picture for the atoms in CH3CH2CHCHCH2NHCH2CHO, using the hash-wedge convention. (You needn't specify lone pairs, and orbitals need not be shown). (5pt) 3. For the structure shown, what is the hybridization, electron-pair geometry, and approximate bond angle (90, 109, 120, or 180) relative to: (7pt, 2 points off for each error) electron-pair bond electron-pair bond hybridization geometry angle hybridization geometry angle C-1 C-4 O-2 N-5 C-3 C-6 4. Assign any formal charges to any appropriate atoms for the structure shown below. (4pt) 123456ONOHOONCH3CH3HO9TTT1. Want normal bonding for all
2. C=O (or C=C in other cases) may help
3. If you have any formal charges (not here), they must sum
to net charge of molecule (zero, in this case)4. Organization must match condensed formula sequence1. The Nitrogen is tetrahedral, so the N-H hydrogen must either be wedged or hashed.
(The lone pair doesn't need to be drawn in, but it impacts the shape of the nitrogen)2. Drawing the correct Lewis structure is essential! Do fifirst!Fine if N-H is hashed
instead of wedgedAnswers, Test 1 Version 22 5. Rank the acidity of the following, from 1 (most) to 4 (least). (4pt) 6. For the following pairs, identify as "isomers" ("I") or "resonance structures" ("R"). (6pt) 7. Draw arrows to show electron-movement in the following reactions. (These are reactions, not resonance.) (5pt) a. b. 8. Rank the series on the basis of boiling point, 1 having highest boiling point, 3 having lowest. (3pt) 9. Rank the series on the basis of water solubility, 1 having highest solubility, 3 having lowest. (3pt) NH2OHHOOOHOHOOOBrO+Br+O+HHOOHOHNH2NH2OHOH10TTT3 Acidity Factors:
1. charge (not relevant here)
2. Eneg
3. ResonanceNo atoms can move!Explain change in:
1. Bonds
2. Charge
3. Lone Pairs2 factors:
1. H-bonding
2. London force (# of carbons)
-both RAISE BP2 factors:1. H-bonding (raises solubility)
2. London force (# of carbons)
-more C's reduces water solubility2 factors:1. H-bonding
2. London force (# of carbons)
-both RAISE BPH-bonding No H-bonding YesExtra C's reduce solubility3 10. Circle whichever of the following could fit the formula C5H10? (3pt) 11. For the following acid-base reaction, a. put a box around the weakest base in the reaction b. put a circle around the weakest acid c. draw an arrow to show whether the equilibrium goes to the right or left. (4pt) 12. Classify the relationship between each pair of molecules as either: (10 pt) same compound structural isomers resonance structures stereoisomers OHNHNa+OONaNH2+OH3COH3COiPrCH3HCH3HHiPrHHCH2CH3HHBrHBrHBrHBrHHNHN11TTTBase Stability factors:
1. charge
2. eneg
3. resonance
1. Equilibrium favors the more stable base
2. More stable base is "weaker" base
3. "Weaker" acid + base on same sideAlkane Acyclic: C
n H 2n+2Alkane Cyclic: C
n H 2nAlkene: C
n H 2n (not expected to remember, but evident if you count)Counting H's can always double-check on this!
4 14. Give the name for the following. (7pt) 15. 16. Identify and write down the names for each of the functional groups in each of the following molecules. (Do not include "alkane", since that isn't "functional".) For each molecule, try to write the names in order, as they appear from left-to-right in the molecules. (8pt) 17. Circle which of the following pair will have the larger rotation barrier, relative to the bonds indicated? (2pt) Identify which reason explains why: steric strain, torsional strain, or angle strain? 18. For the following Newman projections: (6pt total) a. rank them in stability from 1 to 4, 1 being most stable b. identify the "anti", "gauche", and the "totally eclipsed" conformations. c. Is the energy difference between the gauche and the anti conformation based on steric strain, torsional strain, or angle strain? d. In the case of ethane (not shown), staggered conformations are better than eclipsed conformations. Is the difference based on steric strain, torsional strain, or angle strain? 19. Draw both the most stable and the least stable Newman projections for 1-bromopropane, BrCH2CH2CH3, relative to C1-C2 bond. - (3pt) HHHNH2OONHOOOOHCH2CH3HHHHH3CCH2CH3HHCH3HHHH3CH2CHCH3HHHH3CH2CHHHH3C12TTT5-ethyl-3-methyloctanetrans-1-butyl-3-isopropylcyclopentane1. Longest chain
2. Alphabetize substituents
3. Number from end near
substituent1. cis/trans for di-subbed rings2. Alphabetize substituents
3. Numbering
4. Know isopropyl and t-butylGreater steric strain when totally eclipsed.
(Both will have equal torsional strain when totally eclipsed.)Best: staggered and "anti"Worst: Totally eclipsed5 20. Which of the following are correct Lewis structures, including formal charges, for nitric acid, HNO3. (3 pts) 21. a. A only b. B only c. C only d. Both A and C e. All of the above 22. Draw the two chair conformations of cis-1-isopropyl-4-methylcyclohexane. (You don't have to draw all the hydrogens). (5pt) (Use "iPr" as abbreviation). 23. Draw the best chair conformation of the more stable isomer. Which is more stable, cis- or trans-1-butyl-2-methylcyclohexane? (4pt) 24. Draw any 6 of the 9 possible structural isomers for alkanes with formula C7H16. When deciding whether to draw cyclic or acyclic alkanes, make sure that you fit the formula! Be careful not to draw the same isomer twice! I will take off points for duplicating! (You can try to show off by getting more than 6, but if you do still be sure you don't duplicate!) (6pt) NOOOHNOOONOOOHHABC13TTT1. Do not exceed octet
2. If formal charges, must sum to net charge
3. As much "normal bonding" as possible, given
the above constraints.1. Make sure you've really drawn "flflipped" chairs2. What's "ax" in one chair flflip is "eq" in
the other.3. Process cis-trans
4. Draw in H's on substituted carbons
(easier to see ax/eq).1. More stable chair has both substituents equatorial2. Process cis-transAlkane Acyclic: C
n H 2n+2Alkane Cyclic: C
n H 2nBeware of drawing same
thing twice! 141 1 JASPERSE CHEM 350 TEST 1 VERSION 3 Organic Chemistry I - Jasperse Intro and Review Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules Structure, Nomenclature, and Conformation/Stereochemistry of Alkanes 1. (12 points) Give the relationship between the following pairs of structures. The possible relationships are the following: same compound structural isomers resonance structures stereo isomers not isomers (different molecular formula) 2. (8 points) Draw line-angle structures and names for 4 of the 5 structural isomers of C6H14. Br
Br H Br H Br H H a. CC BrH BrH HHCC HH BrBr HH b. BrBrc. d.
e. f.15Answers, Test 1 Version 31. Resonance: No atoms can move!2. Stereo: same
condensed formula3. Structural: different
condensed formulaAlkane Acyclic: C n H 2n+2Alkane Cyclic: C
n H 2nBeware of drawing same
thing twice!TTTStructural.1,2-dibromo vs
1,3-dibromo.Same.
Bond rotation around
single bonds is allowed.Structural.CH3CHCHBr vs CH2CHCH2BrStereo. Trans-cis.
Double bond can't rotate.Same. Both are 4-methylnonaneResonance. Electrons and charge is repositioned, but no atoms moved.butane2,3-dimethylbutane2 2 3. (10 Points) a. For the above structure, what is the hybridization and approximate bond angles (109, 120, or 180) about: C-2 C-4 C-6 O-8 b. In the above structure, N-1 is actually found to have 120º bond angles. (This may seem unexpected to you at this point, but we'll learn why later in the course.) What must be the hybridization of the nitrogen? 4. (2 Points) Bond rotation around C6-C7 in the above structure has a 7 kcal/mol barrier, while rotation around the C4-C5 bond has a 70 kcal/mol barrier. Explain very briefly why it is so much harder to rotate the latter bond? 5. (4 points) For each of the pairs listed, circle the one with the higher boiling point. 6. (6 points) Write a Lewis structure and assign any non-zero formal charges. a. [CH3NH3]+ b. CH3CO2Na c. CH3CHO H
2 N OH O 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 N CH 3 N H a. OHOHb. 162 factors:
1. H-bonding (raises solubility)
2. London force (# of carbons)
-more C's reduces water solubility1. Want normal bonding for all: in absence of metal ions2. C=O (or C=C in other cases) may help
3. If you have any formal charges (not here), they must sum
to net charge of molecule (zero, in this case)4. Organization must match condensed formula sequenceTTTsp2, ~120ºsp2, ~120ºsp3, ~109sp3, ~109sp2. Hybridization, bond angle, and electron geometry are all interlocked.
To know any one of them is to know the others. Single bond versus double bond.A double bond has overlapping p-orbitals.
To rotate a double bond, the p-p overlap would be lost. The full pi-bond would need to break.By contrast, no bonds are broken when you rotate around a single bond. H-bondingExtra carbons, hydrophobic
3 3 7. (5 points) a) Draw the best resonance structure for anion A, and circle the resonance structure that would make the greater contribution to the resonance hybrid. b. For the two resonance structures shown below, circle the resonance structure that would make the greater contribution to the resonance hybrid. 8. (6 points) Rank the acidity of the following molecules, 1 being most acidic, 4 being least acidic. Hint: draw the anions! NH3 CH3CH2OH CH3CO2H HCl 9. (6 point s) Draw a li ne-angle picture for a ll of the atoms i n the mol ecule CH3CH2COCHClCH3, including the hydrogens. Use the hash-wedge convention to indicate atoms that are not in the plane of the paper. 10. (5 points) Rank the ring strain in the following, from 1(most) to 3 (least). Explain very briefly the differences in strain. N
O A NH 2 NH 2 C BA172 Factors:
1. More bonds
(priority)2. Electronegativity
(if bonds are equal)3 Acidity Factors:1. charge (not relevant here)
2. Eneg
3. ResonanceTTTCl could equally well be drawn in the
hashed spotA: has large angle strain (60º angles, not109º angles)
B: By taking on chair conformation, there
is zero angle strain, and zero torsional (no eclipsing)C: If it has ideal angles, then some
eclipsing and torsional strain destabilizes it4 4 11. (6 points) Which of the following are capable of cis-trans stereoisomerism? (Yes/No). a. 3-ethyl-1,1-dimethylcyclopentane b. 3-pentene (name means a double bond is between carbons 3 and 4) c. 1,3-dimethylcyclohexane 12. (9 point s) Identify the funct ional groups in the follow ing molecule s. (Do not include "alkane", since that is not "functional". And do not specify "cyclic".) H
2 NCO 2 H ("GABA: brain neurotransmitter") a. O OH H HH CH 3 H CH 3Testosterone
b. N O O H H O CH 3 O CH 3 c. Cocaine18TTTAmineCarboxylic AcidKetoneAlcoholAlkeneAmineEsterEsterArene or aromaticquotesdbs_dbs31.pdfusesText_37[PDF] ÉTAT DES LIEUX. Informations pratiques
[PDF] METTRE EN ŒUVRE SES OBLIGATIONS DE PUBLICITE ET D INFORMATION
[PDF] Réguler le virtuel : Expérience des jeux en ligne
[PDF] Tarif Tarif Entreprises au départ d un téléphone fixe de La Réunion
[PDF] Présentation du projet de déploiement d un service départemental de recharge de véhicules électriques en Hautes-Pyrénées
[PDF] LA MALADIE D ALZHEIMER
[PDF] NUMÉROS D IDENTIFICATION FISCALE (NIF) Fiche sujet: structure et description du NIF
[PDF] Numéros vert - numéros azur - Coordonnées des structures locales d information et de conseils de l Allier
[PDF] Table des matières. Connaissances. I. Orientation diagnostique devant
[PDF] Support de cours de la formation izi-media
[PDF] SCHEMA DEPARTEMENTAL DES INFRASTRUCTURES PUBLIQUES DE CHARGE POUR VEHICULES ELECTRIQUES OU HYBRIDES RECHARGEABLES
[PDF] TRIBUNAL ADMINISTRATIF DE MARSEILLE N 0605319 RÉPUBLIQUE FRANÇAISE M. B. A. AU NOM DU PEUPLE FRANÇAIS. M. Salvage Rapporteur
[PDF] Séance extraordinaire du conseil municipal tenue jeudi le 5 août 2014 à 19h à la salle municipale dudit Conseil, à laquelle étaient présents :
[PDF] Table des matières. I. ÉPIDÉMIOLOGIE 13 A. Données démographiques 13 B. Données socio-économiques 14
