 Least Squares
Least Squares
17 сент. 2013 г. The MAtlAB function polyfit computes least squares polynomial fits by setting up the design matrix and using backslash to find the ...
 Magic Squares
Magic Squares
2 окт. 2011 г. Write a MAtlAB function ismagic(A) that checks if A is a magic square. 10.2 Magic sum. Show that. 1 n n2. ∑ k=1 k = n3 + n. 2 . 10.3 durerperm ...
 Some important Built-in function in MATLAB 1. Square root b=sqrt(x
Some important Built-in function in MATLAB 1. Square root b=sqrt(x
14 мар. 2020 г. Some important Built-in function in MATLAB. 1. Square root b=sqrt(x) b=sqrt(4). 2. 2. Remainder of dividing x/y a=rem(xy) a=rem(10
 Objective 1 Triangular Wave 2 Square Wave 3 Discrete Time
Objective 1 Triangular Wave 2 Square Wave 3 Discrete Time
2 Square Wave. MATLAB has a built-in function square to generate a periodic square waveform. Following example will help you draw such a waveform. 2.1
 - 1 - Some MATLAB Built-in Functions Function Description sqrt(x
- 1 - Some MATLAB Built-in Functions Function Description sqrt(x
Some MATLAB Built-in Functions. Function. Description sqrt(x). Square root of x nthroot(xn) nth root of x abs(x). Absolute value of x exp(x). Exponential (ex).
 Eigenvalues and Singular Values
Eigenvalues and Singular Values
16 сент. 2013 г. The Matlab function condeig computes eigenvalue condition numbers. ... The qr function in Matlab factors any matrix real or complex
 Quadrature
Quadrature
area—plot the function on graph paper and count the number of little squares that The function functions in Matlab itself usually expect the first argument to.
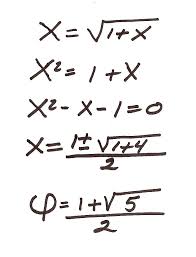 Iteration
Iteration
2 окт. 2011 г. Matlab responds with x = 3. Next enter this statement x = sqrt(1 + x). The abbreviation sqrt is the Matlab name for the square root function.
 Total Least Squares Approach to Modeling: A Matlab Toolbox
Total Least Squares Approach to Modeling: A Matlab Toolbox
In this section we show some applications of the TLS method in static and dynamical modeling by using the created Matlab functions [14]. 3.1 Linear regression
 Implementing the 2D square lattice Boltzmann method in Matlab
Implementing the 2D square lattice Boltzmann method in Matlab
23 февр. 2023 г. In contrast to LGA. LBM deals with distribution function values instead of single particles. The exact denomination for the following described ...
 General Linear Least-Squares and Nonlinear Regression
General Linear Least-Squares and Nonlinear Regression
Applied Numerical Methods with MATLAB for Engineers Chapter 15 & Teaching The least-squares ... function that returns the sum of the squares of the.
 Objective 1 Triangular Wave 2 Square Wave 3 Discrete Time
Objective 1 Triangular Wave 2 Square Wave 3 Discrete Time
MATLAB has a built-in function sawtooth to generate a periodic triangular waveform. Following example will help you draw such a waveform. 1.1 Example. Generate
 Magic Squares
Magic Squares
2011?10?2? An n-by-n magic square is an array containing the integers from 1 to n2 ... squares of order n but the MAtlAB function magic(n) generates a ...
 Least Squares
Least Squares
2013?9?17? The MAtlAB function polyfit computes least squares polynomial fits by setting up the design matrix and using backslash to find the ...
 Some important Built-in function in MATLAB 1. Square root b=sqrt(x
Some important Built-in function in MATLAB 1. Square root b=sqrt(x
2020?3?14? Some important Built-in function in MATLAB. 1. Square root b=sqrt(x) b=sqrt(4). 2. 2. Remainder of dividing x/y a=rem(xy) a=rem(10
 Eigenvalues and Singular Values
Eigenvalues and Singular Values
2013?9?16? A singular value and pair of singular vectors of a square or ... qr function in Matlab factors any matrix real or complex
 Iteration
Iteration
2011?10?2? The abbreviation sqrt is the Matlab name for the square root function. The quantity on the right. /. 1 + x
 DEPARTMENTS OF MATHEMATICS
DEPARTMENTS OF MATHEMATICS
1999?1?4? MAtlAB has included since at least version 3 a function sqrtm for computing a square root of a matrix. The function works by reducing the ...
 INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB FOR ENGINEERING STUDENTS
INTRODUCTION TO MATLAB FOR ENGINEERING STUDENTS
The function diary is useful if you want to save a complete MATLAB session. of vectors in MATLAB are enclosed by square brackets and are separated by ...
 Total Least Squares Approach to Modeling: A Matlab Toolbox
Total Least Squares Approach to Modeling: A Matlab Toolbox
In this section we show some applications of the TLS method in static and dynamical modeling by using the created Matlab functions [14]. 3.1 Linear regression
 MATLAB Basic Functions Reference - MathWorks
MATLAB Basic Functions Reference - MathWorks
Tasks represent a series of MATLAB commands To see the commands that the task runs show the generated code Common tasks available from the Live Editor tab on the desktop toolstrip: • Clean Missing Data • Clean Outlier • Find Change Points • Find Local Extrema • Remove Trends • Smooth Data mathworks com/help/matlab
 Chapter 10 Magic Squares - MathWorks
Chapter 10 Magic Squares - MathWorks
Ann-by-nmagic square is an array containing the integers from 1 ton2arranged so that each of the rows each of the columns and the two principaldiagonals have the same sum For eachn >2 there are many di?erent magicsquares of ordern but theMatlabfunctionmagic(n)generates a particular one Matlabcan generate Lo Shu with = magic(3) which produces
 MATLAB Function Example Handout - University of Wyoming
MATLAB Function Example Handout - University of Wyoming
ical function libraries The Matlab Optimization and Curve Fitting Toolboxes include functions for one-norm and in?nity-norm problems We will limit ourselves to least squares in this book 5 3 censusgui The NCM program censusgui involves several di?erent linear models The data
 Chapter 1 Iteration - MathWorks
Chapter 1 Iteration - MathWorks
In Matlab and most other programming languages the equals sign is the assignment operator It says compute the value on the right and store it in the variable on the left So the statement x = sqrt(1 + x) takes the current value of x computes sqrt(1 + x) and stores the result back in x
 Functions and Scripts - Electrical Engineering and Computer
Functions and Scripts - Electrical Engineering and Computer
Many functions are programmed inside MATLAB as built-in functions and can be used in mathematical expressions simply by typing their name with an argument; examples are sin(x) cos(x) sqrt(x) and exp(x) MATLAB has a plethora of built-in functions for mathematical and scientific computations
 Chapter 1 Introduction to MATLAB - MathWorks
Chapter 1 Introduction to MATLAB - MathWorks
MATLAB An introduction to MATLAB through a collection of mathematical and com-putational projects is provided by Moler’s free online Experiments with MATLAB [6] A list of over 1500 Matlab-based books by other authors and publishers in several languages is available at [12] Three introductions to Matlab are of par-
 MATLAB Getting Started Guide - Massachusetts Institute of
MATLAB Getting Started Guide - Massachusetts Institute of
The load function reads binary files containing matrices generated by earlier MATLAB sessions or reads text files containing numeric data The text file should be organized as a rectangular table of numbers separated by blanks with one row per line and an equal number of elements in each row
 MATLAB Function Tips - Michigan State University
MATLAB Function Tips - Michigan State University
function [xsqrd xcubd] = square(x) xsqrd = x^2 xcubd = x^3 There are two possible places to position this code If you are using MATLAB 5 0 or later this function code can be placed at the end of the main program in the same file as the main program It could also be placed in its own file which must use the function name or for our example
 Matlab Introduction - California State University Long Beach
Matlab Introduction - California State University Long Beach
The batch commands in a file are then executed by typing the name of the file at the Matlab command prompt The advantage to using a ' m' file is that you can make small changes to your code (even in different Matlab sessions) without having to remember and retype the entire set of commands
 6057 Introduction to MATLAB Homework 2 - MIT OpenCourseWare
6057 Introduction to MATLAB Homework 2 - MIT OpenCourseWare
Use magenta square symbols of marker size 10 and line width 4 and no line connecting them You may have to change the x limits to see all 6 symbols (xlim) If the relationship really is exponential it will look linear on a log plot 2 Subplot and axis modes Make a new Square Tight 100 100 200 figure that has a 2x2 grid of axes () subplot 200
 MATLAB Commands and Functions - College of Science and
MATLAB Commands and Functions - College of Science and
MATLAB Commands – 11 M-Files eval Interpret strings containing Matlab expressions feval Function evaluation function Creates a user-defined function M-file global Define global variables nargin Number of function input arguments nargout Number of function output arguments script Script M-files Timing cputime CPU time in seconds
 Searches related to function square matlab filetype:pdf
Searches related to function square matlab filetype:pdf
MATLAB is installed on the engineering instructional facility You can find it in the Start>Programs menu You can also install MATLAB on your own computer This is a somewhat involved process –you need to first register your name at mathworks then wait until they create an account for you there then download MATLAB and activate it
What are the functions of MATLAB?
- MATLAB Function Example Handout. MatLab is a high performance numeric computing environment, which includes numerical analysis, matrix computation, signal processing, and graphics to provide answers to the most troubling of mathematical problems. This handout provides different examples to show the different aspects of MatLab.
How to generate unit step function in MATLAB?
- function [x]=unitstep (x) %This is a unit step "function". The vector keeping track of time is the %input. If time is negative then a zero is returned. If time is zero than %0.5 is returned.
How to generate square wave in MATLAB?
- Square wave is generated using “square” function in Matlab. The command sytax – square (t,dutyCycle) – generates a square wave with period for the given time base. The command behaves similar to “ sin ” command (used for generating sine waves), but in this case it generates a square wave instead of a sine wave.
ISSN 1360-1725
UMISTA Newsqrtmfor Matlab
N. J. Higham
Numerical Analysis Report No. 336
January 1999
Manchester Centre for Computational Mathematics
Numerical Analysis Reports
DEPARTMENTS OF MATHEMATICS
Reports available from:
Department of Mathematics
University of Manchester
Manchester M13 9PL
England
And over the World-Wide Web from URLs
http://www.ma.man.ac.uk/MCCM http://www.ma.man.ac.uk/~nareportsA NewsqrtmforMatlab
Nicholas J. Higham
January 4, 1999
Abstract
Matlab"s functionsqrtmcomputes a square root of a matrix. We propose a replacement for thesqrtminMatlab5.2 that is more accurate and returns useful information about the stability and conditioning of the problem. Key words.matrix square root,Matlab, Schur decomposition, condition number, stabilityAMS subject classifications.65F30
1 Introduction
Matlabhas included since at least version 3 a functionsqrtmfor computing a square root of a matrix. The function works by reducing the matrix toSchur form and then applying a recurrence of Parlett for computing a general function of a triangular matrix. An error estimate is computed and if it is too large then an attempt is made to improve the accuracy of the computed square root. The functionsqrtmin versions ofMatlab up to version 5.2 can be much less accurate than is warranted by the condition of the problem. We propose a replacement forsqrtmthat is more accurate and returns useful information about the stability and conditioning of the problem. In Sections 2 and 3 we present some background theory on the existence of matrix square roots and their stability and conditioning. In Section 4 we describe the existing functionsqrtmand then in Section 5 the proposed replacement. Numerical experiments in Section 6 compare the new and the old routines and conclusions are given in Section 7.2 Matrix Square Roots
We begin by summarizing some salient features of the theory of matrix square roots. Further details can be found in [4], [6, Sec. 6.4]. The matrixX?Cn×nis a square root of A?Cn×nifX2=A. Any nonsingular matrix has a square root, but whether a singular matrix has a square root depends on the Jordan structure of the zero eigenvalues. IfA ?Department of Mathematics, University of Manchester, Manchester, M13 9PL, England (higham@ma.man.ac.uk,http://www.ma.man.ac.uk/~higham/). This work was supported by Engi- neering and Physical Sciences Research Council grant GR/L76532. 1 is nonsingular and hassdistinct eigenvalues then it has precisely 2ssquare roots that are expressible as polynomials in the matrixA; if some eigenvalue appears in more than one Jordan block then there are infinitely many additional square roots, none of which is expressible as a polynomial inA. To illustrate, the singular matrix?0 10 0? (2.1) has no square root, a diagonal matrix diag(di)?Cn×nwith distinct diagonal entries has exactly 2 nsquare roots, diag(±⎷ di), and then×nidentity matrix has infinitely many square roots forn >2, including any Householder matrix. Although a square root is never unique when it exists, there isa distinguished square root of particular interest: the one all of whose eigenvalues lie in the right half-plane. To make this square root uniquely defined, we (arbitrarily) map any eigenvalues on the negative real axis to the positive imaginary axis. This square root is called theprincipal square rootand it is a polynomial in the original matrix. WhenAis symmetric positive definite the principal square root is the unique symmetric positive definite square root, and whenAis real and has a real square root that is a polynomial inA, the principal square root is real.3 Stability and Conditioning of Square Roots
Two measures of the accuracy of a computed square root?XofAare the relative residual ?A-?X2?F/?A?Fand the relative error?X-?X?F/?X?F, whereXis the square root of interest. Here, we are using the Frobenius norm,?A?F= (? i,j|aij|2)1/2. To know how small the relative residual can be expected to be we considerthe correctly rounded exact have where the stability factorα(X) =?X?2F
?A?F=?X?2F?X2?F≥1.(3.2) Thus the best we can expect is that the relative residual of a computed?Xis of order α(?X)u. The stability factorα(X) can be arbitrarily large and it is related to the condition number with respect to inversion,κ(X) =?X?F?X-1?F, byκ(X)
The relative error of
?Xdepends on the conditioning ofX, so we now derive a condition number, following [4]. IfA=X2andA+ΔA= (X+ΔX)2thenXΔX+ΔXX=ΔA-ΔX2, which can be written
F ?(X)ΔX=ΔA-ΔX2, 2 whereF?(X) :Cn×n→Cn×nis the Fr´echet derivative ofF(X) =X2-AatX. Hence ΔX=F?(X)-1(ΔA-ΔX2) and taking norms and solving the resulting quadratic in- equality in?ΔX?Fgives the sharp inequality ?ΔX?F ?F?(X)-1?F?A?F?X?F? ?ΔA?F?A?F+O(?ΔA?2F).(3.3) This leads to the definition of the matrix square root condition numberχ(X) =?F?(X)-1?F?A?F
?X?F.For the Frobenius norm it can be shown that
?F?(X)-1?F=?(I?X+XT?I)-1?2, where?denotes the Kronecker product [6, Chap. 4]. LetXhave the Schur decomposition X=QRQ?, whereQis unitary andRis upper triangular. ThenI?X+XT?I= (
Q?Q)(I?R+RT?I)(QT?Q?),
from which it follows that ?(I?X+XT?I)-1?2=?(I?R+RT?I)-1?2. The matrixW=I?R+RT?I?Cn2×n2has the block lower triangular form illustrated forn= 3 by W=??R+r11I
r12I R+r22I
r13I r23I R+r33I??
We estimate?W-1?2by applying a few steps of the power method on (W?W)-1with starting vector [1,1,...,1]T. The systemsWx=bandWTy=ccan both be solved in n3flops by block substitution; this is of the same order as the cost of computingXby
the methods described in the next two sections, but is considerably less than theO(n5) flops required to computeW-1explicitly.4Matlab5.2"ssqrtm
Matlab5.2"ssqrtmcomputes the principal square root ofA?Cn×n. It first computes the Schur decompositionA=QTQ?. Then it applies a recurrence of Parlett for com- putingf(T), wherefis an arbitrary function [2, Sec. 11.1.3], [7]. Parlett"s recurrence is obtained by solving forF=f(T) in the commutativity relationFT=TF, which involves dividing bytii-tjjfor alli?=j. The recurrence therefore breaks down whenT has repeated diagonal elements, that is, whenAhas multiple eigenvalues. However, the principal square root is still well defined when there are multiple eigenvalues (assumingA has a square root). The practical upshot of using Parlett"s recurrence is thatsqrtmcan produce inaccurate results in situations where the principal square root can be obtained accurately by other means. 3 The functionsqrtminMatlab5.2 is listed in Appendix A.1. It callsfunm, which implements Parlett"s recurrence, and which returns an error estimate, based on the re- ciprocal of min i?=j|tii-tjj|. If this error estimate exceeds a tolerancetol, set to be a multiple of the unit roundoff,sqrtmenters a phase in which it tries to improve the accuracy of the computed square root?X. First, it checks to see if the relative residual ?A-?X2?1/?A?1exceeds the tolerance. This test is of dubious validity because, as we saw in Section 3, even the correctly rounded exact square root may have a large relative residual. If the test is failed then an orthogonal similarity transformation is applied toA, the whole computation is repeated, and the inverse transformation is performed. Then one step of Newton"s method [3] is applied and the relative residual computed once more. The logic behind the similarity transformation and the Newton step is not clear, since the similarity does not change the eigenvalues and so shouldmake little difference to the accuracy offunm, and Newton"s method can increase the error because of its numerical instability [3]. ("Newton"s method" here refers to a method obtained from the true New- ton method by making commutativity assumptions, and these assumptions destroy the self-correcting nature of Newton"s method.)5 A Newsqrtm
Our suggested replacement forsqrtm, which we refer to assqrtm*to avoid confusion, is listed in Appendix A.2. Likesqrtm, it begins by reducingA?Cn×nto Schur form, A=QTQ?. It then computes the principal square rootRofTusing a recurrence of Bj¨orck and Hammarling [1]. This recurrence is derived by considering the equation R2=T. Equating (i,j) elements gives
t ij=j? k=ir ikrkj, j≥i. It is easy to see thatRcan be computed a column at a time as follows: forj= 1:n r jj=t1/2 jjfori=j-1:-1:1 r ij=?tij-?j-1 k=i+1rikrkj?/(rii+rjj) end end The square root ofAis then recovered asX=QRQ?. The routine optionally computes α(X) =α(R) =?R?2F/?T?Fand estimates the condition numberχ(X) by the power method limited to 6 iterations, as described in Section 3. The cost of the algorithm is 25n3flops for the Schur decomposition [2, Sec. 7.5.6] plus n3/3 flops for computing the square root ofT, where a flop is a floating point operation.
The estimation ofχ(X) costs at most 12n3flops, and so increases the operation count by at most 50%. A straightforward rounding error analysis shows that the computed?Rsatisfies 4 whereγk=ku/(1-ku). Hence assuming that??R?F≈ ?R?F. Taking account of the errors in the computation of theSchur decomposition and the transformation from
?Rto?X, we obtain a bound of the form wherefis a cubic polynomial. This is comparable with the bound (3.1) for the correctly rounded square root and so is the best we can expect. For practical error estimation we can takef(n) =n, to obtain a more realistic bound. In view of (3.3) and (5.1), the relative error can be bounded approximately by ?ΔX?F Finally, we note that for real matrices an analogue ofsqrtm*can be written that works with the real Schur decomposition, as explained in [4], so that only real arithmetic is used.6 Numerical Experiments
We describe some numerical experiments that reveal the difference in reliability between sqrtmand the new routine,sqrtm*. We give results for three matrices. The machine precisionu= 2-53≈1.1×10-16.The first matrix and its square root are
A=????1 0 0 1
?0 0 ?01???? , X=????1 0 0 1/2⎷ ?0 0⎷ ?01????quotesdbs_dbs7.pdfusesText_13[PDF] fundamentals of corporate finance pdf
[PDF] fundamentos de administracion y gestion
[PDF] fundamentos de gestión empresarial
[PDF] fundamentos de gestion empresarial definicion
[PDF] fundamentos de gestion empresarial enfoque basado en competencias pdf
[PDF] fundamentos de gestion empresarial enfoque basado en competencias pdf gratis
[PDF] fundamentos de gestion empresarial julio garcia del junco pdf
[PDF] fundamentos de gestion empresarial libro
[PDF] fundamentos de gestion empresarial mc graw hill pdf
[PDF] fundamentos de gestión empresarial pearson pdf
[PDF] fundamentos de gestion empresarial unidad 1
[PDF] fundamentos de marketing kotler 13 edicion pdf
[PDF] fundamentos de marketing kotler 14 edicion pdf
[PDF] fundamentos de marketing kotler 8va edicion pdf
