 Ch31-AC Circuits.pdf
Ch31-AC Circuits.pdf
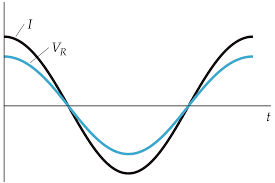
• RLC Circuit - Solution via Complex Numbers. • RLC Circuit - Example The use of complex numbers simplifies the lead-lag nature of the voltage and current in ...
 Practice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits
Practice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits
0.34 A. Page 2. 2 CHAPTER 33. 20. An RLC series circuit has R = 100 ohms C = 25 µF
 QUESTION BANK WITH ANSWERS
QUESTION BANK WITH ANSWERS
Determine the power factor of a RLC series circuit with R=5ohm XL=8ohm and XC=12ohm. (JUNE
 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (I YEAR – II
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (I YEAR – II
Example Problems: 1) Find the Req for the circuit shown in below figure. fig(a). Solution: To get Req we combine resistors in series and in parallel. The 6 ohms
 AC Electrical Circuit Analysis - A Practical Approach James M. Fiore
AC Electrical Circuit Analysis - A Practical Approach James M. Fiore
Apr 22 2021 D: Answers to Selected Odd-Numbered Problems . . . . 408. E: Questions for Selected Odd Answers . . . . . 422. 9. Page 10. 1 Fundamentals. 1.0 ...
 BEE-402; UNIT-I MESH AND NODAL ANALYSIS of AC circuits
BEE-402; UNIT-I MESH AND NODAL ANALYSIS of AC circuits
Assume o=10° radians per second. == Solution 2: Convert the circuit to the phasor domain. Solve the problem using circuit techniques (nodal analysis mesh ...
 0.1. Single Phase AC circuit - JNNCE ECE Manjunath
0.1. Single Phase AC circuit - JNNCE ECE Manjunath
Problems on Three phase AC circuits. 0.4 Problems on Three phase AC circuits Calculate power power factor and current in the circuit. Solution: Z = E. I. =.
 ee301 – phasors complex numbers in ac and impedance
ee301 – phasors complex numbers in ac and impedance
Sep 22 2016 Solving AC circuit problems is greatly simplified through the use of the phasor transform. ... Solution: Example: Given: I1 = 20 sin (ω t) mA. I2 ...
 ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS Lecture Notes Prepared By S
ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS Lecture Notes Prepared By S
A.C TRANSIENT ANALYSIS: Transient response of R-L R-C
 DC NETWORK THEOREMS
DC NETWORK THEOREMS
This method which is particularly well-suited to coupled circuit solutions employs a system of ** Or impedance in the case of a.c. circuits. *. After the ...
 Ch31-AC Circuits.pdf
Ch31-AC Circuits.pdf
Alternating Current Circuits. • Alternating Current - AC Circuits: Resistor; Inductor; Capacitor ... RLC Circuit - Solution via Complex Numbers.
 BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
In order to analyze AC circuit it is necessary to represent multi-dimensional quantities. In Problem: Find impedance Zin of below circuit. Solution: ...
 SINGLE PHASE AC CIRCUITS
SINGLE PHASE AC CIRCUITS
Phasor Algebra for a pure resistive circuit. Problem 2. An ac circuit consists of a pure resistance of 10 and is connected to an ac supply of 230 V 50 Hz.
 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (I YEAR – II
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (I YEAR – II
Example Problems: 1) Find the Req for the circuit shown in below figure. fig(a). Solution: To get Req we combine resistors in series and in parallel.
 CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 7
CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 7
(b) The rms value of current in an ac circuit is 10 A. What is the peak current? Solution: (a). Given. Peak voltage
 Practice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits
Practice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits
0.34 A. Page 2. 2 CHAPTER 33. 20. An RLC series circuit has R = 100 ohms C = 25 µF
 Series and parallel AC circuits This worksheet and all related files
Series and parallel AC circuits This worksheet and all related files
A student measures voltage drops in an AC circuit using three voltmeters and arrives on this problem you realize that neither of the answers proposed.
 A-C Circuit Analysis - Alexander Schure.pdf
A-C Circuit Analysis - Alexander Schure.pdf
A-C CIRCUIT. ANALYSIS publication carefully selected problems afford the reader more profitable in- ... Solution. f = 1/t = l;.0025 = 400 cycles.
 Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis
Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis
E1.1 Circuit Analysis. Problem Sheet 2 - Solutions. Note: In many of the solutions below I have written the voltage at node X as the variable X instead of.
 AC Electrical Circuit Analysis - A Practical Approach James M. Fiore
AC Electrical Circuit Analysis - A Practical Approach James M. Fiore
22?/04?/2021 This AC Electrical Circuit Analysis by James M. Fiore is copyrighted under the terms of ... D: Answers to Selected Odd-Numbered Problems.
AC Electrical Circuit Analysis AC Electrical Circuit Analysis A Practical ApproachA Practical Approach
James M. FioreJames M. Fiore
2 AC Electrical Circuit AnalysisAC Electrical Circuit AnalysisA Practical ApproachA Practical Approach
byJames M. Fiore
Version 1.1.2, 22 April 2021
3 This AC Electrical Circuit Analysis, by James M. Fiore is copyrighted under the terms of a Creative Commons license: This work is freely redistributable for non-commercial use, share-alike with attribution Device data sheets and other product information are copyright by their respective owners and have been obtained through publicly accessible manufacturer's web sites.Published by James M. Fiore via dissidents
ISBN13: 979-8605022282
For more information or feedback, contact:
James Fiore, Professor
Electrical Engineering Technology
Mohawk Valley Community College
1101 Sherman Drive
Utica, NY 13501
jfiore@mvcc.edu For the latest revisions, related titles, and links to low cost print versions, go to: www.mvcc.edu/jfiore or my mirror sites www.dissidents.com and www.jimfiore.orgYouTube Channel: Electronics with Professor Fiore
Cover art, Chapman's Contribution Redux, by the author 4IntroductionIntroduction
Welcome to the AC Electrical Circuit Analysis, an open educational resource (OER). The goal of this text is to
introduce the theory and practical application of analysis of AC electrical circuits. It assumes familiarity with DC
circuit analysis. If you have not studied DC circuit analysis, it is strongly recommended that you read the
companion OER text, DC Electrical Circuit Analysis before continuing. Both texts are offered free of charge
under a Creative Commons non-commercial, share-alike with attribution license. For your convenience, along
with the free pdf and odt files, print copies are available at a very modest charge. Check my web sites for links.
This text is based on the earlier Workbook for AC Electrical Circuits, which it replaces. The original expository
text has been greatly expanded and includes many examples along with computer simulations. For theconvenience of those who used the Workbook, many of the problem sets are the same, with some re-ordering
depending on the chapter.If you are already familiar with DC Electrical Circuit Analysis, the format of this title is similar. This text picks
up where the DC text leaves off; beginning with AC concepts such as sinusoidal waveforms, basic Fourier
decomposition of complex waveforms, complex numbers and the like. Also, reactance and impedance areintroduced along with phasor diagrams. Chapters on series, parallel and series-parallel RLC circuits commence.
Following these, network theorems along with nodal and mesh analysis are discussed for the AC case. The text
completes with chapters on AC power, resonance, and introductions to polyphase systems and magnetic circuits.
Each chapter begins with a set of learning objectives and concludes with practice exercises that are generally
divided into four major types: analysis, design, challenge and simulation. Many SPICE-based circuit simulators
are available, both free and commercial, that can be used with this text. The answers to most odd-numbered
exercises can be found in the Appendix. A table of standard resistor sizes is also in the Appendix, which is useful
for real-world design problems. If you have any questions regarding this workbook, or are interested in
contributing to the project, do not hesitate to contact me.This text is part of a series of OER titles in the areas of electricity, electronics, audio and computer
programming. It includes three other textbooks covering semiconductor devices, operational amplifiers, and
embedded programming using the C language with the Arduino platform. There is a text covering DC electrical
circuits similar to this one, and also seven laboratory manuals; one for each of the five texts plus individual titles
covering computer programming using the Python language, and the science of sound. The most recent versions
of all of my OER texts and manuals may be found at my MVCC web site as well as my mirror site: www.dissidents.comThis text was created using several free and open software applications including Open Office, Dia, SciDAVis,
and XnView.Special thanks to the following individuals for their efforts in reviewing and proofreading the DC and AC
Electrical Circuit Analysis texts: Glenn Ballard, John Markham, João Nuno Carvalho, Mark Steffka and Jim
Noon. 5For the Have-nots and the Has-beens "Well, the people, I would say. There is no patent. Could you patent the sun?"
- Jonas Salk, inventor of the polio vaccine, when asked who owns the patent to it. 6Table of ContentsTable of Contents
Chapter 1: Fundamentals.......10
1.0 Chapter Objectives........ 10
1.1 Introduction......... 10
1.2 Sinusoidal Waveforms....... 11
1.3 Basic Fourier Analysis........ 25
1.4 Complex Numbers........ 29
1.5 Reactance and Impedance....... 31
1.6 Phasor Diagrams........ 37
Summary......... 38
Exercises......... 39
Chapter 2: Series RLC Circuits...... 44
2.0 Chapter Objectives........ 44
2.1 Introduction......... 44
2.2 The Series Connection....... 44
2.3 Series Impedance........ 45
2.4 Series Circuit Analysis........ 48
2.5 Concerning Practical Inductors...... 61
Summary......... 63
Exercises......... 64
Chapter 3: Parallel RLC Circuits..... 80
3.0 Chapter Objectives........ 80
3.1 Introduction......... 80
3.2 The Parallel Connection...... 81
3.3 Parallel Impedance........ 81
3.4 Parallel Circuit Analysis....... 85
Summary.........100
Exercises.........101
Chapter 4: Series-Parallel RLC Circuits....110
4.0 Chapter Objectives........ 110
4.1 Introduction......... 110
4.3 The Series-Parallel Connection...... 110
4.4 Series-Parallel Impedance....... 111
4.5 Series-Parallel Circuit Analysis....... 114
Summary......... 132
Exercises......... 133
7 Chapter 5: Analysis Theorems and Techniques....1445.0 Chapter Objectives........ 144
5.1 Introduction......... 144
5.2 Source Conversions........ 145
5.3 Superposition Theorem ....... 153
5.4 Thévenin's and Norton's Theorems...... 160
5.5 Maximum Power Transfer Theorem...... 170
5.6 Delta-Y (Pi-T) Conversions....... 179
Summary......... 185
Exercises......... 187
Chapter 6: Nodal and Mesh Analysis.....204
6.0 Chapter Objectives........ 204
6.1 Introduction......... 204
6.2 Nodal Analysis........ 205
6.3 Mesh Analysis........ 222
6.4 Dependent Sources........ 234
Summary......... 240
Exercises......... 242
Chapter 7: AC Power.......260
7.0 Chapter Objectives........ 260
7.1 Introduction......... 260
7.2 Power Waveforms........ 261
7.3 Power Triangle........ 273
7.4 Power Systems........ 280
Summary......... 286
Exercises......... 287
Chapter 8: Resonance.......294
8.0 Chapter Objectives........ 294
8.1 Introduction......... 294
8.2 Series Resonance........ 295
8.3 Parallel Resonance........ 310
Summary......... 329
Exercises......... 331
8Chapter 9: Polyphase Power......338
9.0 Chapter Objectives........ 338
9.1 Introduction......... 338
9.2 Polyphase Definition........ 339
9.3 Three-Phase Connections....... 341
9.4 Power Factor Correction....... 354
Summary......... 364
Exercises......... 365
Chapter 10: Decibels and Bode Plots.....372
10.0 Chapter Objectives........ 372
10.1 Introduction........ 372
10.2 The Decibel......... 372
10.3 Bode Plots......... 383
10.4 Combining the Elements - Multi-Stage Effects..... 393
Summary......... 395
Exercises......... 396
Appendices
A: Standard Component Sizes.......399
B: Methods of Solution of Linear Simultaneous Equations...400C: Equation Proofs........405
D: Answers to Selected Odd-Numbered Problems....408E: Questions for Selected Odd Answers.....422
91 1 FundamentalsFundamentals
1.0 Chapter Learning Objectives1.0 Chapter Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter, you should be able to: •Describe sinusoidal waveforms in mathematical terms. •Express complex waveforms using basic Fourier analysis. •Perform mathematical operations using complex numbers. •Draw phasor diagrams for complex numbers. •Compute and plot capacitive and inductive reactance as a function of frequency. •Compute and plot complex impedance as a function of frequency.•Describe the relationships between resistance, reactance, impedance, conductance, susceptance and
admittance1.1 Introduction1.1 Introduction
In this chapter we begin our study of alternating current, or AC, electrical circuit analysis. As such, this chapter
is filled with foundational material that will be used in the remainder of this text. It is critical that the concepts
presented here be fully understood in order to achieve success in later chapters. We start with the mathematical
description of the most simple AC waveform, the sine wave. This includes parameters such as amplitude,
quotesdbs_dbs4.pdfusesText_8[PDF] ac frequency us
[PDF] ac tonnage calculation formula
[PDF] ac unit calculator
[PDF] ac2o dmap mechanism
[PDF] aca american cycling association
[PDF] aca certification accounting
[PDF] aca certification apple
[PDF] aca certification corrections
[PDF] aca certification cost
[PDF] aca certification courses
[PDF] aca certification exam
[PDF] aca certification phlebotomy
[PDF] aca code of ethics
[PDF] aca code of ethics pdf
