 Ch31-AC Circuits.pdf
Ch31-AC Circuits.pdf
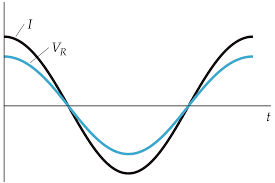
• RLC Circuit - Solution via Complex Numbers. • RLC Circuit - Example The use of complex numbers simplifies the lead-lag nature of the voltage and current in ...
 Practice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits
Practice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits
0.34 A. Page 2. 2 CHAPTER 33. 20. An RLC series circuit has R = 100 ohms C = 25 µF
 QUESTION BANK WITH ANSWERS
QUESTION BANK WITH ANSWERS
Determine the power factor of a RLC series circuit with R=5ohm XL=8ohm and XC=12ohm. (JUNE
 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (I YEAR – II
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (I YEAR – II
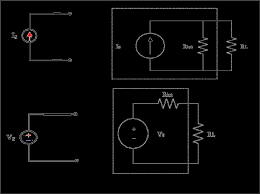
Example Problems: 1) Find the Req for the circuit shown in below figure. fig(a). Solution: To get Req we combine resistors in series and in parallel. The 6 ohms
 AC Electrical Circuit Analysis - A Practical Approach James M. Fiore
AC Electrical Circuit Analysis - A Practical Approach James M. Fiore
Apr 22 2021 D: Answers to Selected Odd-Numbered Problems . . . . 408. E: Questions for Selected Odd Answers . . . . . 422. 9. Page 10. 1 Fundamentals. 1.0 ...
 BEE-402; UNIT-I MESH AND NODAL ANALYSIS of AC circuits
BEE-402; UNIT-I MESH AND NODAL ANALYSIS of AC circuits
Assume o=10° radians per second. == Solution 2: Convert the circuit to the phasor domain. Solve the problem using circuit techniques (nodal analysis mesh ...
 0.1. Single Phase AC circuit - JNNCE ECE Manjunath
0.1. Single Phase AC circuit - JNNCE ECE Manjunath
Problems on Three phase AC circuits. 0.4 Problems on Three phase AC circuits Calculate power power factor and current in the circuit. Solution: Z = E. I. =.
 ee301 – phasors complex numbers in ac and impedance
ee301 – phasors complex numbers in ac and impedance
Sep 22 2016 Solving AC circuit problems is greatly simplified through the use of the phasor transform. ... Solution: Example: Given: I1 = 20 sin (ω t) mA. I2 ...
 ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS Lecture Notes Prepared By S
ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT ANALYSIS Lecture Notes Prepared By S
A.C TRANSIENT ANALYSIS: Transient response of R-L R-C
 DC NETWORK THEOREMS
DC NETWORK THEOREMS
This method which is particularly well-suited to coupled circuit solutions employs a system of ** Or impedance in the case of a.c. circuits. *. After the ...
 Ch31-AC Circuits.pdf
Ch31-AC Circuits.pdf
Alternating Current Circuits. • Alternating Current - AC Circuits: Resistor; Inductor; Capacitor ... RLC Circuit - Solution via Complex Numbers.
 BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
In order to analyze AC circuit it is necessary to represent multi-dimensional quantities. In Problem: Find impedance Zin of below circuit. Solution: ...
 SINGLE PHASE AC CIRCUITS
SINGLE PHASE AC CIRCUITS
Phasor Algebra for a pure resistive circuit. Problem 2. An ac circuit consists of a pure resistance of 10 and is connected to an ac supply of 230 V 50 Hz.
 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (I YEAR – II
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LECTURE NOTES B.TECH (I YEAR – II
Example Problems: 1) Find the Req for the circuit shown in below figure. fig(a). Solution: To get Req we combine resistors in series and in parallel.
 CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 7
CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 7
(b) The rms value of current in an ac circuit is 10 A. What is the peak current? Solution: (a). Given. Peak voltage
 Practice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits
Practice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits
0.34 A. Page 2. 2 CHAPTER 33. 20. An RLC series circuit has R = 100 ohms C = 25 µF
 Series and parallel AC circuits This worksheet and all related files
Series and parallel AC circuits This worksheet and all related files
A student measures voltage drops in an AC circuit using three voltmeters and arrives on this problem you realize that neither of the answers proposed.
 A-C Circuit Analysis - Alexander Schure.pdf
A-C Circuit Analysis - Alexander Schure.pdf
A-C CIRCUIT. ANALYSIS publication carefully selected problems afford the reader more profitable in- ... Solution. f = 1/t = l;.0025 = 400 cycles.
 Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis
Ver 3537 E1.1 Analysis of Circuits (2014) E1.1 Circuit Analysis
E1.1 Circuit Analysis. Problem Sheet 2 - Solutions. Note: In many of the solutions below I have written the voltage at node X as the variable X instead of.
 AC Electrical Circuit Analysis - A Practical Approach James M. Fiore
AC Electrical Circuit Analysis - A Practical Approach James M. Fiore
22?/04?/2021 This AC Electrical Circuit Analysis by James M. Fiore is copyrighted under the terms of ... D: Answers to Selected Odd-Numbered Problems.
1 Practice Problems - Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits Multiple Choice 4. A high-voltage powerline operates at 500 000 V-rms and carries an rms current of 500 A. If the resistance of the cable is 0.050Ω/km, what is the resistive power loss in 200 km of the powerline? a. 250 kW b. 500 kW c. 1 Megawatt d. 2.5 Megawatts e. 250 Megawatts 12. A 10-µF capacitor is plugged into a 110 V-rms 60-Hz voltage source, with an ammeter in series. What is the rms value of the current through the capacitor? a. 0.202 A (rms) b. 0.415 A (rms) c. 0.626 A (rms) d. 0.838 A (rms) e. 0.066 A (rms) 13. A 0.5-H inductor is connected into a 110 V-rms 60-Hz voltage source, with an ammeter in series. What is the rms value of the current through the inductor? a. 0.189 A (rms) b. 0.292 A (rms) c. 0.584 A (rms) d. 1.19 A (rms) e. 0.093 A (rms) 15. The inductance of a tuning circuit of an AM radio is 4 mH. Find the capacitance of the circuit required for reception at 1200 kHz. a. 2.1 pF b. 4.4 pF c. 21.2 pF d. 43.4 pF e. 27.6 pF 18. If an R = 1-kΩ resistor, a C = 1-µF capacitor, and an L = 0.2-H inductor are connected in series with a V = 150 sin (377t) volts source, what is the maximum current delivered by the source? a. 0.007 A b. 27 mA c. 54 mA d. 0.308 A e. 0.34 A
2 CHAPTER 33 20. An RLC series circuit has R = 100 ohms, C = 25 µF, and L = 0.16 H. For what angular frequency of an ac voltage is the current flow maximum? a. 251 rad/s b. 500 rad/s c. 757 rad/s d. 884 rad/s e. 79.6 rad/s 22. Determine the impedance for the circuit. a. 600 Ω b. 1200 Ω c. 1800 Ω d. 2300 Ω e. 1100 Ω 23. Determine the rms current for the circuit. a. 55 mA b. 77 mA c. 99 mA d. 0.190 A e. 61 mA 30. What is the average power dissipation in an RLC series circuit with R = 10Ω, L = 0.1 H, C = 10 µF when driven at resonance by a 100 V-rms source? a. 100 W b. 500 W c. 1000 W d. 2 kW e. 700 W
Alternating Current Circuits 3 32. A transformer is to be designed to increase the 30 kV-rms output of a generator to the transmission-line voltage of 345 kV-rms. If the primary winding has 80 turns, how many turns must the secondary have? a. 6 b. 70 c. 920 d. 9200 e. 12 33. The primary winding of an electric train transformer has 400 turns and the secondary has 50. If the input voltage is 120V(rms) what is the output voltage? a. 15 V (rms) b. 30 V (rms) c. 60 V (rms) d. 2.4 V (rms) e. 960 V (rms) 37. Calculate Vout/Vin for the circuit if R = 2 kΩ, C = 0.02 µF and V = 140V sin(50 000t) a. 0.02 b. 0.45 c. 0.80 d. 0.98 e. 2.23 38. The impedance of the parallel RLC circuit shown is given by a. R
1 + L! 1 + ωC b. ! 2 2 11 L C R -1/2 c. R 1 CL(( 11 d. 2 2 1 C LR e. ! L C R 11 24 CHAPTER 33 46. Whenever the alternating current frequency in a series RLC circuit is halved, a. the inductive reactance is doubled and the capacitive reactance is halved. b. the inductive reactance is doubled and the capacitive reactance is doubled. c. the inductive reactance is halved and the capacitive reactance is halved. d. the inductive reactance is halved and the capacitive reactance is doubled. e. the reactance of the circuit remains the same. 47. The average power input to a series alternating current circuit is minimum when a. there are only a resistor and capacitor in the circuit. b. there are only a resistor and inductor in the circuit. c. there is only a resistor in the circuit. d. XL = XC and the circuit contains a resistor, an inductor and a capacitor. e. there is only a capacitor in the circuit. 48. All three circuits shown below have != 100R
, H 1.0=L and emf E = (5.0 V) sin (377 t). Which statement regarding the angular resonance frequencies A , B and C is correct? a. BAC b. BAC c. CBA d. CAB e. CAB56. A 10-µF capacitor in an LC circuit made entirely of superconducting materials (!= 0R
) is charged to 100 µC. Then a superconducting switch is closed. At t = 0 s, plate 1 is positively charged and plate 2 is negatively charged. At a later time, VV10
ab . At that time, dc V is a. 0 V. b. 3.54 V. c. 5.0 V. d. 7.07 V. e. 10 V.Alternating Current Circuits 5 Open-Ended Problems 57. Suppose the circuit parameters in a series RLC circuit are: L = 1.0 µH, C = 10.0 nF, R = 100Ω, and the source voltage is 220 V. Determine the resonant frequency of the circuit and the amplitude of the current at resonance. 58. A 10-Ω resistor, 10-mH inductor, and 10-µF capacitor are connected in series with a 10-kHz voltage source. The rms current through the circuit is 0.20 A. Find the rms voltage drop across each of the 3 elements. 59. An ac power generator produces 50 A (rms) at 3600 V. The voltage is stepped up to 100 000 V by an ideal transformer and the energy is transmitted through a long distance power line which has a resistance of 100 ohms. What percentage of the power delivered by the generator is dissipated as heat in the long-distance power line?
6 CHAPTER 33 Chapter 33 Alternating Current Circuits 1. c 2. a 3. d 4. d 5. d 6. a 7. a 8. b 9. a 10. d 11. d 12. b 13. c 14. d 15. b 16. b 17. c 18. c 19. d 20. b 21. a 22. c 23. a 24. a 25. a 26. b 27. c 28. b 29. b 30. c 31. a 32. c 33. a 34. b 35. d 36. d 37. b 38. b 39. b 40. a 41. e 42. c 43. d 44. a 45. d 46. d 47. e 48. c 49. c 50. a 51. d 52. c 53. b 54. d 55. d 56. e
Alternating Current Circuits 7 57. 1.59 MHz, 2.2 A 58. 2.0 V, 125.6 V, 0.318 V 59. 0.18%quotesdbs_dbs4.pdfusesText_8[PDF] ac frequency us
[PDF] ac tonnage calculation formula
[PDF] ac unit calculator
[PDF] ac2o dmap mechanism
[PDF] aca american cycling association
[PDF] aca certification accounting
[PDF] aca certification apple
[PDF] aca certification corrections
[PDF] aca certification cost
[PDF] aca certification courses
[PDF] aca certification exam
[PDF] aca certification phlebotomy
[PDF] aca code of ethics
[PDF] aca code of ethics pdf
