Fonctions logarithmes népérien et décimal
La fonction logarithme népérien notée ln
TS courslogarithme
La fonction logarithme décimal
La fonction logarithme décimal. Propriétés analytiques. Pour x strictement positif log(x) = ln(x) ln(10). (avec ln(10) = 2
LogarithmeDecimal
CHAPITRE 11 : FONCTION NEPERIEN. FONCTION LOGARITHME
FONCTION. LOGARITHME DECIMAL. 1. Fonction népérien (logarithme d'une fonction composée). Théorème. Si u
cours chap
FONCTION LOGARITHME NEPERIEN
fonction logarithme décimale notée log est définie par : log(x) = lnx ln10. Conséquences : a) y = lnx avec x > 0 ⇔ x = ey b) ln1= 0 ; lne = 1 ; ln.
LogTS
FONCTION LOGARITHME DÉCIMAL
Yvan Monka – Académie de Strasbourg – www.maths-et-tiques.fr. FONCTION LOGARITHME DÉCIMAL. En 1614 un mathématicien écossais
LogTT
FONCTION LOGARITHME NÉPÉRIEN (Partie 1)
Ceci peut paraître dérisoire aujourd'hui mais il faut comprendre qu'à cette époque
LogT
LOGARITHME NEPERIEN
On note a = ln b ce qui se lit logarithme népérien de b . On appelle fonction logarithme décimal et on note log la fonction définie sur ] 0 ...
ln
Logarithme décimal et acoustique (calculatrice algorithme)
Votre voisin François chanteur amateur
logaritme decimal et acoustique
Etude des besoins mathématiques en physique et en chimie
https://pedagogie.ac-orleans-tours.fr/fileadmin/user_upload/maths/Dossiers_acad%C3%A9miques/Progressions/TermS/2-Lien_2_Logarithmes_pour_le_physicien.pdf
Formulaire : La fonction logarithme népérien
Formulaire : La fonction logarithme népérien. • Fonction continue et dérivable sur ]0;+∞[ Propriétés de la fonction logarithme décimal. • log(10) = 1.
Formulaire logarithme
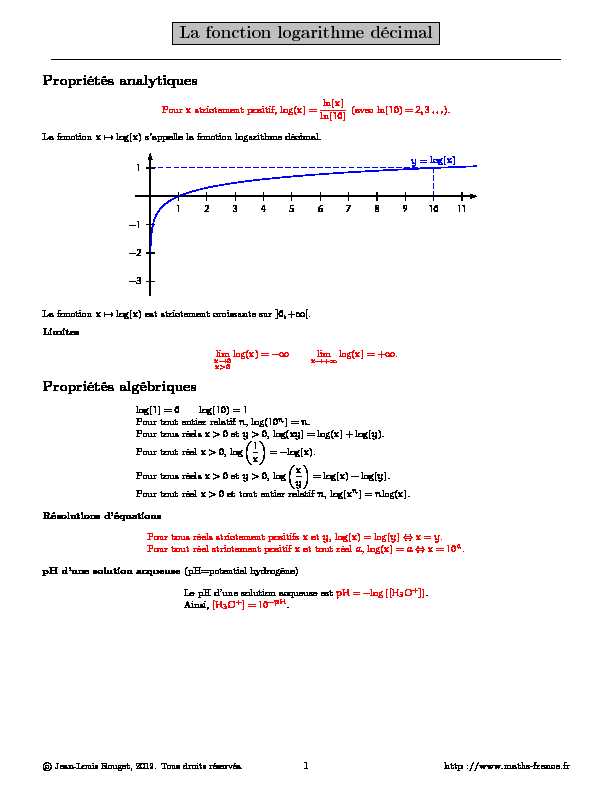
La fonction logarithme décimal
Propriétés analytiques
Pourxstrictement positif, log(x) =ln(x)ln(10)(avec ln(10) =2,3...). La fonctionx?→log(x)s"appelle la fonction logarithme décimal. 1 -1 -2 -31 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11y=log(x) La fonctionx?→log(x)est strictement croissante sur]0,+∞[.Limites
limx→0x>0log(x) = -∞limx→+∞log(x) = +∞.Propriétés algébriques
log(1) =0log(10) =1Pour tout entier relatifn, log(10n) =n.
Pour tous réelsx > 0ety > 0, log(xy) =log(x) +log(y).Pour tout réelx > 0, log?1
x? = -log(x).Pour tous réelsx > 0ety > 0, log?x
y? =log(x) -log(y). Pour tout réelx > 0et tout entier relatifn, log(xn) =nlog(x).Résolutions d"équations
Pour tous réels strictement positifsxety, log(x) =log(y)?x=y. Pour tout réel strictement positifxet tout réela, log(x) =a?x=10a. pH d"une solution acqueuse(pH=potentiel hydrogène)Le pH d"une solution acqueuse est
pH= -log([H3O+]).Ainsi,
[H3O+] =10-pH. c ?Jean-Louis Rouget, 2012. Tous droits réservés.1 http ://www.maths-france.frLa fonction logarithme décimal
Propriétés analytiques
Pourxstrictement positif, log(x) =ln(x)ln(10)(avec ln(10) =2,3...). La fonctionx?→log(x)s"appelle la fonction logarithme décimal. 1 -1 -2 -31 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11y=log(x) La fonctionx?→log(x)est strictement croissante sur]0,+∞[.Limites
limx→0x>0log(x) = -∞limx→+∞log(x) = +∞.Propriétés algébriques
log(1) =0log(10) =1Pour tout entier relatifn, log(10n) =n.
Pour tous réelsx > 0ety > 0, log(xy) =log(x) +log(y).Pour tout réelx > 0, log?1
x? = -log(x).Pour tous réelsx > 0ety > 0, log?x
y? =log(x) -log(y). Pour tout réelx > 0et tout entier relatifn, log(xn) =nlog(x).Résolutions d"équations
Pour tous réels strictement positifsxety, log(x) =log(y)?x=y. Pour tout réel strictement positifxet tout réela, log(x) =a?x=10a. pH d"une solution acqueuse(pH=potentiel hydrogène)Le pH d"une solution acqueuse est
pH= -log([H3O+]).Ainsi,
[H3O+] =10-pH. c ?Jean-Louis Rouget, 2012. Tous droits réservés.1 http ://www.maths-france.fr- relation logarithme décimal et népérien