 Least Squares
Least Squares
17 сент. 2013 г. The MAtlAB function polyfit computes least squares polynomial fits by setting up the design matrix and using backslash to find the ...
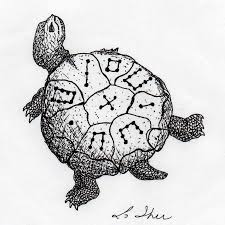 Magic Squares
Magic Squares
2 окт. 2011 г. Write a MAtlAB function ismagic(A) that checks if A is a magic square. 10.2 Magic sum. Show that. 1 n n2. ∑ k=1 k = n3 + n. 2 . 10.3 durerperm ...
 Some important Built-in function in MATLAB 1. Square root b=sqrt(x
Some important Built-in function in MATLAB 1. Square root b=sqrt(x
14 мар. 2020 г. Some important Built-in function in MATLAB. 1. Square root b=sqrt(x) b=sqrt(4). 2. 2. Remainder of dividing x/y a=rem(xy) a=rem(10
 Objective 1 Triangular Wave 2 Square Wave 3 Discrete Time
Objective 1 Triangular Wave 2 Square Wave 3 Discrete Time
2 Square Wave. MATLAB has a built-in function square to generate a periodic square waveform. Following example will help you draw such a waveform. 2.1
 - 1 - Some MATLAB Built-in Functions Function Description sqrt(x
- 1 - Some MATLAB Built-in Functions Function Description sqrt(x
Some MATLAB Built-in Functions. Function. Description sqrt(x). Square root of x nthroot(xn) nth root of x abs(x). Absolute value of x exp(x). Exponential (ex).
 Eigenvalues and Singular Values
Eigenvalues and Singular Values
16 сент. 2013 г. The Matlab function condeig computes eigenvalue condition numbers. ... The qr function in Matlab factors any matrix real or complex
 Quadrature
Quadrature
area—plot the function on graph paper and count the number of little squares that The function functions in Matlab itself usually expect the first argument to.
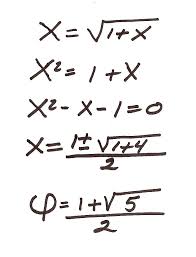 Iteration
Iteration
2 окт. 2011 г. Matlab responds with x = 3. Next enter this statement x = sqrt(1 + x). The abbreviation sqrt is the Matlab name for the square root function.
 Total Least Squares Approach to Modeling: A Matlab Toolbox
Total Least Squares Approach to Modeling: A Matlab Toolbox
In this section we show some applications of the TLS method in static and dynamical modeling by using the created Matlab functions [14]. 3.1 Linear regression
 Implementing the 2D square lattice Boltzmann method in Matlab
Implementing the 2D square lattice Boltzmann method in Matlab
23 февр. 2023 г. In contrast to LGA. LBM deals with distribution function values instead of single particles. The exact denomination for the following described ...
 General Linear Least-Squares and Nonlinear Regression
General Linear Least-Squares and Nonlinear Regression
Applied Numerical Methods with MATLAB for Engineers Chapter 15 & Teaching The least-squares ... function that returns the sum of the squares of the.
 Objective 1 Triangular Wave 2 Square Wave 3 Discrete Time
Objective 1 Triangular Wave 2 Square Wave 3 Discrete Time
MATLAB has a built-in function sawtooth to generate a periodic triangular waveform. Following example will help you draw such a waveform. 1.1 Example. Generate
 Magic Squares
Magic Squares
2011?10?2? An n-by-n magic square is an array containing the integers from 1 to n2 ... squares of order n but the MAtlAB function magic(n) generates a ...
 Least Squares
Least Squares
2013?9?17? The MAtlAB function polyfit computes least squares polynomial fits by setting up the design matrix and using backslash to find the ...
 Some important Built-in function in MATLAB 1. Square root b=sqrt(x
Some important Built-in function in MATLAB 1. Square root b=sqrt(x
2020?3?14? Some important Built-in function in MATLAB. 1. Square root b=sqrt(x) b=sqrt(4). 2. 2. Remainder of dividing x/y a=rem(xy) a=rem(10
 Eigenvalues and Singular Values
Eigenvalues and Singular Values
2013?9?16? A singular value and pair of singular vectors of a square or ... qr function in Matlab factors any matrix real or complex
 Iteration
Iteration
2011?10?2? The abbreviation sqrt is the Matlab name for the square root function. The quantity on the right. /. 1 + x
 DEPARTMENTS OF MATHEMATICS
DEPARTMENTS OF MATHEMATICS
1999?1?4? MAtlAB has included since at least version 3 a function sqrtm for computing a square root of a matrix. The function works by reducing the ...
 INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB FOR ENGINEERING STUDENTS
INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB FOR ENGINEERING STUDENTS
The function diary is useful if you want to save a complete MATLAB session. of vectors in MATLAB are enclosed by square brackets and are separated by ...
 Total Least Squares Approach to Modeling: A Matlab Toolbox
Total Least Squares Approach to Modeling: A Matlab Toolbox
In this section we show some applications of the TLS method in static and dynamical modeling by using the created Matlab functions [14]. 3.1 Linear regression
 MATLAB Basic Functions Reference - MathWorks
MATLAB Basic Functions Reference - MathWorks
Tasks represent a series of MATLAB commands To see the commands that the task runs show the generated code Common tasks available from the Live Editor tab on the desktop toolstrip: • Clean Missing Data • Clean Outlier • Find Change Points • Find Local Extrema • Remove Trends • Smooth Data mathworks com/help/matlab
 Chapter 10 Magic Squares - MathWorks
Chapter 10 Magic Squares - MathWorks
Ann-by-nmagic square is an array containing the integers from 1 ton2arranged so that each of the rows each of the columns and the two principaldiagonals have the same sum For eachn >2 there are many di?erent magicsquares of ordern but theMatlabfunctionmagic(n)generates a particular one Matlabcan generate Lo Shu with = magic(3) which produces
 MATLAB Function Example Handout - University of Wyoming
MATLAB Function Example Handout - University of Wyoming
ical function libraries The Matlab Optimization and Curve Fitting Toolboxes include functions for one-norm and in?nity-norm problems We will limit ourselves to least squares in this book 5 3 censusgui The NCM program censusgui involves several di?erent linear models The data
 Chapter 1 Iteration - MathWorks
Chapter 1 Iteration - MathWorks
In Matlab and most other programming languages the equals sign is the assignment operator It says compute the value on the right and store it in the variable on the left So the statement x = sqrt(1 + x) takes the current value of x computes sqrt(1 + x) and stores the result back in x
 Functions and Scripts - Electrical Engineering and Computer
Functions and Scripts - Electrical Engineering and Computer
Many functions are programmed inside MATLAB as built-in functions and can be used in mathematical expressions simply by typing their name with an argument; examples are sin(x) cos(x) sqrt(x) and exp(x) MATLAB has a plethora of built-in functions for mathematical and scientific computations
 Chapter 1 Introduction to MATLAB - MathWorks
Chapter 1 Introduction to MATLAB - MathWorks
MATLAB An introduction to MATLAB through a collection of mathematical and com-putational projects is provided by Moler’s free online Experiments with MATLAB [6] A list of over 1500 Matlab-based books by other authors and publishers in several languages is available at [12] Three introductions to Matlab are of par-
 MATLAB Getting Started Guide - Massachusetts Institute of
MATLAB Getting Started Guide - Massachusetts Institute of
The load function reads binary files containing matrices generated by earlier MATLAB sessions or reads text files containing numeric data The text file should be organized as a rectangular table of numbers separated by blanks with one row per line and an equal number of elements in each row
 MATLAB Function Tips - Michigan State University
MATLAB Function Tips - Michigan State University
function [xsqrd xcubd] = square(x) xsqrd = x^2 xcubd = x^3 There are two possible places to position this code If you are using MATLAB 5 0 or later this function code can be placed at the end of the main program in the same file as the main program It could also be placed in its own file which must use the function name or for our example
 Matlab Introduction - California State University Long Beach
Matlab Introduction - California State University Long Beach
The batch commands in a file are then executed by typing the name of the file at the Matlab command prompt The advantage to using a ' m' file is that you can make small changes to your code (even in different Matlab sessions) without having to remember and retype the entire set of commands
 6057 Introduction to MATLAB Homework 2 - MIT OpenCourseWare
6057 Introduction to MATLAB Homework 2 - MIT OpenCourseWare
Use magenta square symbols of marker size 10 and line width 4 and no line connecting them You may have to change the x limits to see all 6 symbols (xlim) If the relationship really is exponential it will look linear on a log plot 2 Subplot and axis modes Make a new Square Tight 100 100 200 figure that has a 2x2 grid of axes () subplot 200
 MATLAB Commands and Functions - College of Science and
MATLAB Commands and Functions - College of Science and
MATLAB Commands – 11 M-Files eval Interpret strings containing Matlab expressions feval Function evaluation function Creates a user-defined function M-file global Define global variables nargin Number of function input arguments nargout Number of function output arguments script Script M-files Timing cputime CPU time in seconds
 Searches related to function square matlab filetype:pdf
Searches related to function square matlab filetype:pdf
MATLAB is installed on the engineering instructional facility You can find it in the Start>Programs menu You can also install MATLAB on your own computer This is a somewhat involved process –you need to first register your name at mathworks then wait until they create an account for you there then download MATLAB and activate it
What are the functions of MATLAB?
- MATLAB Function Example Handout. MatLab is a high performance numeric computing environment, which includes numerical analysis, matrix computation, signal processing, and graphics to provide answers to the most troubling of mathematical problems. This handout provides different examples to show the different aspects of MatLab.
How to generate unit step function in MATLAB?
- function [x]=unitstep (x) %This is a unit step "function". The vector keeping track of time is the %input. If time is negative then a zero is returned. If time is zero than %0.5 is returned.
How to generate square wave in MATLAB?
- Square wave is generated using “square” function in Matlab. The command sytax – square (t,dutyCycle) – generates a square wave with period for the given time base. The command behaves similar to “ sin ” command (used for generating sine waves), but in this case it generates a square wave instead of a sine wave.
Chapter 10
Eigenvalues and Singular
Values
This chapter is about eigenvalues and singular values of matrices. Computational algorithms and sensitivity to perturbations are both discussed.10.1 Eigenvalue and Singular Value Decompositions
Aneigenvalueandeigenvectorof a square matrixAare a scalarλand a nonzero vectorxso thatAx=λx.
Asingular valueand pair ofsingular vectorsof a square or rectangular matrixA are a nonnegative scalarσand two nonzero vectorsuandvso thatAv=σu,
AHu=σv.
The superscript onAHstands forHermitian transposeand denotes the complex conjugate transpose of a complex matrix. If the matrix is real, thenATdenotes the same matrix. InMatlab, these transposed matrices are denoted byA'. The term "eigenvalue" is a partial translation of the German "eigenwert." A complete translation would be something like "own value" or "characteristic value," but these are rarely used. The term "singular value" relates to the distance between a matrix and the set of singular matrices. Eigenvalues play an important role in situations where the matrix is a trans- formation from one vector space onto itself. Systems of linear ordinary differential equations are the primary examples. The values ofλcan correspond to frequencies of vibration, or critical values of stability parameters, or energy levels of atoms. Singular values play an important role where the matrix is a transformation from one vector space to a different vector space, possibly with a different dimension. Systems of over- or underdetermined algebraic equations are the primary examples.September 16, 2013
12Chapter 10. Eigenvalues and Singular Values
The definitions of eigenvectors and singular vectors do not specify their nor- malization. An eigenvectorx, or a pair of singular vectorsuandv, can be scaled by any nonzero factor without changing any other important properties. Eigenvectors of symmetric matrices are usually normalized to have Euclidean length equal to one, ∥x∥2= 1. On the other hand, the eigenvectors of nonsymmetric matrices often have different normalizations in different contexts. Singular vectors are almost always normalized to have Euclidean length equal to one,∥u∥2=∥v∥2= 1. You can still multiply eigenvectors, or pairs of singular vectors, by-1 without changing their lengths. The eigenvalue-eigenvector equation for a square matrix can be written (A-λI)x= 0, x̸= 0. This implies thatA-λIis singular and hence that det(A-λI) = 0. This definition of an eigenvalue, which does not directly involve the corresponding eigenvector, is thecharacteristic equationorcharacteristic polynomialofA. The degree of the polynomial is the order of the matrix. This implies that ann-by-n matrix hasneigenvalues, counting multiplicities. Like the determinant itself, the characteristic polynomial is useful in theoretical considerations and hand calcula- tions, but does not provide a sound basis for robust numerical software. Letλ1,λ2,...,λnbe the eigenvalues of a matrixA, letx1,x2,...,xnbe a set of corresponding eigenvectors, let Λ denote then-by-ndiagonal matrix with theλj on the diagonal, and letXdenote then-by-nmatrix whosejth column isxj. ThenAX=XΛ.
It is necessary to put Λ on the right in the second expression so that each column of Xis multiplied by its corresponding eigenvalue. Now make a key assumption that is not true for all matrices - assume that the eigenvectors are linearly independent.ThenX-1exists and
A=XΛX-1,
with nonsingularX. This is known as theeigenvalue decompositionof the matrixA. If it exists, it allows us to investigate the properties ofAby analyzing the diagonal matrix Λ. For example, repeated matrix powers can be expressed in terms of powers of scalars: A p=XΛpX-1. If the eigenvectors ofAare not linearly independent, then such a diagonal decom- position does not exist and the powers ofAexhibit a more complicated behavior.IfTis any nonsingular matrix, then
A=TBT-1
is known as asimilarity transformationandAandBare said to besimilar. If Ax=λxandx=Ty, thenBy=λy. In other words, a similarity transforma- tion preserves eigenvalues. The eigenvalue decomposition is an attempt to find a similarity transformation to diagonal form.10.1. Eigenvalue and Singular Value Decompositions3
Written in matrix form, the defining equations for singular values and vectors areAV=UΣ,
AHU=VΣH.
Here Σ is a matrix the same size asAthat is zero except possibly on its main diagonal. It turns out that singular vectors can always be chosen to be perpendicular to each other, so the matricesUandV, whose columns are the normalized singular vectors, satisfyUHU=IandVHV=I. In other words,UandVareorthogonal if they are real, orunitaryif they are complex. Consequently,A=UΣVH,
with diagonal Σ and orthogonal or unitaryUandV. This is known as thesingular value decomposition, orSVD, of the matrixA. In abstract linear algebra terms, eigenvalues are relevant if a square,n-by-n matrixAis thought of as mappingn-dimensional space onto itself. We try to find a basis for the space so that the matrix becomes diagonal. This basis might be complex even ifAis real. In fact, if the eigenvectors are not linearly independent, such a basis does not even exist. The SVD is relevant if a possibly rectangular, m-by-nmatrixAis thought of as mappingn-space ontom-space. We try to find one change of basis in the domain and a usually different change of basis in the range so that the matrix becomes diagonal. Such bases always exist and are always real ifAis real. In fact, the transforming matrices are orthogonal or unitary, so they preserve lengths and angles and do not magnify errors. IfAismbynwithmlarger thann, then in the full SVD,Uis a large, square m-by-mmatrix. The lastm-ncolumns ofUare "extra"; they are not neededA = USV'A = USV'
Figure 10.1.Full and economy SVDs.
4Chapter 10. Eigenvalues and Singular Values
to reconstructA. A second version of the SVD that saves computer memory ifA is rectangular is known as theeconomy-sizedSVD. In the economy version, only the firstncolumns ofUand firstnrows of Σ are computed. The matrixVis the samen-by-nmatrix in both decompositions. Figure 10.1 shows the shapes of the various matrices in the two versions of the SVD. Both decompositions can be writtenA=UΣVH, even though theUand Σ in the economy decomposition are submatrices of the ones in the full decomposition.10.2 A Small Example
An example of the eigenvalue and singular value decompositions of a small, square matrix is provided by one of the test matrices from theMatlabgallery.A = gallery(3)
The matrix is
A=
-149-50-154537 180 546
This matrix was constructed in such a way that the characteristic polynomial factors nicely: det(A-λI) =λ3-6λ2+ 11λ-6 = (λ-1)(λ-2)(λ-3). Consequently, the three eigenvalues areλ1= 1,λ2= 2, andλ3= 3, and 1 0 0 0 2 0 The matrix of eigenvectors can be normalized so that its elements are all integers:X=
1-4 7 -3 9-49 It turns out that the inverse ofXalso has integer entries: X -1= 130 43 13327 9 28
These matrices provide the eigenvalue decomposition of our example:A=XΛX-1.
The SVD of this matrix cannot be expressed so neatly with small integers. The singular values are the positive roots of the equation6-668737σ4+ 4096316σ2-36 = 0,
but this equation does not factor nicely. The Symbolic Toolbox statement10.3. eigshow5
svd(sym(A)) returns exact formulas for the singular values, but the overall length of the result is922 characters. So we compute the SVD numerically.
[U,S,V] = svd(A) produces U = -0.2691 -0.6798 0.68220.9620 -0.1557 0.2243
-0.0463 0.7167 0.6959 S =817.759700
0 2.47500
00 0.0030
V =0.6823 -0.6671 0.2990
0.2287 -0.1937 -0.9540
0.6944 0.7193 0.0204
The expressionU*S*V'generates the original matrix to within roundoff error. Forgallery(3), notice the big difference between the eigenvalues, 1, 2, and3, and the singular values, 817, 2.47, and 0.003. This is related, in a way that we
will make more precise later, to the fact that this example is very far from being a symmetric matrix.10.3 eigshow
The functioneigshowis available in theMatlabdemosdirectory. The input to eigshowis a real, 2-by-2 matrixA, or you can choose anAfrom a pull-down list in the title. The defaultAisA=(1/4 3/4
1 1/2)
Initially,eigshowplots the unit vectorx= [1,0]′, as well as the vectorAx, which starts out as the first column ofA. You can then use your mouse to movex, shown in green, around the unit circle. As you movex, the resultingAx, shown in blue, also moves. The first four subplots in Figure 10.2 show intermediate steps asx traces out a green unit circle. What is the shape of the resulting orbit ofAx? An important, and nontrivial, theorem from linear algebra tells us that the blue curve is an ellipse.eigshowprovides a "proof by GUI" of this theorem. The caption foreigshowsays "MakeAxparallel tox." For such a direction x, the operatorAis simply a stretching or magnification by a factorλ. In other words,xis an eigenvector and the length ofAxis the corresponding eigenvalue.6Chapter 10. Eigenvalues and Singular Valuesx
A*x x A*x xA*xx A*x xA*x x A*xFigure 10.2.eigshow.
The last two subplots in Figure 10.2 show the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of our 2-by-2 example. The first eigenvalue is positive, soAxlies on top of the eigenvectorx. The length ofAxis the corresponding eigenvalue; it happens to be5/4 in this example. The second eigenvalue is negative, soAxis parallel tox, but
points in the opposite direction. The length ofAxis 1/2, and the corresponding eigenvalue is actually-1/2. You might have noticed that the two eigenvectors are not the major and minor axes of the ellipse. They would be if the matrix were symmetric. The default eigshowmatrix is close to, but not exactly equal to, a symmetric matrix. For other matrices, it may not be possible to find a realxso thatAxis parallel tox. These examples, which we pursue in the exercises, demonstrate that 2-by-2 matrices can have fewer than two real eigenvectors. The axes of the ellipse do play a key role in the SVD. The results produced by thesvdmode ofeigshoware shown in Figure 10.3. Again, the mouse moves xaround the unit circle, but now a second unit vector,y, followsx, staying per- pendicular to it. The resultingAxandAytraverse the ellipse, but are not usually perpendicular to each other. The goal is to make them perpendicular. If they are,10.4. Characteristic Polynomial7xyA*x
A*yFigure 10.3.eigshow(svd).
they form the axes of the ellipse. The vectorsxandyare the columns ofUin the SVD, the vectorsAxandAyare multiples of the columns ofV, and the lengths of the axes are the singular values.10.4 Characteristic Polynomial
LetAbe the 20-by-20 diagonal matrix with 1,2,...,20 on the diagonal. Clearly, the eigenvalues ofAare its diagonal elements. However, the characteristic polynomial det(A-λI) turns out to be20-210λ19+ 20615λ18-1256850λ17+ 53327946λ16
-1672280820λ15+ 40171771630λ14-756111184500λ13 +2432902008176640000.The coefficient of-λ19is 210, which is the sum of the eigenvalues. The coefficient ofλ0, the constant term, is 20!, which is the product of the eigenvalues. The other coefficients are various sums of products of the eigenvalues. We have displayed all the coefficients to emphasize that doing any floating- point computation with them is likely to introduce large roundoff errors. Merely representing the coefficients as IEEE floating-point numbers changes five of them. For example, the last 3 digits of the coefficient ofλ4change from 776 to 392. To
16 significant digits, the exact roots of the polynomial obtained by representing the
coefficients in floating point are as follows.8Chapter 10. Eigenvalues and Singular Values
1.000000000000001
2.000000000000960
2.999999999866400
4.000000004959441
4.999999914734143
6.000000845716607
6.999994555448452
8.000024432568939
8.999920011868348
10.000196964905369
10.999628430240644
12.000543743635912
12.999380734557898
14.000547988673800
14.999626582170547
16.000192083038474
16.999927734617732
18.000018751706040
18.999996997743892
20.000000223546401
We see that just storing the coefficients in the characteristic polynomial as double- precision floating-point numbers changes the computed values of some of the eigen- values in the fifth significant digit. This particular polynomial was introduced by J. H. Wilkinson around 1960. His perturbation of the polynomial was different than ours, but his point was the same, namely that representing a polynomial in its power form is an unsatisfactoryquotesdbs_dbs7.pdfusesText_13[PDF] fundamentals of corporate finance pdf
[PDF] fundamentos de administracion y gestion
[PDF] fundamentos de gestión empresarial
[PDF] fundamentos de gestion empresarial definicion
[PDF] fundamentos de gestion empresarial enfoque basado en competencias pdf
[PDF] fundamentos de gestion empresarial enfoque basado en competencias pdf gratis
[PDF] fundamentos de gestion empresarial julio garcia del junco pdf
[PDF] fundamentos de gestion empresarial libro
[PDF] fundamentos de gestion empresarial mc graw hill pdf
[PDF] fundamentos de gestión empresarial pearson pdf
[PDF] fundamentos de gestion empresarial unidad 1
[PDF] fundamentos de marketing kotler 13 edicion pdf
[PDF] fundamentos de marketing kotler 14 edicion pdf
[PDF] fundamentos de marketing kotler 8va edicion pdf
